UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K/A
Amendment No. 1
(Mark One)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended DECEMBER 31, 2012
Or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from TO
Commission File Number: 0-16159
AXOGEN, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| MINNESOTA | 41-1301878 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 13859 Progress Blvd., Suite 100 Alachua, FL | 32615 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (386)-462-6800
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share
|
(Title of class) |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted in its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | x |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
As of June 29, 2012, the value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $29,987,223 based upon the last reported sale price of the Common Stock at that date by the Over-the-Counter Bulletin Board.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s Common Stock as of March 11, 2013 was 11,127,869 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
None.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
AxoGen, Inc. (the “Company”) is filing this Amendment No. 1 (this “Amendment”) to its Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 (the “Form 10-K”) in response to comments received from the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) regarding a request for confidential treatment of certain portions of Exhibit 10.6.1 (Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement (the “Royalty Contract”), dated as of October 5, 2012, between the Company and PDL BioPharma, Inc. (“PDL”)) and Exhibit 10.6.2 originally filed with the Form 10-K. In response to SEC comments, this Amendment is being filed solely to (i) update certain sections of the Form 10-K to disclose certain information relating to the Royalty Contract that were omitted in the Form 10-K in accordance with the confidential treatment request, and (ii) file revised Exhibits 10.6.1 and 10.6.2 to disclose such additional information in the Royalty Contract and supply missing schedules and exhibits to Exhibits 10.6.1 and 10.6.2. Certain portions of Exhibits 10.6.1 and 10.6.2 remain omitted in accordance with a request for confidential treatment that the Company has submitted to the SEC.
Each of Exhibits 10.6.1 and Exhibit 10.6.2 filed with this Amendment supersedes in its entirety the version of Exhibit 10.6.1 and Exhibit 10.6.2, respectively, previously filed with the Form 10-K.
In addition, as required by Rule 12b-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, new certifications by our principal executive officer and principal financial officer are filed as exhibits to this Amendment.
This Amendment is limited in scope to the items identified above and should be read in conjunction with the Form 10-K. This Amendment does not reflect events that occurred after the filing of the Form 10-K and no revisions are being made to the Company’s financial statements pursuant to this Amendment, other than certain changes to disclose additional information relating to the Royalty Contract described above. Other than the filing of the information identified above, this Amendment does not modify or update the disclosure in the Form 10-K in any way.
i
| Page | ||||||
| PART I | ||||||
| Item 1. | Business | 3 | ||||
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 29 | ||||
| PART II | ||||||
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 43 | ||||
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | 49 | ||||
| PART IV | ||||||
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | 74 | ||||
| Signatures | 77 | |||||
| Exhibit Index | 78 | |||||
1
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
From time to time, in reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (including this Form 10-K), in press releases, and in other communications to shareholders or the investment community, the Company may provide forward-looking statements concerning possible or anticipated future results of operations or business developments. These statements are based on management’s current expectations or predictions of future conditions, events or results based on various assumptions and management’s estimates of trends and economic factors in the markets in which we are active, as well as our business plans. Words such as “expects”, “anticipates”, “intends”, “plans”, “believes”, “seeks”, “estimates”, “projects”, “forecasts”, “may”, “should”, variations of such words and similar expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements may include, without limitation, statements regarding product development, product potential, regulatory environment, sales and marketing strategies, capital resources or operating performance. The forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, which may cause results to differ materially from those set forth in the statements. Forward-looking statements in this Form 10-K should be evaluated together with the many uncertainties that affect the Company’s business and its market, particularly those discussed in the risk factors and cautionary statements in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including as described in “Risk Factors” included in Item 1A of this Form 10-K. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, and actual results may differ materially from those projected. The forward-looking statements are representative only as of the date they are made, and the Company assumes no responsibility to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
2
PART I
General
The Company is a leading regenerative medicine company dedicated to advancing the science and commercialization of peripheral nerve repair solutions. Peripheral nerves provide the pathways for both motor and sensory signals throughout the body and their damage can result in the loss of function and feeling. In order to improve surgical reconstruction and regeneration of peripheral nerves, the Company has developed and licensed patented and patent pending technologies. The Company’s innovative approach to regenerative medicine has resulted in first-in-class products that will define their product categories. AxoGen’s products offer a full suite of surgical nerve reconstruction solutions including Avance® Nerve Graft, the only commercially available processed nerve allograft for bridging severed nerves without the comorbidities associated with a second surgical site, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a porcine submucosa ExtraCellular Matrix (“ECM”) coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed nerves, and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect injured peripheral nerves and reinforce coaptation sites while preventing soft tissue attachments.
AxoGen’s products are used by surgeons during surgical interventions to repair a wide variety of traumatic nerve injuries ranging from a simple laceration of a finger to a complex brachial plexus case. The Avance® Nerve Graft, unlike hollow-tube conduits, provides surgeons with the essential three-dimensional structure of a natural nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities without the complication, expense and morbidity of harvesting peripheral nerve from the patient (nerve autograft). Additionally, the Avance® Nerve Graft has product and sales synergies with the AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector. AxoGuard® products provide the unique features of pliability, suturability, and translucence for visualization of the underlying nerve, while also allowing the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve epineurium.
Regenerative Medical Products Industry
Regenerative medical products enable the repair, restoration, replacement or regeneration of tissue or organ systems of the body. Regenerative medical products are becoming common in various medical arenas because they have been shown to be effective repairing injured or defective tissues, such as bone, tendons, dermis and other tissues of the body. Surgeons utilize regenerative medical products because they can provide the complex structure required for implant integration and regeneration in the body.
The primary driver of sustained growth in the regenerative medical product market is continued favorable efficacy as compared to autograft and synthetic medical products, and a wider understanding of this advantage by practitioners. Repair with nerve autograft requires a secondary recovery procedure to remove tissue from another location of the body to repair the injured area and can result in loss of function at the site of donation. Nerve autograft may also be costly and time consuming and may result in complications such as infection. In addition to nerve allograft (Avance® Nerve Graft), alternatives to nerve autograft include hollow-tube synthetic or collagen-based medical products that are designed to provide some restoration of function but may be limited by biocompatibility with the body or manufacturing technologies and capabilities. Regenerative medical products often provide more desirable conditions for reconstruction and regeneration of tissue, creating a superior solution for patients and physicians. AxoGen follows this trend, providing regenerative medical products for peripheral nerve reconstruction.
Regenerative medicine products typically consist of:
| i. | A scaffold or ECM to support the cells and/or provide the architecture of the tissue: and/or |
| ii. | Cells to regenerate or recellularize the scaffold. |
3
AxoGen provides a simple solution for the reconstruction of peripheral nerves; its products are scaffolds, and the patients’ own body provides the cells to regenerate or recellularize these scaffolds.
Peripheral Nerves and Their Regeneration
The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, consists of nerves that either extend outside of, or reside outside of, the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). Peripheral nerves provide the pathway for signals between the central nervous system and target organs, regulating movement (motor nerves) and touch (sensory nerves). Therefore, if a peripheral nerve is crushed, severed, or otherwise damaged, its ability to deliver signals to the target organs is eliminated, or significantly reduced, and could result in a loss of sensation and/or functionality. The axon portion of the nerve cell, consisting of cell cytoplasm and resembling a hair-like fiber, carries signals from the cell body to the target organ. Axons can be quite long, even exceeding one meter, but are only a few micrometers in diameter. A typical nerve consists of hundreds of axons that lie within long, thin tubes (basal lamina tubes). Analogous to a fiber-optic cable, these basal lamina tubes are bundled together in groups called fascicles, and each nerve may contain numerous fascicles. This sheath structure provides protection for the axons and support for regeneration in the event of injury. Nerve injury occurs when a sufficient number of axons have been crushed or transected (severed), thereby disrupting signals to the target motor or sensory organ.
Given the right conditions, peripheral nerves have the ability to regenerate. Regenerating axons require the proper environmental conditions including; structure and guidance of axons in a tension and compression free environment. In an untreated severe crush injury or transected nerve, errant axons that are not guided by the nerve sheath structure, or other mechanism, can form painful and ineffective nerve proliferation (neuromas). This can then require revision surgery to relieve pain or bring back sensory and/or motor functionality. Therefore, the surgical treatment of nerve injuries is typically focused on restoring nerve functionality by providing structural guidance to regenerating axons while alleviating compression and tension on the nerve.
Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Market Overview
Everyday patients suffer traumatic wounds to peripheral nerves severe enough to require surgical treatment, including injuries from motor vehicle accidents, collisions, gun wounds, dislocations, fractures, lacerations, or other forms of penetrating trauma. Specifically, military service men and women may suffer severe wounds from explosions and other military-related injuries. The peripheral nerves commonly injured from these traumas include the digital, median, ulnar, radial, facial, spinal accessory and brachial plexus nerves. Based upon epidemiological studies regarding the number of trauma patients and incidence of peripheral nerve injury in the population, , each year in the U.S. more than 1.3 million people suffer traumatic injuries to peripheral nerves resulting in at least 400,000 nerve repair procedures in the U.S. annually. (“Health”, United States, 2011, Publication of US Department of Health & Human Services; Noble, et al. J of Trauma Injury Infection and Critical Care 1998).
Beyond traumatic injury to nerves, nerve damage also occurs due to surgical intervention. Some of these nerve cases occur after dental or oral surgery when patients lose sensory and taste function in the mouth, including complications from third molar extractions and dental implants. Also, nerves that support erectile function may be injured or removed following a surgical prostatectomy to remove prostate cancer. Further, breast cancer patients may have reduced sensation in the tissue used to reconstruct the breast after mastectomy. Finally, nerves are also damaged or compromised due to repetitive stress or compression injuries. For instance, severe and recurrent carpal tunnel cases may result in complications and damage to the nerve that requires further surgical intervention and protection of the nerve.
Peripheral nerve injury is a major source of disability impairing the ability to move muscles or to feel normal sensations. Failure to treat nerve damage can in severe cases lead to full loss of function and sometimes amputation. Many peripheral nerve injury patients who receive treatment do not optimally recover. They may suffer from both reduced, or no, muscle strength and reduced, or no, sensitivity.
4
In the cases where a nerve is severed, if the gap between the two ends of the nerve is extremely small, the surgeon can reconnect the nerve without tension through direct suturing. Because a tension-free repair is important, when the gap is more than a few millimeters in length, the surgeon typically needs to bridge the gap between the nerve ends. Historically, to repair a severed nerve gap, surgeons have relied on an autotransplantation (autologous grafting or autograft). In autograft procedures, surgeons remove nerve from another part of the patient’s body, frequently from the back of the lower leg, to repair the damaged nerve. Autografting is often effective in repairing a damaged peripheral nerve, but it presents a tradeoff — fix the damaged nerve while creating a nerve deficit. For example, a patient may opt to get movement and feeling back in their finger while losing some sensation in their foot. Additionally, the secondary surgery to obtain the needed autograft also increases operating time, and thus medical expenses, and increases the risk of surgical infection and other complications. In the case of extreme trauma where multiple nerves need to be repaired, it may not be possible to recover enough nerve from the patient to complete the repair.
Drawbacks of repair with autograft eventually led to the development of hollow-tube conduits, or hollow-tube nerve cuffs, for peripheral nerve repair made of, for instance, bovine collagen or polyglycolic acid. The nerve cuff is typically an absorbable hollow tube that, unlike natural nerve, does not have basal lamina tubes to support regenerating axons; as a result, it is deficient in the qualities that natural nerve possesses to support nerve regeneration. Hollow-tube conduits may also lack pliability and structural integrity needed when used around joints and may be difficult to use in a confined space. Additionally, hollow-tube conduits do not provide familiar handling characteristics to the surgeon and in some instances are contraindicated for use in infected wound beds. Clinical data has demonstrated that conduits are most effective only when used in very short gaps and the reliability of successful nerve recovery diminishes as gap length increases. However, with surgeons seeking alternatives to autografts, the annual number of procedures using hollow-tube conduits has grown. AxoGen believes this demand has resulted in hollow-tube conduits being used for gap lengths where their likelihood of effectiveness is greatly diminished.
The growth of hollow-tube conduit use demonstrates there is market demand for products that do not have the drawbacks of autografting. However, as stated above, the shortcomings of conduits limit where they may be used effectively. Thus, the nerve repair market needs an alternative off-the-shelf product that provides the natural ECM scaffold and three-dimensional structure of a typical nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities without the complication, expense and morbidity of autografting a nerve. AxoGen believes its product portfolio meets this market need.
AxoGen’s Product Portfolio
Overview of AxoGen’s Products
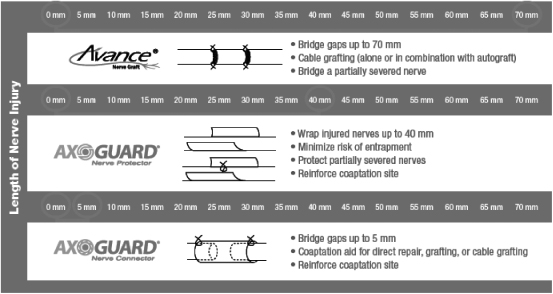
AxoGen’s proprietary products and technologies are designed to overcome fundamental challenges in nerve repair. AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft is the alternative to autografts for nerve gaps up to 70mm in length. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is the surgical solution for nerve gaps of less than 5mm in length, or where surgeons wish to provide additional protection to suture sites when autograft or Avance® Nerve Graft are used. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector completes the product portfolio by allowing a protective wrap in cases of nerves damaged by compression, or where the surgeon wants to protect and isolate the nerve during the healing process after surgery. This product portfolio, depicted below, provides surgeons off-the-shelf solutions for a wide variety of peripheral nerve injuries.
5
The following table provides a summary of certain peripheral nerve injuries for which AxoGen products are used:

Avance® Nerve Graft
Avance® Nerve Graft is intended for the surgical repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities (a gap created when the nerve is severed) to support regeneration across defects of 5mm to 70mm in length. It is intended to act as a bridge in order to guide and structurally support axonal regeneration across a nerve gap caused by traumatic injury or surgical intervention. Avance® Nerve Graft is decellularized and sterile extracellular matrix (ECM) processed from human peripheral nerve tissue. AxoGen developed the Avance® Nerve Graft by following the guiding principle that the human body created the optimal nerve structure. AxoGen, through its licensing efforts and research, developed a proprietary method for processing recovered human peripheral nerve tissue in a manner that preserves the essential structure of the ECM while cleansing away cellular and noncellular debris. Avance® Nerve Graft provides the natural nerve structure of an autograft and the ease and availability of an off-the-shelf product. AxoGen believes that Avance® Nerve Graft is the first and only commercially available allograft nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities. The Avance® Nerve Graft is comprised of bundles of small diameter endoneurial tubes that are held together by an outer sheath called the epineurium. Avance® Nerve Graft has been processed to remove cellular and noncellular factors such as cells, fat, blood, axonal debris and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, (“CSPG”), while preserving the three-dimensional scaffold, basal lamina tubular structure, epineurium and microvasculature of the peripheral nerve. After processing, Avance® Nerve Graft is flexible and pliable, and its epineurium can be sutured in place allowing for tension-free approximation of the proximal and distal peripheral nerve stumps. The design results in a product that has clean and clear pathways for the regenerating axons to grow through. During the healing process, the body revascularizes and gradually remodels the graft into the patient’s own tissue while allowing the processed nerve allograft to physically support axonal regeneration across the nerve discontinuity.
Avance® Nerve Graft provides the natural nerve structure of an autograft and the ease and availability of an off-the-shelf product. AxoGen believes that Avance® Nerve Graft is the only commercially available processed nerve allograft for bridging nerve discontinuities.
With lengths up to 70 mm and diameters up to 5 mm, the Avance® Nerve Graft allows surgeons to choose the correct length for the relevant nerve gap for repairs up to 70 mm, as well as to match the diameter to the proximal and distal end of the severed nerve. The Avance® Nerve Graft is stored frozen and utilizes packaging
6
that maintains the graft in a sterile condition. The packaging is typical for medical products so the surgical staff is familiar with opening the package for transfer of the Avance® Nerve Graft into the sterile surgical field. Such packaging also provides protection during shipment and storage and a reservoir for the addition of sterile fluid to aid in thawing the product. The Avance® Nerve Graft thaws in less than 10 minutes, and once thawed, it is ready for implantation.
The Avance® Nerve Graft provides the following key advantages:
| • | Provides a three-dimensional bioscaffold for bridging a nerve gap; |
| • | No patient donor-nerve surgery, therefore no loss of donor nerve function; |
| • | Available in a variety of diameters, 1-2 mm to 4-5mm, to meet a range of anatomical needs |
| • | Available in a variety of lengths, 15mm to 70mm, to meet a range of gap lengths, |
| • | Decellularized and cleansed extracellular matrix that remodels into patient’s own tissue; |
| • | Structurally supports the body’s own regeneration process; |
| • | Handles similar to an autograft, and is flexible and pliable; |
| • | Alleviates tension at the repair site; |
| • | Three year shelf life; and |
| • | Supplied sterile. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is a porcine submucosa ECM coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed nerves. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is a tubular, multilaminar extracellular matrix with an open lumen where the severed nerve ends are placed. Typically, the AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is used to align and connect nerves with less than a 5mm gap between the severed nerve ends. The AxoGuard® Nerve Connector material allows the body’s natural healing process to repair the nerve by isolating and protecting it during the healing process. The patient’s own cells incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve epineurium. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is provided sterile, for single use only, and in a variety of sizes to meet the surgeon’s needs.
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector can be used to:
| • | Bridge gaps up to 5 mm; |
| • | Aid coaptation in direct repair, grafting, or cable grafting repairs; and |
| • | Reinforce the coaptation site. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector has the following advantages:
| • | Only porcine submucosa extra-cellular matrix coaptation product to bridge gaps up to 5 mm; |
| • | Alleviates tension at the repair site; |
| • | Reduces the number of required sutures (versus direct repair); |
| • | Moves location of sutures away from the coaptation face; |
| • | Reduces potential for fascicular mismatch; |
| • | Allows visualization of underlying nerve; |
| • | Strong and flexible, easy to suture; and |
| • | Stored at room temperature with an 18 month shelf life. |
7
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector
The AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect injured peripheral nerves and reinforce coaptation sites while preventing soft tissue attachments surgical implant that provides protection for peripheral nerves. It is designed to protect and isolate the nerve during the healing process after surgery. AxoGuard® is a multilaminar extracellular matrix that separates and protects the nerve from the surrounding tissues during the healing process. The patient’s own cells incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve epineurium. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is provided sterile, for single use only, and in a variety of sizes to meet the surgeon’s needs.
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector can be used to:
| • | Wrap injured nerves; |
| • | Minimize risk of entrapment in compressed nerves; |
| • | Protect partially severed nerves; |
| • | Protect nerves in a traumatized wound bed; and |
| • | Reinforce a coaptation site. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector has the following advantages:
| • | Only porcine submucosa bioscaffold used to reinforce a coaptation site, wrap a partially severed nerve or protect nerve tissue; |
| • | Isolates and protects the nerve in a traumatized wound bed; |
| • | Easily conforms and wraps the injured nerve; |
| • | Minimizes the potential for soft tissue attachments and nerve entrapment by physically isolating the nerve during the healing process; |
| • | Allows nerve gliding; |
| • | Strong and flexible, plus easy to suture; |
| • | Stored at room temperature with an 18 month shelf life. |
Tissue Recovery and Processing for Avance® Nerve Graft
Avance® Nerve Graft Processing Overview
Over several years, AxoGen has developed advanced and proprietary techniques to process the Avance® Nerve Graft from donated peripheral nerve tissue. The process requires special training over several months for each manufacturing associate who processes Avance® Nerve Grafts. The processing and manufacturing system for Avance® Nerve Graft has required significant capital investment, and AxoGen plans to make additional investments to continually improve its manufacturing and quality assurance processes and systems.
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft processing requires several steps, including peripheral nerve tissue recovery and testing, donor medical review and release, processing, packaging, and sterilization to meet or exceed all applicable FDA, state, and international regulations and American Association of Tissue Banks (“AATB”) standards. As an FDA registered tissue establishment, AxoGen utilizes both its own personnel and a variety of subcontractors for recovery, storage, testing, processing and sterilization of the donated peripheral nerve tissue. Additionally, independent certified laboratories have been contracted by AxoGen and its subcontractors to perform testing. The safety of Avance® Nerve Graft is supported by donor screening, process validation, process controls, and validated terminal sterilization methods. The AxoGen Quality System has built in redundancies so that each Avance® Nerve Graft released for implantation meets AxoGen’s stringent quality control and product requirements.
8
Avance® Nerve Graft Tissue Recovery and Processing
AxoGen partners with FDA registered tissue establishments and AATB accredited recovery agencies or recovery agencies in compliance with AATB standards to recover human peripheral nerve tissue for Avance® Nerve Graft processing. After consent for donation is obtained, donations are screened and tested in detail for safety in compliance with the federal regulations and AATB standards on communicable disease transmission. AxoGen processes and packages Avance® Nerve Graft using its employees and equipment located at LifeNet Health, Virginia Beach, Virginia, an FDA registered tissue establishment, from the donated nerve tissue. Under the agreement with LifeNet Health, AxoGen pays LifeNet Health a facility fee. Either party may terminate the agreement with six months’ written notice. The LifeNet Health facility provides a cost effective, quality controlled and licensed facility, however, AxoGen could reproduce a manufacturing space that would meet its needs if it no longer continued its relationship with LifeNet. AxoGen’s processing methods and process controls have been developed and validated to ensure product uniformity and quality.
Avance® Nerve Graft Packaging
After processing, each Avance® Nerve Graft is visually inspected and organized by size (length and diameter) into finished product codes. It is then packaged in individual medical grade clamshells and primary packaging. The outer pouch is the primary sterility and moisture barrier. The packaging operation is performed in a controlled environment at LifeNet Health.
Avance® Nerve Graft Sterilization and Labeling
After being processed and packaged, Avance® Nerve Graft is then irradiated and returned to AxoGen’s headquarters in Alachua, Florida. There, the product receives its final labels and is released following a final stringent technical and quality review. Orders for Avance® Nerve Graft are placed with AxoGen’s customer care team and product is shipped from the distribution facilities.
Avance® Nerve Graft Product Release
The AxoGen Quality System meets the requirements set forth under 21 CFR § 1271 for Human Cells, Tissues and Cellular and Tissue-Based Products, including Good Tissue Practices (“GTP”) and is compliant with the 21 CFR § 820 Quality System Regulations (“QSR”). AxoGen has established quality procedures for review of tissue recovery, relevant donor medical record review and release to processing that meet or exceed FDA requirements as defined in 21 CFR §1271, state regulations, international regulations and AATB standards. Furthermore, AxoGen utilizes validated processes for the handling of raw material components, environmental control, processing, packaging and terminal sterilization. In addition to ongoing monitoring activities for product conformity to specifications and sterility, product biocompatibility, shipping methods and shelf life have been validated in accordance with applicable industry standards.
Manufacturing for the AxoGuard® Product Line
AxoGuard® is manufactured by Cook Biotech Incorporated, West Lafayette, Indiana (“Cook Biotech”), which was established in 1995 to develop and manufacture tissue grafts utilizing porcine extracellular matrix technology. AxoGen decided to expand its portfolio of products and felt that the unique ECM material offered by Cook Biotech provided the combination of properties needed in nerve reconstruction; Cook Biotech’s ECM material is pliable, suturable, translucent and allows the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve’s epineurium. In August 2008, Cook Biotech entered into an agreement with AxoGen to distribute its product worldwide in the field of peripheral nerve repair, and the parties subsequently amended the agreement in March, 2012. The agreement has an initial seven-year term from the date of the original agreement and following such initial term, the agreement automatically renews for an additional seven (7) year period provided that the parties agree to meet at least ninety (90) days before the end of such initial term to review whether the purchase price of the products obtained from Cook Biotech need to be
9
adjusted and reasonably agree to such adjustment in writing, where such agreement shall not be unreasonably withheld. The Cook Biotech agreement also requires certain minimum purchases, although through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforce such provision, and establishes a formula for the transfer cost of the AxoGuard® products. Under the agreement, AxoGen provides purchase orders to Cook Biotech, and Cook Biotech fulfills the purchase orders.
Sales and Marketing
Overview
The AxoGen portfolio of nerve repair solutions offers a full range of products for all surgical peripheral nerve reconstruction needs. AxoGen is focused on the developing market of peripheral nerve reconstruction and regeneration and is committed to improving awareness of new peripheral nerve reconstruction options, as well as building additional scientific and clinical data to assist surgeons and patients in making informed choices. AxoGen believes this approach will solidify its position as a leader in the field of products for peripheral nerve injuries. The following provides the key elements of AxoGen’s sales and marketing strategy.
Increase Awareness of AxoGen’s Products Bridging Nerve Gaps
Prior to the introduction of AxoGen’s portfolio of products, surgeons had a limited number of options available for the reconstruction of nerve injuries. AxoGen entered the market to improve the standard of care for patients. It has brought the science of nerve repair to life by developing reconstruction options based on extracellular matrix tissue. Unlike other off-the-shelf nerve reconstruction options, an extracellular matrix remodels into the patient’s own tissue and provides physical support for the body’s natural healing process.
AxoGen intends to increase market share by improving awareness of its products through the use of educational conferences and presentations, surgical resident and fellow training, scientific publications, and a knowledgeable and professional sales team. AxoGen expects to increase usage with existing customers as well as expand the overall customer base. Initially, AxoGen will focus on plastic reconstructive surgeons and orthopedic and plastic surgeons who perform surgeries on patients suffering traumatic nerve injuries and who perform hand reconstructive surgeries. In select hospital accounts, AxoGen is also expanding into the market for the reconstruction of nerve injuries in oral surgery.
Expand Clinical and Scientific Data Regarding the Performance of AxoGen Products
Data will be a mainstay of AxoGen’s marketing strategy. AxoGen will continue to accept patients in its RANGER® clinical study (defined below in “Government Regulations”), a utilization registry of Avance® Nerve Graft. A multicenter prospective randomized comparative pilot study of hollow tube conduits and Avance® Nerve Graft is in process. A case series in digital nerve repair has already been published and other studies have been completed. Case series in brachial plexus, military trauma, prostate cancer neurotization of breast reconstruction and compressive neuropathy are also being developed. AxoGen also supports outside research and will continue to work with investigators working on grants with a translational focus.
Expand the AxoGen Sales Team for National Coverage
AxoGen provides full sales and distribution services through both a direct sales force and a team of independent distributors. AxoGen provides support and resources for independent distributors and is increasing its direct sales force in selected territories. AxoGen provides products to hospitals, surgery centers and military hospitals, calling on plastic reconstructive surgeons and orthopedic and plastic hand surgeons to review the benefits of the AxoGen products. While surgeons make the decision to implant the products in appropriate patients, hospitals make the decision to buy the products from AxoGen. In today’s budget constrained environment, hospital committees review new technologies for cost effectiveness as well as quality. AxoGen believes that it has been successful in meeting the needs of these hospital committees by demonstrating the cost/benefit of its products and providing a fair value to the hospital.
10
AxoGen Strengths
AxoGen believes that it has the following strengths in the field of nerve reconstruction and regeneration:
Established Nerve Repair Reconstruction and Regeneration Expertise
AxoGen has made a significant investment in understanding nerve reconstruction and regeneration through interaction with leading academic centers throughout the United States and by building an outstanding internal team of technical and clinical experts.
Surgical Implant Commercialization Experience
The AxoGen commercialization team consists of sales, marketing, and customer service professionals with backgrounds in the medical device and biotechnology industries. The commercial team has been instrumental in beginning to establish the Avance® Nerve Graft and the AxoGuard® product line as a new standard of care for the surgical treatment of nerve injuries. AxoGen believes it can leverage these capabilities in expanding the commercial success of the current AxoGen products and future product opportunities.
Avance® Nerve Graft Performance
AxoGen has worked with leading institutions, researchers and surgeons to support innovation in the field of peripheral nerve reconstruction. To date, AxoGen’s RANGER® study (defined below in “Government Regulations”) is the largest multi-center clinical study conducted in peripheral nerve gap repair. AxoGen’s RECON study will also continue AxoGen’s clinical work, providing a new multi-center, prospective, randomized, clinical study on the Avance® Nerve Graft. The January, 2012 edition of Microsurgery and November 2012 edition of The Journal of Hand Surgery each contain an article summarizing the RANGER® study results. To date the use of Avance®, Nerve Graft has been associated with meaningful motor and sensory recovery ranging from 80% to 86% in nerve discontinuities between 5 and 50 mm in the upper extremity. Additionally no implant related adverse events have been reported. (Brooks, D. N., Weber, R. V., Chao, J. D., Rinker, B. D., Zoldos, J., Robichaux, M. R., Ruggeri, S. B., Anderson, K. A., Bonatz, E. E., Wisotsky, S. M., Cho, M. S., Wilson, C., Cooper, E. O., Ingari, J. V., Safa, B., Parrett, B. M. and Buncke, G. M. (2012), Processed nerve allografts for peripheral nerve reconstruction: A multicenter study of utilization and outcomes in sensory, mixed, and motor nerve reconstructions. Microsurgery, 32: 1–14. doi: 10.1002/micr.20975 and Cho, et al. 2012, J Hand Surg Am 37(11):2340-9). A meta-analysis of available clinical outcomes data from published papers on the leading synthetic collagen conduit showed meaningful improvement in only 53% of cases bridging a gap in the nerve.
International Opportunity for Product Sales
AxoGen currently focuses on the U.S. market, with additional Avance® Nerve Graft foreign sales in Canada, Italy, Austria and Switzerland. The need for reconstruction of injured nerves is a global issue. Through its foreign sales, AxoGen has shown the capability to take its current product offering into new geographical markets. AxoGen does not currently have EU-wide approval for the Avance® Nerve Graft or the AxoGuard® products, but has a regulatory strategy for Europe and certain other international regions.
Research and Development
AxoGen believes it provides the most extensive product portfolio for peripheral nerve repair available. Our current development focus is to expand clinical data in both traumatic nerve repair and other surgical applications. Additional product line extensions of the Avance® and AxoGuard® products may be developed. AxoGen’s current intention is to spend limited direct resources on extensive research into new unmet peripheral nerve needs. AxoGen does, however, work with academic intuitions in the expansion of treatments for peripheral nerve. For the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, AxoGen spent $1,427,211, and $697,355, respectively, on research and development expenses.
11
Competition
The medical device and biotechnology industries are characterized by rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition and a strong emphasis on proprietary products. As such, AxoGen cannot predict what products may be offered in the future that may compete with AxoGen’s products. Currently, AxoGen competes primarily against autograft and hollow-tube conduits based on product features and performance, price, surgical application, ease of use and healthcare provider education. AxoGen’s major competitors for off-the-shelf repair option in hollow-tube conduits are the following companies:
| • | Integra LifeSciences Holding Corporation (NASDAQ: IART) (“Integra”). Integra offers NeuraGen®, a hollow bovine collagen conduit and NeuraWrapTM, a nerve repair conduit also made from bovine collagen; |
| • | Baxter International, Inc. (NYSE: BAX) (“Baxter”). Baxter acquired Synovis that offered the Neurotube, which is a hollow conduit comprised of polyglycolic acid; and |
| • | Stryker Corporation (NYSE: SYK), (“Stryker”). Stryker offers the NeuroMatrix and Neuroflex products, both of which are hollow conduits derived from bovine collagen. |
AxoGen believes that surgeons use Avance® Nerve Graft because, unlike hollow-tube conduits, it provides them with the natural three-dimensional structure of a typical nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities (severed nerves) without the complications, expense and morbidity of autografting a nerve. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector provide the unique features of pliability, suturability, and translucence for visualization of the underlying nerve while also allowing the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve epineurium.
AxoGen believes any current or future competitors face the following important barriers to entry as it relates to the market for its products. AxoGen’s intellectual property, and that of its partners, including patents and patents-pending, is believed to be an important barrier. Additionally, AxoGen has developed knowledge and experience in understanding and meeting FDA regulatory requirements for Avance® Nerve Graft, including having made a substantial investment in validating, testing for, and meeting and preparing a submission for a FDA Biologics License Application (“BLA”) requirements. However, due to its limited resources, its smaller size and its relatively early stage, AxoGen believes it may face competitive challenges and barriers that are difficult to overcome and could negatively impact its growth.
Intellectual Property
Overview
AxoGen relies on a combination of patent, trademark, trade secret, and copyright, as well as other intellectual property (“IP”) laws, to protect IP rights. In addition, AxoGen utilizes license, non-disclosure, and assignment agreements to protect these IP rights. Specifically, AxoGen requires vendors, contract organizations, consultants, advisors and employees to execute nondisclosure agreements. AxoGen also requires consultants, advisors and employees who develop IP to assign to AxoGen any of their rights to all IP conceived in connection with their relationship with AxoGen.
License Agreements
AxoGen has entered into license agreements with University of Florida Research Foundation (the “UFRF”) and the University of Texas at Austin (“UTA”). Under the terms of these license agreements, AxoGen has exclusive worldwide licenses for the underlying technologies used by AxoGen in repairing and regenerating nerves. The license agreements include both the right to issued patents and patents pending in the U.S. and international markets. The effective term of the license agreements extends through the term of the related
12
patents In the event of default, licensors may also terminate an agreement (after written notice) if AxoGen fails to cure a breach. The license agreements contain the following key terms:
| • | Payment of annual license maintenance fees, some of which may be credited against future royalty payments; |
| • | Payment of royalty fees of 1%-3% based on net sales of the licensed products, the level depending on the agreement, which may include a minimum quarterly royalty payment with discounts off royalty rates when royalty stacking applies; |
| • | Payment of a percentage of sublicense fees received; |
| • | Reimbursement of certain legal expenses incurred for patent prosecution and defense; and |
| • | Other payments of various amounts based on achieving certain milestones. |
Currently, AxoGen pays royalties to UFRF and UTA specific to the licensed technologies related to the Avance® Nerve Graft.
Patents
As of the date of this Form 10-K, AxoGen owned or was the exclusive licensee of six issued U.S. patents, five pending U.S. patent applications, three issued international patents and nine pending international patent applications with regard to its peripheral nerve products. In Mexican cases PA/A/2004/001334, 2007/012379, 2007/012380, and 2007/012382, Notices of Allowance have been issued, and the four patents are awaiting issuance. Additionally, the granted European Patent No. EP1425390 is in the process of being validated in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. The following table illustrates the issued patents owned or licensed by AxoGen with regard to it peripheral nerve products, including the patent number, a description of each patent, and the estimated expiration date of each patent.
| Patent No. | Description | Estimated expiration date | ||
| US 6,972,168 |
Materials and Methods for Nerve Grafting, Selection of Nerve Grafts, and in vitro Nerve Tissue Culture | August 13, 2021 | ||
| US 7,402,319 |
Cell Free Tissue Replacement for Tissue Engineering | September 26, 2023 | ||
| US 7,732,200 |
Materials and Methods for Nerve Grafting, Selection of Nerve Grafts, and in vitro Nerve Tissue Culture | December 21, 2022 | ||
| US 6,696,575 |
Biodegradable, electrically conducting polymer for tissue engineering applications | March 27, 2021 | ||
| US 7,851,447 |
Materials and Methods for Nerve Repair | November 18, 2023 | ||
| US 7,772,185 |
Materials and Methods for Promotion of Nerve Regeneration | November 18, 2023 | ||
| Japan No. 4,749,667 |
Materials and Methods to Promote Repair of Nerve Tissue | August 13, 2022 | ||
| Europe No. EP1425390 |
Materials and Methods to Promote Repair of Nerve Tissue | August 12, 2022 | ||
| Japan No. 4,773,976 |
Materials and Methods for Promotion of Nerve Regeneration | January 31, 2025 | ||
Additionally, AxoGen entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Cook Biotech in August 2008, as subsequently amended in March 2012, to distribute its ECM technology in the form of the Surgisis® Nerve Cuff, the form of a nerve wrap or patch, or the form of any other mutually- agreed-to configuration in the field of peripheral nervous system and central nervous system use. AxoGen has subsequently rebranded the Surgisis products under the AxoGuard® name. Cook Biotech holds multiple issued and pending U.S. and international
13
patents covering its ECM technology. The following table illustrates the two non-licensed U.S. patents held by Cook Biotech that are specifically identified on AxoGen’s AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector product labeling. The table includes the U.S. Patent number, a description of each patent, and the estimated expiration date of each patent.
| U.S. Patent No. | Description | Estimated expiration date | ||
| 6,206,931 |
Graft Prosthesis Material | August 23, 2016 | ||
| 6,241,981 |
Composition and Method for Repairing Neurological Tissue | September 16, 2016 | ||
Because of the length of time and expense associated with bringing new products through development and the governmental approval process, medical technology companies have traditionally placed considerable importance on obtaining and maintaining patent protection for significant new technologies, products and processes. AxoGen intends to seek patent protection for appropriate proprietary technologies by filing patent applications when possible in the U.S. and selected other jurisdictions. AxoGen’s policy is to seek patent protection for the inventions that it considers important to the development of its business. AxoGen also intends to use its scientific expertise to pursue and file patent applications on new developments with respect to uses, methods, and compositions to enhance its intellectual property (“IP”) position in the areas that are important to the development of its business.
Finally, AxoGen continues to hold IP, including patents, related to LecTec’s original hydrogel patch technology and hand sanitizer patch. AxoGen has not been able to monetize the IP regarding the hand sanitizer patch and issues regarding the enforceability of such IP has resulted in AxoGen determining that it has no future value. AxoGen continues to take all action necessary to maintain relevant patents licensed to Novartis Consumer Health, Inc., however, Novartis has discontinued sale of products related to the license in certain countries and as such AxoGen has determined that the value of the Novartis license has been impaired.
Trademarks, Trade Secrets, Copyrights and Domain Names
AxoGen has registered and filed numerous trademark applications with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and appropriate offices in foreign countries in order to distinguish its products from competitors’ products. It possesses trade secrets and material know-how in the following general subject matters: nerve processing, nerve repair, product testing methods, and pre-clinical and clinical expertise. AxoGen has registered copyrights for training tools and artistic renderings. It has entered into an agreement with an independent artistic creator, under which the artistic director retains copyright rights to any copyrighted material under agreement with AxoGen and provides AxoGen a license to such copyrights. AxoGen has also registered approximately 50 domain names.
Government Regulations
U.S. Government Regulation Overview
AxoGen’s products are subject to regulation by the FDA, as well as other federal and state regulatory bodies in the U.S. and comparable authorities in other countries. In addition, its Avance® Nerve Graft must comply with the standards of the tissue bank industry’s accrediting organization, the American Association of Tissue Banks.
AxoGen distributes for Cook Biotech the AxoGuard® product line and Cook Biotech is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the AxoGuard product line. AxoGuard® products are regulated as medical devices and subject to 21 CFR § 820 (“Quality System Regulation”) and related laws and regulations. Cook Biotech has obtained a 510(k) marketing clearance from the FDA for porcine small intestine submucosa for the repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities where gap closure can be achieved by flexion of the extremity. AxoGuard® products represent the product for which 510(k) clearance was obtained.
14
In 2007, AxoGen began to process and distribute its Avance® Nerve Graft pursuant to section 361 of the Public Health Service Act and 21 CFR § 1271 Human Cell & Tissue Products (“HCT/P”) controls. Such action was based on AxoGen’s good faith belief that the Avance® Nerve Graft product was a 361 HCT/P tissue product. From October 2008 through early 2010, AxoGen was in communication with the FDA concerning the regulatory status of the Avance® Nerve Graft product. In April 2010, in response to a Request For Designation (“RFD”) filed by AxoGen, the FDA determined that the Avance® Nerve Graft was a biological product that would be reviewed and regulated by Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (“CBER”) under the biologics licensing provision of the Public Health Service Act (the “PHS Act”).
AxoGen has been working with CBER on developing the design for a phase 3 clinical trial that would support a premarket submission for Avance® Nerve Graft. AxoGen met with CBER in July 2010 and, in the time period between July 2010 and November 2010, provided information to CBER that resulted in the FDA issuing a letter in November 2010 stating the agency’s intent to exercise enforcement discretion with respect to the introduction or delivery into interstate commerce of the Avance® Nerve Graft provided that:
| • | AxoGen transitions to compliance with the Section 501(a)(2)(B) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FD&C Act”), the current good manufacturing practice regulations in 21 CFR § 210 and 211 and the applicable regulations and standards in 21 CFR § 600-610 prior to initiation of a phase 3 clinical trial; |
| • | AxoGen conduct a phase 3 clinical trial to demonstrate safety, purity and potency of the Avance® Nerve Graft under a Special Protocol Assessment; and |
| • | AxoGen continues to comply with the regulations and standard for 21 CFR § 1271 and exercises due diligence in executing the transition. |
The FDA will end the period of enforcement discretion upon final FDA action on the BLA submission or if the FDA finds that AxoGen does not meet the conditions for the transition plan. Until final action on the Avance® Nerve Graft submission, and assuming AxoGen’s compliance with the provisions in the transition plan, AxoGen is able to continue to distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft.
The BLA application and commercial distribution of the Avance® Nerve Graft, if approved, will require a potentially substantial user fee payment to the FDA, although certain exemptions, waivers and discounts of the user fees may apply, including certain waivers or discounts for small businesses. AxoGen has continued to communicate with CBER since the acceptance of the transition plan on clinical trial design and Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (“CMC”) and continues to move with diligence toward the completion of the BLA. A Special Protocol Assessment has been submitted, reviewed and approved by CBER. In compliance with the transition plan established by the FDA, AxoGen is able to continue to distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft.
FDA — General
FDA regulations govern nearly all the activities that AxoGen performs, or that are performed on its behalf, to ensure that medical products distributed domestically or exported internationally are safe and effective for their intended uses. The activities the FDA regulates include the following:
| • | product design, development and manufacture; |
| • | product safety, testing, labeling and storage; |
| • | pre-clinical testing in animals and in the laboratory; |
| • | clinical investigations in humans; |
| • | premarketing clearance or approval and licensing; |
| • | record-keeping and document-retention procedures; |
| • | advertising and promotion; |
15
| • | the import and export of products; |
| • | product marketing, sales and distribution; |
| • | post-marketing surveillance and medical device reporting, including reporting of deaths, serious injuries, communicable diseases, device malfunctions or other adverse events; and |
| • | corrective actions, removals and recalls. |
Failure to comply with applicable FDA regulatory requirements may subject AxoGen to a variety of administrative or judicially-imposed penalties or sanctions and/or prevent it from obtaining or maintaining required approvals, clearances or licenses to manufacture and market its products. Such failure to comply with the applicable FDA requirements may subject AxoGen to stringent administrative or judicial actions or sanctions, such as agency refusal to approve pending applications, warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution of products, injunctions, or civil or criminal prosecution.
FDA’s Premarket Clearance and Approval Requirements — Medical Devices
Unless an exemption applies, each medical device distributed commercially in the U.S. requires either prior 510(k) clearance or approval of a PMA from the FDA. Medical devices are classified into one of three classes — Class I, Class II, or Class III — depending on the degree of risk and the level of control necessary to assure the safety and effectiveness of each medical device. Medical devices deemed to pose lower risks are generally placed in either Class I or II. Pre-market review and clearance by the FDA for Class I and II medical devices is accomplished through the 510(k) pre-market notification procedure, unless the device is exempt. Most Class I medical devices are exempt from the 510(k) premarket notification requirement. Devices deemed by the FDA to pose the greatest risk, such as life-sustaining, life-supporting or implantable devices, or devices deemed not substantially equivalent to a previously cleared 510(k) device are generally placed in Class III. Class III devices requiring an approved PMA to be marketed are devices that were regulated as new drugs prior to May 28, 1976 (transitional devices), devices not found substantially equivalent to a predicate device, and Class III pre-amendment devices that by regulation require pre-market approval. A PMA must be supported by extensive data, including, but not limited to, technical, preclinical, clinical trials, manufacturing and labeling to demonstrate to the FDA’s satisfaction, the safety and effectiveness of the device.
FDA’s Premarket Clearance and Approval Requirements — Biologic Products
Biologics License Application (BLA) Pathway
In order to be approved as a biologic product, a BLA must demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the product candidate based on results of CMC, preclinical studies and clinical trials. A BLA must also contain extensive manufacturing information, and the applicant must pass an FDA pre-approval inspection or review of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which, or operations by which, the biologic product is produced to assess compliance with the FDA’s current good manufacturing practice. Satisfaction of FDA approval requirements for biologics typically takes several years and the actual time required may vary substantially based on the type, complexity and novelty of the product. AxoGen cannot be certain that any BLA approvals for its products will be granted on a timely basis, or at all.
The steps for obtaining FDA approval of a BLA to market a biologic product in the U.S. include:
| • | completion of preclinical laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies under the FDA’s good laboratory practices regulations; |
| • | submission to the FDA of an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”), for human clinical testing, which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin and which must include independent Institutional Review Board (IRB), approval at each clinical site before the trials may be initiated; |
16
| • | performance of adequate and well-controlled clinical trials in accordance with Good Clinical Practices to establish the safety and efficacy of the product for each indication; |
| • | submission to the FDA of a BLA, which contains detailed information about the CMC for the product, reports of the outcomes and full data sets of the clinical trials, and proposed labeling and packaging for the product; |
| • | satisfactory review of the contents of the BLA by the FDA, including the satisfactory resolution of any questions raised during the review; |
| • | satisfactory completion of an FDA Advisory Committee review, if applicable; |
| • | satisfactory completion of an FDA inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which the product is produced to assess compliance with cGMP regulations, to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to ensure the product’s identity, strength, quality and purity; and |
| • | FDA approval of the BLA including agreement on post-marketing commitments, if applicable. |
Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluations of product chemistry, toxicity and formulation, as well as animal studies. An IND sponsor must submit the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information and analytical data, to the FDA as part of the IND. Some preclinical testing may continue after the IND is submitted. The IND must become effective before human clinical trials may begin. An IND will automatically become effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions about issues such as the conduct of the trials and or supporting preclinical data as outlined in the IND. In that case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding FDA concerns or questions before clinical trials can proceed. In other words, submission of an IND may not result in the FDA allowing clinical trials to commence.
FDA’s Pre-Approval and Pre-Licensing Requirements.
Before approving a BLA, the FDA generally inspects the facility or the facilities at which the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the product if it finds that the facility does not appear to be in cGMP compliance. If the FDA determines the application, manufacturing process or manufacturing facilities are not acceptable, it will either not approve the application or issue an approvable letter in which it will outline the deficiencies in the BLA and provide the applicant an opportunity to meet with FDA representatives and subsequently to submit additional information or data to address the deficiencies. Notwithstanding the submission of any requested additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval.
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and each may take several years to complete. Data obtained from clinical activities are not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. The FDA may not grant approval on a timely basis, or at all. AxoGen may encounter difficulties or unanticipated costs in its efforts to secure necessary governmental approvals, which could delay or preclude it from marketing its products. The FDA may limit the indications for use or place other conditions on any approvals that could restrict the commercial application of the products. After approval, some types of changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications, manufacturing changes and additional labeling claims, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Post-Approval Requirements
After regulatory approval of a product is obtained, AxoGen may be required to comply with a number of post-approval requirements. For example, as a condition of approval of a BLA, the FDA may require post marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the product’s safety or efficacy. In addition, holders of an approved BLA are required to keep extensive records, to report certain adverse reactions and production problems to the
17
FDA, to provide updated safety and efficacy information and to comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotional labeling for their products. Also, quality control and manufacturing procedures must continue to conform to cGMP regulations as well as the manufacturing conditions of approval set forth in the BLA. The FDA periodically inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMP regulations, which imposes certain procedural, substantive and recordkeeping requirements. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain compliance with cGMP and other aspects of regulatory compliance.
Future FDA inspections may identify compliance issues at AxoGen’s facilities or at the facilities of its contract manufacturers that may disrupt production or distribution, or require substantial resources to correct and prevent recurrence of any deficiencies. In addition, discovery of problems with a product or the failure to comply with applicable requirements may result in restrictions on a product, manufacturer or holder of an approved BLA, including withdrawal or recall of the product from the market or other voluntary, FDA-initiated or judicial action that could delay or prohibit further marketing. Newly discovered or developed safety or effectiveness data may require changes to a product’s approved labeling, including the addition of new warnings and contraindications. Finally, new government requirements, including those resulting from new legislation, may be established that could delay or prevent regulatory approval of AxoGen products that are currently under development or regulatory activity.
The FDA has broad regulatory compliance and enforcement powers. If the FDA determines that AxoGen failed to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, it can take a variety of compliance or enforcement actions, such as issuing a FDA Form 483 notice of inspectional observations, warning letter, or untitled letter, imposing civil money penalties, suspending or delaying issuance of approvals, requiring product recall, imposing a total or partial shutdown of production, withdrawal of approvals or clearances already granted, and pursuing product seizures, consent decrees or other injunctive relief, and criminal prosecution through the Department of Justice. The FDA can also require AxoGen to repair, replace or refund the cost of devices that it manufactured or distributed. If any of these events were to occur, it could materially adversely affect AxoGen’s business.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are required to support a BLA and are sometimes required for 510(k) clearance. Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational product to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators. Clinical trials are conducted under strict requirements to ensure the protection of human subjects participating in the trial and under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used in monitoring and safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND or IDE. In addition, an IRB at each site at which the study is conducted must approve the protocol, subject consent form and any amendments. All research subjects must be informed, among other things, about the risks and benefits of the investigational product and provide their informed consent in writing.
Clinical trials under an IND typically are conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap or be combined. In AxoGen’s case, the Company believes that the Phase 3 clinical trial study for the Avance® Nerve Graft represents the only new clinical data that will be required to evaluate safety and effectiveness. Phase 1 clinical trials usually involve the initial introduction of the investigational product into a small group of healthy volunteers (e.g., 10 to 20) to evaluate the product’s safety, (dosage tolerance and pharmacokinetics if a biologic product) and, if possible, to gain an early indication of its effectiveness. Phase 2 clinical trials usually involve controlled trials in a larger but limited patient population (e.g., a few hundred) to:
| • | evaluate dosage tolerance and appropriate dosage; |
| • | identify possible adverse effects and safety risks; and |
| • | provide a preliminary evaluation of the efficacy of the product for specific indications. |
18
Phase 3 clinical trials usually further evaluate clinical efficacy and test further for safety in an expanded patient population (e.g., a hundred to several thousand). Phase 3 clinical trials usually involve comparison with placebo, standard treatments or other comparators. Usually at least one well-controlled large Phase 3 or pivotal clinical trial demonstrating safety and efficacy is required to support a BLA. These trials are intended to establish the overall risk-benefit profile of the product and provide an adequate basis for physician labeling. Phase 3 trials are usually larger, more time consuming, complex and costly than Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials. FDA regulators may accept a single study for the Avance® Nerve Graft on a smaller number of patients than would typically be required for pharmaceutical products in general, provided the data are sufficiently robust. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical testing may not be completed successfully within any specified period, if at all. Furthermore, the FDA or AxoGen may suspend or terminate clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk, have experienced a serious and unexpected adverse event, or that continued use in an investigational setting may be unethical. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of research if the research is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the research has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
Investigational New Drug (IND) Application
For a biologic product, an IND must be submitted prior to the initiation of the clinical study. The IND application must contain information in three broad areas:
| • | Animal Pharmacology and Toxicology Studies — Preclinical data to permit an assessment as to whether the product is reasonably safe for initial testing in humans. Also included are any previous experiences with the product in humans (often foreign use). |
| • | Manufacturing Information — Information pertaining to the composition, manufacturer, stability, and controls used for manufacturing of the drug substance and the drug product. This information is assessed to ensure that the company can adequately produce and supply consistent batches of the drug. |
| • | Clinical Protocols and Investigator Information — Detailed protocols for proposed clinical studies to assess whether the initial-phase trials will expose subjects to unnecessary risks. Also, information on the qualifications of clinical investigators — professionals (generally physicians) who oversee the administration of the experimental compound — to assess whether they are qualified to fulfill their clinical trial duties. Finally, commitments to obtain informed consent from the research subjects, to obtain review of the study by an IRB, and to adhere to the investigational new drug regulations. |
Once the IND is submitted, the sponsor must wait 30 calendar days before initiating any clinical trials. During this time, FDA has an opportunity to review the IND for safety to assure that research subjects will not be subjected to unreasonable risk.
AxoGen Clinical Trials
AxoGen is currently performing three clinical studies to gather data on the Avance® Nerve Graft. The studies are “A Multicenter Retrospective Study of Avance® Nerve Graft Utilization, Evaluations and Outcomes in Peripheral Nerve Injury Repair (“RANGER®”)”, “A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study of Hollow Nerve Conduit and Avance® Nerve Graft Evaluation Recovery Outcomes of the Nerve Repair in the Hand (“CHANGE”)” and a pilot study to evaluate the use of Avance® Nerve Graft in the reconstruction of nerves following prostatectomy. AxoGen intends to continue to enroll patients in RANGER® over the next several years. The CHANGE study is being run as a pilot comparative study and enrollment is now completed.
Clinical trials are subject to extensive recordkeeping and reporting requirements. AxoGen’s clinical trials must be conducted under the oversight of an IRB for the relevant clinical trial sites and must comply with FDA regulations, including but not limited to those relating to good clinical practices. AxoGen is also required to obtain the patients’ written informed consent in form and substance that complies with both FDA requirements
19
and state and federal privacy and human subject protection regulations. AxoGen, the FDA or the IRB may suspend a clinical trial at any time for various reasons, including a belief that the risks to study subjects outweigh the anticipated benefits. Even if a trial is completed, the results of clinical testing may not adequately demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the device or may otherwise not be sufficient to obtain FDA approval to market the product in the U.S. Similarly, in Europe, the clinical study must be approved by a local ethics committee and, in some cases, including studies with high-risk devices, by the ministry of health in the applicable country.
Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws
Educational Grants
The FDA permits a medical product manufacturer to provide financial support, including support by way of grants, to third-parties for the purpose of conducting medical educational activities. If these funded activities are considered by the FDA to be independent of the manufacturer, then the activities fall outside the restrictions on promotion to which the manufacturer is subject.
The FDA considers several factors in determining whether an educational event or activity is independent from the substantive influence of the product manufacturer and therefore nonpromotional, including, but not limited to, the following:
| • | whether the intent of the funded activity is to present clearly defined educational content, free from commercial influence or bias; |
| • | whether the third-party grant recipient and not the manufacturer has maintained control over selecting the faculty, speakers, audience, program content and materials; |
| • | whether the program focuses on a single product of the manufacturer without a discussion of other relevant existing competitive products or treatment options; |
| • | whether there was meaningful disclosure to the audience, at the time of the program, regarding the manufacturer’s funding of the program, any significant relationships between the provider, presenters, or speakers and the supporting manufacturer; whether any unapproved uses will be discussed; |
| • | whether there are legal, business, or other relationships between the supporting manufacturer and provider or its employees that could permit the supporting manufacturer to exert influence over the content of the program |
| • | whether the individuals employed by the provider and involved in designing or conducting the educational activities are also involved in advising or assisting the company with respect to sales or marketing; and |
| • | whether the information about the company’s products is further disseminated after the initial program, by or at the direction of the company, other than in response to an unsolicited request or through an independent provider. |
AxoGen seeks to ensure that the activities it supports pursuant to educational grants program are in accordance with these criteria for independent educational activities. However, AxoGen cannot provide an assurance that the FDA or other government authorities would view the programs supported as being independent.
20
Pervasive and Continuing Regulation
There are numerous regulatory requirements that apply after a product is cleared or approved. These include: the FDA’s Quality System Regulation (QSR) per 21 CFR § 820 for medical devices, the FDA’s Good Tissue Practices (GTP) per 21 CFR §1271 for HCT/P tissue products and the FDA’s Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) per 21 CFR § 210, 211, and 600 for biologic products. These regulations require manufacturers, including third-party manufacturers:
| • | to follow stringent design, testing, control, documentation and other quality assurance procedures during all aspects of the manufacturing process; |
| • | to comply with labeling regulations and FDA prohibitions against the false or misleading promotion or the promotion of products for uncleared, unapproved or off-label use or indication; |
| • | to comply with requirements to obtain clearance or approval of product modifications that could significantly affect safety or efficacy or that would constitute a major change in intended use; |
| • | to report to the FDA certain adverse events, adverse reactions and deviations: (a) for medical devices, a report to FDA is required if the device may have caused or contributed to a death or serious injury or malfunctioned in a way that would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if the malfunction were to recur; (b) for biologics, a deviation from current good manufacturing practice or an unexpected or unforeseeable event that may affect the safety, purity, or potency of the product must be reported; and (c) for 361 HCT/P tissue products, FDA requires reporting of certain adverse reactions involving a communicable disease related to an HCT/P that the company made available for distribution; |
| • | to comply with post-approval restrictions or conditions, including post-approval study commitments; |
| • | to follow post-market surveillance regulations that may apply when necessary to protect the public health or to provide additional safety and effectiveness data for the device; and |
| • | to follow requirements to issue notices of correction or removal, or conduct market withdrawals or recalls where quality or other issues arise. |
AxoGen has not had any adverse events concerning the Avance® Nerve Graft or the AxoGuard® products and has not had to submit any Medical Device Reports (“MDRs”), biological deviation reports, or tissue adverse reaction reports to the FDA. Although AxoGen has had no adverse events to date, there may have been other incidents, including patient deaths, which may have occurred during procedures utilizing AxoGen’s products without AxoGen being aware of any such incidents. In addition, there can be no assurance that in the future AxoGen will not have an adverse event or will not submit any MDR’s, biological deviation reports, or tissue adverse reaction reports to the FDA.
The advertising and promotion of medical products are also regulated by the Federal Trade Commission and by state regulatory and enforcement authorities. Recently, some promotional activities for FDA-regulated products have been the subject of enforcement action brought under healthcare reimbursement laws and consumer protection statutes. In addition, under the Federal Lanham Act and similar state laws, competitors and others can initiate litigation relating to advertising claims.
AxoGen has registered with the FDA as a tissue establishment for the Avance® Nerve Graft. The FDA has broad post-market and regulatory enforcement powers. AxoGen is subject to unannounced inspections by the FDA to determine compliance with the QSR, GTP and other regulations, and these inspections may also include the manufacturing facilities of suppliers.
21
Failure by AxoGen or by AxoGen’s suppliers to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can result in enforcement action by the FDA or other federal or state authorities, which may include any of the following sanctions, among others:
| • | warning letters, fines, injunctions, consent decrees and civil penalties; |
| • | customer notifications, repair, replacement, refunds, recall or seizure of our products; |
| • | operating restrictions, partial suspension or total shutdown of production; |
| • | suspension or termination of our clinical trials; |
| • | refusing our premarket approval (PMA or BLA) of new products, new intended uses or modifications to existing products; |
| • | withdrawing premarket approvals that have already been granted; and |
| • | criminal prosecution. |
Fraud, Abuse and False Claims
AxoGen is directly and indirectly subject to various federal and state laws governing relationships with healthcare providers and pertaining to healthcare fraud and abuse, including anti-kickback laws. In particular, the federal healthcare program Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in exchange for or to induce either the referral of an individual, or the furnishing, arranging for or recommending a good or service for which payment may be made in whole or part under federal healthcare programs, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Penalties for violations include criminal penalties and civil sanctions such as fines, imprisonment and possible exclusion from Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs. The Anti-Kickback Statute is broad and prohibits many arrangements and practices that are lawful in businesses outside of the healthcare industry. In implementing the statute, the Office of Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (“OIG”) has issued a series of regulations, known as the “safe harbors.” These safe harbors set forth provisions that, if all their applicable requirements are met, will assure healthcare providers and other parties that they will not be prosecuted under the Anti-Kickback Statute. The failure of a transaction or arrangement to fit precisely within one or more safe harbors does not necessarily mean that it is illegal or that prosecution will be pursued. However, conduct and business arrangements that do not fully satisfy each applicable element of a safe harbor may result in increased scrutiny by government enforcement authorities, such as the OIG.
The Federal False Claims Act (“FCA”) imposes civil liability on any person or entity that submits, or causes the submission of, a false or fraudulent claim to the U.S. Government. Damages under the FCA can be significant and consist of the imposition of fines and penalties. The FCA also allows a private individual or entity with knowledge of past or present fraud against the federal government to sue on behalf of the government to recover the civil penalties and treble damages. The U.S. Department of Justice (“DOJ”) on behalf of the government has previously alleged that the marketing and promotional practices of pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers included the off-label promotion of products or the payment of prohibited kickbacks to doctors violated the FCA resulting in the submission of improper claims to federal and state healthcare entitlement programs such as Medicaid. In certain cases, manufacturers have entered into criminal and civil settlements with the federal government under which they entered into plea agreements, paid substantial monetary amounts and entered into corporate integrity agreements that require, among other things, substantial reporting and remedial actions going forward.
AdvaMed is one of the primary voluntary U.S. trade associations for medical device manufacturers. This association has established guidelines and protocols for medical device manufacturers in their relationships with healthcare professionals on matters including research and development, product training and education, grants and charitable contributions, support of third-party educational conferences, and consulting arrangements. Adoption of the AdvaMed Code by a medical device manufacturer is voluntary, and while the OIG and other
22
federal and state healthcare regulatory agencies encourage its adoption and may look to the AdvaMed Code, they do not view adoption of the AdvaMed Code as proof of compliance with applicable laws. AxoGen has incorporated the principles of the AdvaMed Code in its standard operating procedures, sales force training programs, and relationships with doctors. Key to the underlying principles of the AdvaMed Code is the need to focus the relationships between manufacturers and healthcare professionals on matters of training, education and scientific research, and limit payments between manufacturers and healthcare professionals to fair market value for legitimate services provided and payment of modest meal, travel and other expenses for a healthcare professional under limited circumstances. AxoGen has incorporated these principles into its relationships with healthcare professionals under its consulting agreements, payment of travel and lodging expenses, research and educational grant procedures and sponsorship of third-party conferences. In addition, AxoGen has conducted training sessions on these principles. However, AxoGen cannot provide any assurance that regulatory or enforcement authorities will view these arrangements as being in compliance with applicable laws.
Regulation Outside of the United States
Sales of medical products outside of the U.S. are subject to foreign governmental regulations that vary substantially from country to country. The time required to obtain certification or approval by a foreign country may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA clearance or approval and the requirements may be different.
There are restrictions under U.S. law on the export from the U.S. of medical devices and biologic product that cannot be legally distributed in the U.S. If a Class I or Class II medical device does not have 510(k) clearance, and the manufacturer reasonably believes that the device could obtain 510(k) clearance in the U.S., then the device can be exported to a foreign country for commercial marketing without the submission of any type of export request or prior FDA approval, if the device is not sold or offered for sale in the U.S., is labeled for export only and satisfies certain criteria relating primarily to specifications of the foreign purchaser and compliance with the laws of the country to which it is being exported, known as Importing Country Criteria. An unapproved Class III medical device can be exported if it complies with the criteria discussed above for devices that could obtain 510(k) clearance, meets certain other quality and labeling requirements, and has a valid marketing authorization from one of a list of countries listed in the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. If an unapproved Class III medical device does not have a valid marketing authorization from one of the listed countries, an export permit from the FDA is required in order to export it. An unapproved biologic product can be exported without submitting an export request to FDA if the product has received a marketing authorization in one of a list of countries listed in the FD&C Act and it meets applicable requirements of the FD&C Act and the laws of the country to which it is exported. An investigational biologic product may also be exported under an IND if a listed investigator is in a foreign country and certain requirements specified in FDA’s regulations are met. AxoGen currently complies with applicable regulations when exporting its products and intends to continue such compliance in the event there are any regulatory changes regarding its products in the United States.
The primary regulatory body in Europe is that of the European Union (EU), which has adopted numerous directives and promulgated voluntary standards regulating the design, manufacture and labeling of, and clinical trials and adverse event reporting for, medical devices. Devices that comply with the requirements of a relevant directive will be entitled to bear CE marking, indicating that the device conforms to the essential requirements of the applicable directives and, accordingly, can be commercially distributed throughout the member states of the EU and other countries that comply with or mirror these directives. The method for assessing conformity varies depending on the type and class of the product, but normally involves an assessment by the manufacturer and a third-party assessment by a notified body, an independent and neutral institution appointed by a country to conduct the conformity assessment. This third-party assessment may consist of an audit of the manufacturer’s quality system and specific testing of the manufacturer’s device. Such an assessment is required for a manufacturer to commercially distribute the product throughout these countries. AxoGen has prepared the Quality System and is ready for an assessment by the International Organization for Standardization, (ISO) 13485:2003 Quality Management System. Compliance establishes the presumption of conformity with the essential requirements for a CE Marking.
23
Tissue products are not currently regulated under the CE Mark
Although some standards of harmonization exist, each country in which AxoGen conducts business has its own specific regulatory requirements. AxoGen procures and processes its tissue products in the U.S., and markets in the U.S., Canada, Switzerland, Austria and Italy under compliance with the individual country regulations. These requirements are dynamic in nature and, as such, are continually changing. New regulations may be promulgated at any time and with limited notice. While AxoGen believes that it is in compliance with all existing pertinent international and domestic laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that changes in governmental administrations and regulations will not negatively impact AxoGen’s operations.
The FDA and international regulatory bodies conduct periodic compliance inspections of AxoGen’s U.S. processing facilities. AxoGen’s operations are registered with the U.S. FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, (CBER), as a tissue establishment. AxoGen is also accredited by the AATB and is licensed in the states of Florida, New York, California, Maryland, Delaware, Oregon and Illinois. AxoGen believes that worldwide regulation of tissue products is likely to intensify as the international regulatory community focuses on the growing demand for these implant products and the attendant safety and efficacy issues of citizen recipients. Changes in governing laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s financial condition and results of operations. AxoGen management further believes that it can help to mitigate this exposure by continuing to work closely with government and industry regulators.
Environmental
AxoGen’s products, as well as the chemicals used in processing, are handled and disposed of in accordance with country-specific, federal, state and local regulations. Since 2007, AxoGen has used outside third parties to perform all biohazard waste disposal.
AxoGen contracts with independent, third parties to perform sterilization of its allografts. In view of the engagement of a third party to perform irradiation services, the requirements for compliance with radiation hazardous waste do not apply, and therefore AxoGen does not anticipate that having any material adverse effect upon its capital expenditures, results of operations or financial condition. However, AxoGen is responsible for assuring that the service is being performed in accordance with applicable regulations. Although AxoGen believes it is in compliance with all applicable environmental regulations, the failure to fully comply with any such regulations could result in the imposition of penalties, fines and/or sanctions which could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business.
LecTec Corporation Merger
On September 30, 2011, LecTec Corporation (“LecTec”) completed its business combination with AxoGen Corporation (“AC”) in accordance with the terms of an Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 31, 2011, by and among LecTec, Nerve Merger Sub Corp., a subsidiary of LecTec (“Merger Sub”), and AC, which the parties amended on September 30, 2011 and August 9, 2011 (as amended, the “Merger Agreement”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub merged with and into AC, with AC continuing after the merger as the surviving corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of LecTec (the “Merger”). Immediately following the Merger, LecTec changed its name to AxoGen, Inc.
PDL BioPharma, Inc. Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement
General
On October 5, 2012, AxoGen entered into a Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement (the “Royalty Contract”) with PDL BioPharma, Inc. (“PDL”), pursuant to which AxoGen sold to PDL the right to receive specified royalties on AxoGen’s Net Revenues generated by the sale, distribution or other use of AxoGen’s products Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and
24
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector. The Royalty Contract has a term of eight years. Under the Royalty Contract, PDL is to receive royalty payments based on a 9.95% royalty rate of AxoGen’s Net Revenues, subject to certain agreed upon minimum payment requirements of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter, which begin in the fourth quarter of 2014 as provided in the Royalty Contract. The total consideration PDL paid to AxoGen was the Funded Amount of $20,800,000, including $19,050,000 PDL paid to AxoGen on October 5, 2012, and $1,750,000 PDL paid to AxoGen on August 14, 2012 pursuant to an Interim Revenue Interest Purchase Agreement between AxoGen and PDL, dated August 14, 2012 (the “Interim Royalty Contract”). Upon the closing of PDL’s purchase of the specified royalties described above, which was concurrent with the execution of the Royalty Contract, the Interim Royalty Contract was terminated.
Put Option
Under the Royalty Contract, on October 5, 2016, or in the event of the occurrence of a material adverse event, our transfer of revenue interest or substantially all of our interest in the products or AxoGen’s bankruptcy or material breach of the Royalty Contract, PDL may require AxoGen to repurchase the Assigned Interests at the “Put Price.” The Put Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a 20% internal rate of return to PDL on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by AxoGen, and (ii) any “Delinquent Assigned Interest Payment” (as defined in the Royalty Contract) AxoGen owed to PDL.
Change of Control; Call Option
In addition, in the event of a “Change of Control”, AxoGen must repurchase the assigned Interests from PDL for a repurchase price equal to the “Change of Control Price” on or prior to the third business day after the occurrence of the Change of Control. The Change of Control Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a 32.5% internal rate of return to PDL on all payments made by PDL pursuant to the Royalty Contract as of the date of the Change of Control Payment (as defined in the Royalty Contract), taking into account the amount and timing of all payments made by AxoGen to PDL (and retained by PDL) prior to and as of the date of payment of the Change of Control Payment, plus (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment owed. In addition, at any time after October 5, 2016, AxoGen, at its option, can call the Royalty Contract for a price equal to the Change of Control Price.
Board Designee
Under the Royalty Contract, during the term of the Royalty Contract, PDL is entitled to designate, and AxoGen shall appoint an individual designated by PDL, who shall serve on the Board of Directors of AxoGen (the “Board”) until AxoGen’s 2013 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the “2013 Annual Meeting”). For the 2013 Annual Meeting and each annual meeting thereafter during the term of the Royalty Contract, the Board shall nominate and recommend the PDL designee as a director nominee to serve on the Board until the next annual meeting and shall include such nomination in AxoGen’s proxy statement for the 2013 Annual Meeting and each annual meeting thereafter, provided that the election of the PDL designee is subject to shareholders’ approval. Should at any time there become a vacancy on the Board as a result of (i) the resignation, death or removal of the PDL designee or (ii) such PDL designee failing to obtain the requisite approval of AxoGen’s shareholders at any annual or special meeting of AxoGen’s shareholders and where no other individual is elected to such vacancy, PDL shall have the right to designate an individual to fill such vacancy, and AxoGen shall take such actions necessary to appoint, such individual to the Board. AxoGen was required to have taken all actions necessary at or prior to the Closing to ensure there is a vacancy on the Board as of the Closing to permit the appointment of the PDL designee to the Board as of the Closing. PDL has exercised this right and nominated John P. McLaughlin, PDL’s President and Chief Executive Officer. On October 5, 2012, upon the Closing, the Board approved to increase its size from seven directors to eight directors, and Mr. McLaughlin was elected to the Board to serve until the 2013 Annual Meeting.
25
Preemptive Rights
Under the Royalty Contract, PDL has preemptive rights with respect to new issuances of AxoGen’s equity securities and securities convertible, exchangeable or exercisable into such equity securities, subject to certain restrictions, including restrictions regarding issuance of securities in a registered public offering by the Company.
Restriction on Dividends
Under the Royalty Contract, during the period from the October 5, 2012 to December 4, 2016 (or the payment of the Put Price in the event PDL exercises its put option on or prior to December 4, 2016), AxoGen shall not, nor shall it permit any subsidiary to, declare, pay or make any dividend or distribution on any shares of the common stock or preferred stock of such entity (other than dividends or distributions payable in its stock, or split-ups or reclassifications of its stock) or apply any of its funds, property or assets to the purchase, redemption or other retirement of any common or preferred stock, or of any options to purchase or acquire any such shares of common or preferred stock of any such entity (collectively, “Restricted Payments”), except that: (i) each subsidiary may make direct or indirect Restricted Payments to AxoGen; and (ii) AxoGen and each subsidiary may purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire Equity Interests issued by it solely with the proceeds received from the substantially concurrent issue of new shares of its common stock or other common Equity Interests. For purposes of the Royalty Contract, “Equity Interests” of any person means any and all shares, rights to purchase, options, warrants, general, limited or limited liability partnership interests, member interests, participation or other equivalents of or interest in (regardless of how designated) equity of such entity, whether voting or nonvoting, including common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities or any other “equity security” (as such term is defined in Rule 3a11-1 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended).
Guarantee and Collateral Agreement
In connection with the Royalty Contract, on October 5, 2012, AxoGen and AxoGen Corporation (“AC”) entered into a Guarantee and Collateral Agreement (the “Guarantee and Collateral Agreement”) with PDL, pursuant to which (i) AC unconditionally and irrevocably guarantees to PDL the prompt and complete payment and performance by AxoGen when due of the “Secured Obligations,” which include AxoGen’s obligations under the Royalty Contract, and any other obligations that AxoGen may owe to PDL under the Royalty Contract and other transaction documents; and (ii) each of AxoGen and AC grants to PDL a security interest in certain collateral as specified in the Guarantee and Collateral Agreement for the prompt and complete payment and performance when due of the Secured Obligations.
Employees
At December 31, 2012, the Company had 57 full time employees which included 10 in administration, information technology and finance, 14 in manufacturing and quality control, 7 in research and development and regulatory and 26 in sales and marketing. As of the date of this 10-K AxoGen has not had a work stoppage and no employees are represented by a labor union. AxoGen believes its relationship with its employees is satisfactory.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Prior to the Merger, Mr. Gregory Freitag was LecTec’s only executive officer serving as CEO and CFO. The following table, except as noted, lists the names and positions of the individuals who have served since the completion of the Merger, and who are, as of March 12, 2013, executive officers the Company:
| Name |
Title | |
| Karen Zaderej |
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director | |
| Gregory G. Freitag, J.D. CPA |
Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel and Director | |
| John P. Engels |
Vice President | |
| Jill F. Schiaparelli |
Senior Vice President, Business Strategy and Marketing | |
| Mark Friedman, Ph.D. |
Vice President of Regulatory and Quality | |
| David Hansen |
Corporate Controller | |
| Shawn McCarrey |
Senior Vice President of Sales |
26
Biographical information for each of our executive officers is included below.
Karen Zaderej, President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Age 51)
Ms. Zaderej has served as AxoGen’s President, Chief Executive Officer and a member of its board of directors since September, 2011. She has served as AC’s Chief Executive Officer and a member of its board of directors since May 2010. Ms. Zaderej joined AC in May 2006 and served as Vice President of Marketing and Sales from May 2006 to October 2007 and as Chief Operating Officer from October 2007 to May 2010. From October 2004 to May 2006, Ms. Zaderej worked for Zaderej Medical Consulting, a consulting firm she founded, which assisted medical device companies build and execute successful commercialization plans. From 1987 to 2004, Ms. Zaderej worked at Ethicon, Inc., a Johnson & Johnson company, where she held senior positions in marketing, business development, and research & development, as well as ran a manufacturing business. Ms. Zaderej has a MBA from the Kellogg Graduate School of Business and a BS in Chemical Engineering from Purdue University.
Gregory G. Freitag, J.D., CPA, Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel and Director (Age 51)
Mr. Freitag, J.D., CPA, has been AxoGen’s Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel and a member of its Board of Directors since September 2011 and was LecTec’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and board member from June 2010 through September 2011. From May 2009 to the present, Mr. Freitag has been a principal of FreiMc, LLC, a consulting and advisory firm he founded that provides strategic guidance and business development advisory services. Mr. Freitag also founded and is a principal of EmployRx. Inc., a business that provides services to self-insured employers relating to prescription drug benefits. Prior to founding FreiMc, LLC and EmployRx, Inc., Mr. Freitag was a Director of Business Development at Pfizer Health Solutions, a former subsidiary of Pfizer, Inc., from January 2006 to May 2009. From July 2005 to January 2006, Mr. Freitag worked for Guidant Corporation in their business development group. Prior to Guidant Corporation, Mr. Freitag was the Chief Executive Officer of HTS Biosystems, a biotechnology tools start-up company, from March 2000 until its sale in early 2005. Mr. Freitag was the Chief Operating Officer, Chief Financial Officer and General Counsel of Quantech, Ltd., a public point of care diagnostic company, from December 1995 to March 2000. Prior to that time, Mr. Freitag practiced corporate law in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Mr. Freitag is also a director of the Foundation Board of HealthEast Care System Foundation, a health care system in Minnesota.
John P. Engels, Vice President (Age 41)
Mr. Engels has served as AxoGen’s Vice President since September, 2011. He is a co-founder of AC and has served as AC’s Vice President since June 2006, providing operational and financial leadership and managing AxoGen’s strategic and product development partnerships. From 1999 to 2002, Mr. Engels worked as a consultant for the University of Florida, Saffron Hill Ventures and PA Early Stage Partners, among other companies. From 1993 to 1997, Mr. Engels was an analyst and associate at CACM, a boutique investment banking firm. Mr. Engels is currently a member of the board of directors of Oxicool, Inc., a privately-held company developing new cooling technologies. Mr. Engels holds a MBA in Management and Operations from the Wharton School of Business at the University of Pennsylvania, and a BA from the University of Chicago.
Jill F. Schiaparelli, Senior Vice President, Business Strategy & Marketing (Age 47)
Ms. Schiaparelli has served as AxoGen’s Senior Vice President, Business Strategy & Marketing since February 2012. From January 2011 to February 2012 and from June, 2007 to December 2008, Ms. Schiaparelli was employed by JS Strategic Partners, LLC, a consulting firm she founded to provide business strategy, commercialization and marketing services to biotechnology companies and health care providers. From December 2008 to December 2010, Ms. Schiaparelli was the Vice President, Commercial Strategy & Business Development for ApaTech, a venture-back global orthopedic graft company based in the UK that was later acquired by Baxter Healthcare. From 1996 to 2007, Ms. Schiaparelli was employed by Johnson & Johnson family of companies where she held several senior positions in strategic marketing, marketing, sales operations
27
and healthcare analytics within the Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Ethicon and Healthcare Systems operating companies. Prior to working in the healthcare industry, Ms. Schiaparelli worked for 8 years in the investment banking and financial services industry. Ms. Schiaparelli has an MBA from the Stern School of Business at New York University and a BS in Business Administration from Boston University.
Mark Friedman, Ph.D., Vice President of Regulatory and Quality (Age 55)
Dr. Friedman has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Regulatory and Quality since September, 2011. He has served as AC’s Vice President of Regulatory and Quality since June 2011 and served as AC’s Director of Quality Assurance and Regulatory Affairs from September 2006 to June 2011. Prior to joining AxoGen, Dr. Friedman held several regulatory and quality leadership positions at Enable Medical Corporation, a medical device company, including Director of Quality Assurance from 1997 to 1998 and Vice President of Quality and Regulatory from 1998 to 2001 and from 2004 to 2005. Dr. Friedman also worked for AtriCure, Inc., a company that develops, manufactures and sells surgical ablation systems to treat atrial fibrillation, as Vice President of Quality and Regulatory from 2001 to 2004 and as Vice President of Operations in 2004. AtriCure acquired Enable Medical in 2005. Mr. Friedman has over 24 years of experience in developing and directing regulatory strategy and quality systems for medical products, including 15 years with start-up medical product firms. Dr. Friedman has a Ph.D. in Chemistry specializing in protein biochemistry from the University of Cincinnati.
David Hansen, Corporate Controller (Age 52)
Mr. Hansen has served as AxoGen’s Corporate Controller since September, 2011. He has served as AC’s Corporate Controller since June 2006. Mr. Hansen was Vice President of Finance — Corporate Controller and Treasurer of Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc., a publicly-traded environmental services company, and held other corporate and regional accounting positions at Perma-Fix Environmental Services from 1995 to 2005. Mr. Hansen was also Controller at Kraft Foodservice, Inc. from 1994 to 1995 and held other accounting and procurement positions at Kraft Foodservice, Inc. from 1985 to 1994. Mr. Hansen has over 20 years of experience in senior financial positions at both publicly traded and private companies. Mr. Hansen holds a Bachelor of Business Administration degree in Accounting from the University of Oklahoma.
Shawn McCarrey, Vice President of Sales (Age 55)
Mr. McCarrey has served as AxoGen’s Senior Vice President of Sales since February, 2013. Mr. McCarrey was Executive Vice President of North American Cardiovascular Sales at Bayer Interventional/MEDRAD Interventional from January, 2009 to May 2012. Bayer HealthCare, a subgroup of Bayer AG, is one of the world’s leading, innovative companies in the healthcare and medical products industry. Bayer Interventional, now doing business as part of Bayer Medical Care’s Radiology and Interventional business, is the Interventional franchise formerly operated under Bayer’s MEDRAD brand. From 1998 to 2009, Mr. Carrey held multiple escalating positions with Possis Medical, Inc., a company that developed, manufactured, and marketed medical devices for the cardiovascular and vascular treatment markets, and served as Director or Sales, VP of US Sales, VP of Worldwide Sales and EVP of Worldside Sales & Marketing. . For more than 15 years prior to joining Possis, Mr. McCarrey served in a series of progressively responsible roles with two divisions of C.R. Bard, United States Catheter and Instrument Corporation (USCI) which specialized in the treatment of coronary disease in the cardiac catheterization laboratory and Davol, an operating room division that promoted Thoraclex® and Simpulse® to cardiovascular and orthopedic surgeons. Mr. McCarrey holds a Bachelor of Science degree in Marketing from Central Michigan University.
AxoGen has a key-person life insurance policy for $3,000,000 insuring the life of Ms. Zaderej.
28
AxoGen’s business involves a number of risks, some of which are beyond its control. The risk and uncertainties described below are not the only ones the Company faces. Set forth below is a discussion of the risks and uncertainties that management believes to be material to AxoGen.
AxoGen has not experienced positive cash flow from its operations, and the ability to achieve positive cash flow from operations will depend on increasing sales of its products, which may not be achievable.
AxoGen has historically operated with negative cash flow from its operations. As of December 31, 2012, AxoGen had an accumulated deficit of approximately $58 million. If AxoGen product sales do not increase as anticipated, then it will continue to experience negative cash flows and adverse operating conditions. AxoGen’s continuing capital needs and other factors, could cause the Company to raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or from other sources. The sale of additional equity may result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that AxoGen will be able to secure funding on terms acceptable to it, or at all.
AxoGen’s revenue growth depends on its ability to expand its sales force and develop new customers, and there can be no assurance that these efforts will result in significant increase in sales.
AxoGen is in the process of investing in its sales channel composed of a combination of its direct sales force and independent distributors to allow it to reach new customers. The Company is also in the process of hiring a Vice President of Sales to lead AxoGen’s sales force. There can be no assurance that these efforts will be successful in expanding AxoGen’s product sales. AxoGen currently sells products directly through its employees and indirectly through distributor relationships. AxoGen is engaged in a major initiative to build and further expand sales and marketing capabilities. The incurrence of these expenses impacts AxoGen’s operating results, and there can be no assurance of their effectiveness. If AxoGen is unable to develop its sales force and new customers, it may not be able to grow revenue or maintain its current level of revenue generation.
AxoGen’s revenue depends solely on three products.
All of AxoGen’s revenue is currently derived from only three products, the Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, for the treatment of peripheral nerve damage. Its ability to generate revenue is dependent on the success of these products. Accordingly, any disruption in AxoGen’s ability to generate revenue from the sale of these products will have a material adverse impact on its business, results of operations, financial condition and growth prospects. In addition, AxoGen’s expenditures for research and development are minimal and funding to develop, or increase efforts to find collaboration or licensing opportunities to obtain, additional products will be necessary.
The AxoGuard® products are only available through an exclusive distribution agreement with Cook Biotech Incorporated. Such contract is for an initial seven year term and following such initial term, the agreement automatically renews for an additional seven (7) year period provided that the parties agree to meet at least ninety (90) days before the end of such initial term to review whether the purchase price of the products obtained from Cook Biotech need to be adjusted and reasonably agree to such adjustment in writing, where such agreement shall not be unreasonably withheld. However, there are conditions for continuation of the agreement, including payment terms and minimum purchase requirements, that if breached could result in an earlier termination of the agreement; except that through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforce such minimum purchase provision. Although there are products that AxoGen believes it could develop or obtain that would replace the AxoGuard® products, the loss of the ability to sell the AxoGuard® products could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business until other replacement products are available.
29
AxoGen’s success will be dependent on continued acceptance of its products by the medical community.
Continued market acceptance of AxoGen’s products will depend on its ability to demonstrate that its products are an attractive alternative to existing nerve reconstruction treatment options. Its ability to do so will depend on surgeons’ evaluations of clinical safety, efficacy, ease of use, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of AxoGen’s nerve repair products. For example, although AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft follows stringent safety standards, including sterilization by gamma irradiation, AxoGen believes that a small portion of the medical community has lingering concerns over the risk of disease transmission through the use of allografts in general. Furthermore, AxoGen believes that even if its products receive general acceptance within the medical community, acceptance and clinical recommendations by influential surgeons will be important to the commercial success of AxoGen’s products.
Negative publicity concerning methods of donating human tissue and screening of donated tissue, in the industry in which AxoGen operates, may reduce demand for its Avance® Nerve Graft product and negatively impact the supply of available donor tissue.
AxoGen is highly dependent on its ability to recover cadaveric nerves from tissue donors for its Avance® Nerve Graft product. The availability of acceptable donors is relatively limited, and this availability is impacted by regulatory changes, general public opinion of the donation process and AxoGen’s reputation for its handling of the donation process. Media reports or other negative publicity concerning both improper methods of tissue recovery from donors and disease transmission from donated tissue for other allografts (i.e., bones, tendon, etc.) may limit widespread acceptance of AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft allograft. Unfavorable reports of improper or illegal tissue recovery practices, both in the U.S. and internationally, as well as incidents of improperly processed tissue leading to transmission of disease, may broadly affect the rate of future tissue donation and market acceptance of allograft technologies. Potential patients may not be able to distinguish AxoGen products, technologies, and tissue recovery and processing procedures from others engaged in tissue recovery. In addition, unfavorable reports could make families of potential donors from whom AxoGen is required to obtain consent before processing tissue reluctant to agree to donate tissue to for-profit tissue processors. Any disruption in the supply could have negative consequences for AxoGen’s revenue, operating results and continued operations.
AxoGen is highly dependent on the continued availability of its facilities and could be harmed if the facilities are unavailable for any prolonged period of time.
Any failure in the physical infrastructure of AxoGen’s facilities, including the facility it leases from LifeNet Health, could lead to significant costs and disruptions that could reduce its revenues and harm its business reputation and financial results. Any natural or man-made event that impacts AxoGen’s ability to utilize its facilities could have a significant impact on its operating results, reputation and ability to continue operations. This includes termination of the LifeNet Health facility lease which can occur upon six months’ notice from either party. Although AxoGen believes it can find and make operational a new facility in less than six months, the regulatory process for approval of facilities is time-consuming and unpredictable. AxoGen’s ability to rebuild or find acceptable lease facilities would take a considerable amount of time and expense and could cause a significant disruption in service to its customers. Although AxoGen has business interruption insurance which would, in instances other than lease termination, cover certain costs, it may not cover all costs nor help to regain AxoGen’s standing in the market.
AxoGen must maintain high quality manufacturing and processing.
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product requires careful calibration and precise, high-quality processing and manufacturing. Achieving precision and quality control requires skill and diligence by its personnel. If it fails to achieve and maintain these high quality controls, processing and manufacturing standards, including avoidance of manufacturing errors, defects or product failures, AxoGen could experience recalls or withdrawals of its product, delays in delivery, cost overruns or other problems that would adversely affect its business. AxoGen cannot completely eliminate the risk of errors, defects or failures. In addition, AxoGen may experience
30
difficulties in scaling-up manufacturing of its Avance® product, including problems related to yields, quality control and assurance, tissue availability, adequacy of control policies and procedures, and lack of skilled personnel. If AxoGen is unable to process and produce its allografts on a timely basis, at acceptable quality and costs, and in sufficient quantities, or if it experiences unanticipated technological problems or delays in production, its business would be adversely affected.
AxoGen relies on third-party suppliers, some of which are currently the only source for the respective components or materials they supply to it.
Although most of the raw materials used in the production of Avance® Nerve Graft are available from more than one supplier, AxoGen currently obtains one of the chemicals it uses in the manufacture of Avance® Nerve Graft from only one supplier. Some of the test results and reagents AxoGen uses in its manufacturing process are also obtained from single suppliers. FDA approval of a new supplier may be required if these materials become unavailable from AxoGen’s current suppliers. Although there may be other suppliers that have equivalent materials that would be available to AxoGen, FDA approval of any alternate suppliers if required could take several months or years to obtain, if able to be obtained at all. Any delay, interruption or cessation of production by AxoGen’s third-party suppliers of important materials, or any delay in qualifying new materials, if necessary, would prevent or delay AxoGen’s ability to manufacture products. In addition, an uncorrected impurity, a supplier’s variation in a raw material or testing, either unknown to AxoGen or incompatible with its manufacturing process, or any other problem with AxoGen’s materials, testing or components, would prevent or delay its ability to manufacture products. These delays may limit AxoGen’s ability to meet demand for its products and delay its clinical trial, which would have a material adverse impact on its business, results of operations and financial condition.
AxoGen relies on third parties to perform many necessary services for the commercialization of Avance® Nerve Graft, including services related to the recovery, distribution, storage and transportation.
AxoGen relies upon third parties for certain recovery, distribution, and transportation services. In accordance with product specifications, these third parties ship Avance® Nerve Graft in specially validated shipping containers at frozen temperatures. If any of the third parties that AxoGen relies upon in its recovery, distribution, storage or transportation process fail to comply with applicable laws and regulations, fail to meet expected deadlines, or otherwise do not carry out their contractual duties to AxoGen, or encounter physical damage or natural disaster at their facilities, AxoGen’s ability to deliver product to meet commercial demand may be significantly impaired.
AxoGen is dependent on its relationships with distributors to generate revenue.
AxoGen derives material revenues through its relationships with distributors. If such distributor relationships were terminated for any reason, it could materially and adversely affect AxoGen’s ability to generate revenues and profits. AxoGen intends to obtain the assistance of additional distributors to continue its sales growth. It may not be able to find additional distributors who will agree to market and distribute its products on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If it is unable to establish new distribution relationships or renew current distribution agreements on commercially acceptable terms, operating results could suffer.
Loss of key members of management, who it needs to succeed, could adversely affect its business.
AxoGen’s future success depends on the continued efforts of the members of its senior management team. Competition for experienced management personnel in the healthcare industry is intense. If one or more of AxoGen’s senior executives or other key personnel are unable or unwilling to continue in their present positions, or if AxoGen is unable to attract and retain high quality senior executives or key personnel in the future, its business may be adversely affected.
31
AxoGen’s operating results will be harmed if it is unable to effectively manage and sustain its future growth.
There can be no assurance that AxoGen will be able to manage its future growth efficiently or profitably. Its business is unproven on a large scale and actual revenue and operating margins, or revenue and margin growth, may be less than expected. If AxoGen is unable to scale its production capabilities efficiently, it may fail to achieve expected operating margins, which would have a material and adverse effect on its operating results. Growth may also stress AxoGen’s ability to adequately manage its operations, quality of products, safety and regulatory compliance. If growth significantly decreases AxoGen’s cash reserves, it may be required to obtain additional financing, which may increase indebtedness or result in dilution to shareholders. Further, there can be no assurance that AxoGen would be able to obtain additional financing on acceptable terms if all at.
There may be significant fluctuations in AxoGen’s operating results.
Significant quarterly fluctuations in AxoGen’s results of operations may be caused by, among other factors, its volume of revenues, seasonal changes in nerve repair activity, timing of sales force expansion and general economic conditions. There can be no assurance that the level of revenues and profits, if any, achieved by AxoGen in any particular fiscal period, will not be significantly lower than in other comparable fiscal periods. AxoGen’s expense levels are based, in part, on its expectations as to future revenues. As a result, if future revenues are below expectations, net income or loss may be disproportionately affected by a reduction in revenues, as any corresponding reduction in expenses may not be proportionate to the reduction in revenues.
AxoGen’s revenues depend upon prompt and adequate reimbursement from public and private insurers and national health systems.
Political, economic and regulatory influences are subjecting the healthcare industry in the U.S. to fundamental change. The ability of hospitals to pay fees for AxoGen’s products depends in part on the extent to which reimbursement for the costs of such materials and related treatments will continue to be available from governmental health administration authorities, private health coverage insurers and other organizations. Major third-party payers of hospital services and hospital outpatient services, including Medicare, Medicaid and private healthcare insurers, annually revise their payment methodologies, which can result in stricter standards for reimbursement of hospital charges for certain medical procedures or the elimination of reimbursement. Further, Medicare, Medicaid and private healthcare insurer cutbacks could create downward price pressure on AxoGen’s products.
AxoGen may be subject to future product liability litigation that could be expensive and its insurance coverage may not be adequate.
Although AxoGen is not currently subject to any product liability proceedings, and it has no reserves for product liability disbursements, it may incur material liabilities relating to product liability claims in the future, including product liability claims arising out of the usage of AxoGen products. AxoGen currently carries product liability insurance in an amount consistent with industry averages, however, its insurance coverage and any reserves it may maintain in the future for product related liabilities may not be adequate and AxoGen’s business could suffer material adverse consequences.
Technological change could reduce demand for AxoGen’s products.
The medical technology industry is intensely competitive. AxoGen competes with both U.S. and international companies that engage in the development and production of medical technologies and processes including:
| • | biotechnology, orthopedic, pharmaceutical, biomaterial, chemical and other companies; |
| • | academic and scientific institutions; and |
| • | public and private research organizations. |
32
AxoGen products compete with autograft and hollow-tube conduits, as well as with alternative medical procedures. For the foreseeable future, AxoGen believes a significant number of surgeons will continue to choose to perform autograft procedures when feasible, despite the necessity of performing a second operation and its drawbacks. In addition, many members of the medical community will continue to prefer the use of hollow-tube conduits due in part to their familiarity with these products and the procedures required for their use. Also, steady improvements have been made in synthetic human tissue substitutes, which could compete with AxoGen’s products. Unlike allografts, synthetic tissue technologies are not dependent on the availability of human or animal tissue. Although AxoGen’s growth strategy contemplates the introduction of new technologies, the development of these technologies is a complex and uncertain process, requiring a high level of innovation, as well as the ability to accurately predict future technology and market trends. AxoGen may not be able to respond effectively to technological changes and emerging industry standards, or to successfully identify, develop or support new technologies or enhancements to existing products in a timely and cost-effective manner, if at all. Finally, there can be no assurance that in the future AxoGen’s competitors will not develop products that have superior performance or are less expensive relative to its products rendering them obsolete or noncompetitive.
AxoGen may be unsuccessful in commercializing its products outside the U.S.
To date, AxoGen has focused its commercialization efforts in the U.S., except for minor revenues from the Avance® Nerve Graft in Switzerland, Italy, Austria and Canada. It intends to expand sales beyond these countries outside the U.S. and will need to comply with applicable foreign regulatory requirements, including obtaining the requisite approvals to do so. Additionally, AxoGen will need to either enter into distribution agreements with third parties or develop a direct sales force in these foreign markets. If it does not obtain adequate levels of reimbursement from third-party payers outside of the U.S., it may be unable to develop and grow its product sales internationally. Outside of the U.S., reimbursement systems vary significantly by country. Many foreign markets have government-managed healthcare systems that govern reimbursement for medical devices and procedures. Additionally, some foreign reimbursement systems provide for limited payments in a given period and therefore result in extended payment periods. If AxoGen is unable to successfully commercialize its products internationally, its long term growth prospects may be limited.
If AxoGen does not manage tissue and tissue donation in an effective and efficient manner, it could adversely affect its business.
Many factors affect the supply, level and timing of donor medical releases, such as effectiveness of donor screening (currently performed by donor recovery groups), the effective recovery of tissue, the timely receipt, recording and review of required medical documentation, and employee loss and turnover in AxoGen’s and its contractor’s recovery department. AxoGen can provide no assurance that tissue recovery or donor medical releases will occur at levels that will maximize processing efficiency and minimize AxoGen’s cost per allograft processed.
If AxoGen does not manage product inventory in an effective and efficient manner, it could adversely affect profitability.
Many factors affect the efficient use and planning of product inventory, such as effectiveness of predicting demand, effectiveness of preparing manufacturing to meet demand, efficiently meeting product mix and product demand requirements and product expiration. AxoGen may be unable to manage its inventory efficiently, keep inventory within expected budget goals, keep its work-in-process inventory on hand or efficiently, or keep sufficient product on hand to meet demand, and AxoGen can provide no assurance that it can keep inventory costs within its target levels. Failing to do so may require AxoGen to raise additional cash resources or may harm long term growth prospects.
33
AxoGen is a party to a Royalty Contract which requires it to pay royalty fees that could materially adversely affect its financial position.
On October 5, 2012, AxoGen entered intothe Royalty Contract with PDL, pursuant to which AxoGen sold to PDL the right to receive specified royalties on AxoGen’s Net Revenues generated by the sale, distribution or other use of AxoGen’s products Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector (the Assigned Interests as defined in the Royalty Contract). The Royalty Contract has a term of eight years. Under the Royalty Contract, PDL is to receive royalty payments, currently paid weekly, based on a 9.95% royalty rate of AxoGen’s Net Revenues, subject to certain agreed upon minimum guaranteed quarterly payment amounts of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter that commence in the quarter ending December 31, 2014. The minimum annual payment amounts are as follows: 2014 — $1,250,805, 2015 — $6,781,440, 2016 — $9,232,642, 2017 and 2018 — $9,000,000, 2019 — $9,063,000 and 2020 — $6,939,000. Further, on October 5, 2016, or in the event of the occurrence of a material adverse event, our transfer of revenue interest or substantially all of our interest in the products or AxoGen’s bankruptcy or material breach of the Royalty Contract, PDL may require AxoGen to repurchase the Assigned Interests (the “Put”) at the Put Price (as defined in the Royalty Contract). The Put Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a 20% internal rate of return to PDL (the “Put Rate”) on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by AxoGen, and (ii) any “Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment” (as defined in the Royalty Contract) AxoGen owed to PDL. For purposes of estimating the effective interest rate of the Royalty Contract, we considered that the effective rate of 20% (currently the Put Rate) is currently slightly higher than the implicit rate of return and, as a result, we assume for accounting purposes that PDL will exercise its put option in order to receive the higher rate of return. However we have no actual knowledge or other indications of PDL’s intent to do so.
During 2012, AxoGen’s monthly expenses exceeded its revenues and thus it operated at a cash loss. Royalty payments to PDL are owed without consideration to any negative affect it has on AxoGen’s cash or loss position. In addition, minimum payments under the Royalty Contract start in October 2014 and if AxoGen is required to pay an amount greater than the royalty fee, AxoGen would have an even greater cash burden. Finally, there is no assurance that AxoGen will have sufficient capital to pay the Put Price if it was exercised. If AxoGen does not have sufficient cash to pay PDL, AxoGen would need to raise additional capital. The sale of additional equity to further finance the company may result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that if AxoGen is required to secure funding it can do so on terms acceptable to it, or at all. The increasing need for capital as the PDL transaction matures could also make it more difficult to obtain funding through either equity or debt. See “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — Footnote 7 Long-Term Debt/Note Payable.”
PDL Royalty Contract has Change of Control provision that could have material impact on price received by AxoGen shareholders in the event of a Change of Control.
In the event of a “Change of Control” (as defined in the Royalty Contract), AxoGen must repurchase the Assigned Interests from PDL for a repurchase price equal to the “Change of Control Price” on or prior to the third business day after the occurrence of the Change of Control. The Change of Control Price is the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate an internal rate of return to PDL of thirty-two and one half percent (32.5%) on all payments made by PDL pursuant to the Royalty Contract as of the date of the Change of Control Payment (as defined in the Royalty Contract), taking into account the amount and timing of all payments made by AxoGen to PDL (and retained by PDL) prior to and as of the date of payment of the Change of Control Payment, plus (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment owed. For purposes of example only, the Change of Control payment at December 31, 2012 would have been $22,064,000. Payment of the Change of Control Price could materially reduce the consideration to be received by AxoGen shareholders if the Change of Control event was in conjunction with the acquisition of the Company.
AxoGen incurs costs as a result of operating as a public company, and its management is required to devote substantial time to compliance initiatives.
As a public company, AxoGen incurs legal, accounting and other expenses to comply with relevant securities laws and regulations, including, without limitation, the requirement of establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and corporate governance practices. AxoGen’s management devotes substantial time and financial resources to these compliance initiatives. Failure to comply with public company requirements could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business.
The price of AxoGen’s common stock could be highly volatile due to a number of factors.
The trading price of AxoGen’s common stock may fluctuate widely as a result of a number of factors, including:
| • | trading of AxoGen common stock on the OTCBB; |
| • | limited daily trading volume resulting in the lack of a liquid market; |
| • | fluctuations in price and volume due to investor speculation and other factors that may not be tied to the financial performance of AxoGen; |
34
| • | performance by AxoGen in the execution of its business plan; |
| • | financial viability; |
| • | regulatory developments in both the United States and foreign countries; |
| • | performance of products sold and advertised by licensees in the marketplace; |
| • | economic and other external factors; and |
| • | period-to-period fluctuations in financial results. |
AxoGen does not meet the criteria to list its common stock on an exchange such as the NYSE — AMEX or NASDAQ Stock Market and its common stock lacks liquidity and may be difficult to sell.
Trading of AxoGen’s common stock is conducted on the OTCBB. Generally, securities that are quoted on the OTCBB lack liquidity and analyst coverage. This may result in lower prices for its common stock than might otherwise be obtained if it met the criteria to list its securities on a larger or more established exchange, such as the NYSE — AMEX or NASDAQ Capital Market and could also result in a larger spread between the bid and asked prices for its common stock.
In addition, there has been only limited trading activity in AxoGen’s common stock. The relatively small trading volume will likely make it difficult for AxoGen shareholders to sell their common stock as, and when, they choose.
Risks Related to the Regulatory Environment in which AxoGen Operates
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product is currently allowed to be sold pursuant to a transition plan with the FDA and a change in position by the FDA regarding its use of enforcement discretion to permit the sale of Avance would have a material adverse effect on AxoGen.
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product is currently allowed to be sold pursuant to a transition plan with the FDA See “Business — Government Regulations — U.S. Government Regulation Review.” AxoGen is continuing to communicate with CBER since the acceptance of the transition plan on clinical trial design and CMC for the Avance® Nerve Graft. Until final action on the Avance® Nerve Graft premarket submission, if AxoGen remains in compliance with the transition plan, it is able to continue to provide the Avance® Nerve Graft for sale. In the event that the FDA changed its position regarding its use of enforcement discretion to permit AxoGen to provide the Avance® Nerve Graft product in accordance with the transition plan, AxoGen would no longer be able to sell the Avance® Nerve Graft product, which would have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s operations and financial viability. In addition, if AxoGen fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements or fails to comply with the ongoing requirements of the premarket submission to become a biological product, the FDA could deny approval of the premarket application, or impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures or product recalls and, in extreme cases, criminal sanctions.
AxoGen’s AxoGuard® products are subject to FDA and other regulatory requirements.
AxoGen’s AxoGuard® product line is regulated as a medical device under the FD&C Act and subject to 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation) and other FDA regulations. AxoGen distributes for Cook Biotech Incorporated the AxoGuard® product line and Cook Biotech is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the AxoGuard® product line. Cook Biotech has obtained a 510(k) marketing clearance from the FDA for porcine small intestine submucosa for the repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities where gap closure can be achieved by flexion of the extremity. If AxoGen or Cook Biotech Incorporated fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements the FDA could deny marketing clearance or approval, withdraw approvals, or impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures or product recalls and, in extreme cases, criminal sanctions.
35
AxoGen’s business is subject to continuing regulatory compliance by the FDA and other authorities which is costly and could result in negative effects on its business.
AxoGen is subject to extensive regulation. Its products are subject to regulation by the FDA in the U.S., the Center for Medicare Services of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and other federal governmental agencies and, in some jurisdictions, by state and foreign governmental authorities. The FDA regulates the development, distribution, manufacturing, labeling, and record-keeping procedures for human tissue for transplantation such as that of AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product. The FDA also regulates medical devices, such as the AxoGuard® products. The process of obtaining marketing clearance from the FDA for new products and new applications for existing products can be time consuming and expensive. Some of the future products and enhancements to such products that AxoGen expects to develop and market may require marketing clearance or approval from the FDA. There can be no assurance, however, that clearance or approval will be granted with respect to any of AxoGen’s products or enhancements or that FDA review will not involve delays that would adversely affect AxoGen’s ability to market such products or enhancements. In addition, there can be no assurance that AxoGen products or enhancements will not be subject to a lengthy and expensive approval process with the FDA.
It is possible that if regulatory approvals to market a product are obtained from the FDA, the approvals may contain limitations on the indicated uses of such product and other uses may be prohibited. Product approvals by the FDA can also be withdrawn due to failure to comply with regulatory standards or the occurrence of unforeseen problems following initial approval. Also, the FDA could limit or prevent the distribution of AxoGen products and has the power to require the recall of such products. FDA regulations depend heavily on administrative interpretation, and there can be no assurance that future interpretations made by the FDA or other regulatory bodies will not adversely affect AxoGen’s operations. AxoGen, and its facilities, may be inspected by the FDA from time to time to determine whether it is in compliance with various regulations relating to specification, development, documentation, validation, testing, quality control, and product labeling. A determination that AxoGen is in violation of such regulations could lead to imposition of civil penalties, including fines, product recalls or product seizures and, in extreme cases, criminal sanctions.
The use, misuse or off-label use of AxoGen’s products may harm its reputation or the image of its products in the marketplace, or result in injuries that lead to product liability suits, which could be costly to AxoGen’s business or result in FDA sanctions if they are deemed to have engaged in off-label promotion. AxoGen is seeking FDA approval for Avance® Nerve Graft under specific circumstances. Its promotional materials and training methods must comply with FDA requirements and other applicable laws and regulations, including the prohibition on the promotion of a medical device for an indication that has not been approved or cleared by the FDA, or an off-label use. The FDA does not restrict or regulate a physician’s use of a medical device within the practice of medicine, and AxoGen cannot prevent a physician from using its products for an off-label use. However, the FD&C Act and the FDA’s regulations restrict the kind of communications that may be made about AxoGen’s products and if the FDA determines that its promotional or training materials constitute the unlawful promotion of an off-label use, it could request that AxoGen modify its training or promotional materials or subject it to regulatory or enforcement actions, including the issuance of an untitled letter, a warning letter, civil money penalties, criminal fines and penalties, and exclusion from participation in federal health programs. Other federal, state or foreign governmental authorities might also take action if they consider AxoGen promotion or training materials to constitute promotion of an uncleared or unapproved use, which could result in significant fines or penalties under other statutory authorities, such as laws prohibiting false claims for reimbursement. In that event, AxoGen’s reputation could be damaged and the use of its products in the marketplace could be impaired.
In addition, there may be increased risk of injury if physicians or others attempt to use AxoGen products off-label. Furthermore, the use of AxoGen’s product for indications other than those for which its products have been approved or cleared by the FDA may not effectively treat such conditions, which could harm AxoGen’s reputation in the marketplace among physicians and patients. Physicians may also misuse AxoGen’s product or
36
use improper techniques if they are not adequately trained in the particular use, potentially leading to injury and an increased risk of product liability. Product liability claims are expensive to defend and could divert management’s attention from its primary business and result in substantial damage awards against AxoGen. Any of these events could harm AxoGen’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Defective AxoGen product could lead to recall or other negative business conditions.
If AxoGen’s products are defective or otherwise pose safety risks, the FDA could require their recall, or AxoGen may initiate a voluntary recall of its products. The FDA may require recall of a marketed product in the event that it determines that due to material deficiencies or defects that use of the product poses an unacceptable risk to health. In addition, manufacturers may, on their own initiative, recall a product to remove or correct a deficiency or to remedy a violation of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act that may pose a risk to health. A government-mandated or a voluntary recall could occur as a result of an unacceptable risk to health, failures, manufacturing errors, design or labeling defects or other deficiencies and issues. Recalls, corrections or removals of any of AxoGen’s products would divert managerial and financial resources and have an adverse effect on its business, results of operations and financial condition. A recall could harm AxoGen’s reputation with customers and negatively affect its sales. AxoGen may initiate removals involving some of its products in the future that it determines do not require notification of the FDA. If the FDA were to disagree with AxoGen’s determinations, it could request that it report those actions as recalls, and take regulatory or enforcement action relating to the product.
If AxoGen’s products cause or contribute to a death, a serious injury or any adverse reaction involving a communicable disease related to its products, or malfunction in certain ways, it will be subject to reporting regulations, which can result in voluntary corrective actions or agency enforcement actions. See “Business — Regulation — Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws — Pervasive and Continuing Regulation.” If AxoGen fails to report these events to the FDA within the required timeframes, or at all, the FDA could take regulatory or enforcement action against AxoGen. Any adverse event involving AxoGen’s products could result in future voluntary corrective actions, such as recalls or customer notifications, or agency action, such as inspection, mandatory recall or other enforcement action. Any corrective action, whether voluntary or involuntary, as well as AxoGen defending itself in a lawsuit, would require the dedication of time and capital, distract management from operating its business, and may harm AxoGen’s reputation, business, results of operations and financial condition.
AxoGen’s manufacturing operations must comply with FDA and other governmental requirements.
AxoGen’s manufacturing operations require it to comply with the FDA’s and other governmental authorities’ laws and regulations regarding the manufacture and production of medical products, which is costly and could subject AxoGen to enforcement action. See Business — Government Regulations — Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws — Pervasive and Continuing Regulation.” Any of these actions could impair AxoGen’s ability to produce its products in a cost-effective and timely manner in order to meet customer demands. AxoGen may also be required to bear other costs or take other actions that may have an adverse impact on its future sales and its ability to generate profits. Furthermore, AxoGen key material suppliers, licensors and processor may not continue to be in compliance with all applicable regulatory requirements, which could result in AxoGen’s failure to produce its products on a timely basis and in the required quantities, if at all.
Sales of AxoGen products outside the U.S. are subject to foreign regulatory requirements that vary from country to country. In the European Union (the “EU”) regulations, if applicable, differ from one EU member state to the next. Because of the absence of a harmonized regulatory framework and the proposed regulation for advanced therapy medicinal products in the EU, as well as for other countries, the approval process for human derived cell or tissue based medical products may be extensive, lengthy, expensive and unpredictable. AxoGen products will be subject to EU member states’ regulations that govern the donation, procurement, testing, coding,
37
traceability, processing, preservation, storage, and distribution of human tissues and cells and cellular or tissue-based products. In addition, some EU member states have their own tissue banking regulations. The inability to meet foreign regulatory requirements could materially affect AxoGen’s future growth and compliance with such requirements could place a significant financial burden on AxoGen.
Clinical trials can be long, expensive and ultimately uncertain which could jeopardize AxoGen’s ability to obtain regulatory approval and continue to market its Avance® Nerve Graft product.
AxoGen is required to perform a clinical trial for its Avance® Nerve Graft pursuant to requirements of the FDA to obtain a biologics license for the product. This trial is expensive, is expected to take several years to execute, and is subject to factors within and outside of AxoGen’s control. The outcome of this trial is uncertain.
AxoGen has continued to communicate with FDA regarding clinical trial design, preclinical studies and CMC for the Avance® Nerve Graft, and will have significant work to continue to meet the requirements asked of AxoGen by the FDA for each of these components to begin its clinical study and receive its BLA. If AxoGen is unable to agree, or unable to meet the standards required of it by the FDA, regarding preclinical studies, clinical studies and CMC, AxoGen’s BLA may be impossible, delayed and/or may add significant costs to the ongoing production of Avance® Nerve Graft.
The results of non-clinical studies do not necessarily predict future clinical trial results, and predecessor clinical trial results may not be repeated in subsequent clinical trials. Additionally, the FDA may disagree with AxoGen’s interpretation of the data from its non-clinical studies and clinical trials and may require it to pursue additional non-clinical studies or clinical trials, or not approve AxoGen’s BLA or supplement, which could further delay the BLA of AxoGen’s products. If AxoGen is unable to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of its products through its clinical trials, it will be unable to obtain regulatory approval to market its products and will not be able to continue to sell its Avance® Nerve Graft.
AxoGen will rely on third parties to conduct its clinical trial and they may not perform as contractually required or expected.
AxoGen will rely on third parties, such as contract research organizations (“CROs”), medical institutions, clinical investigators and contract laboratories to conduct its clinical trial and certain nonclinical studies. AxoGen and its CROs are required to comply with all applicable regulations governing clinical research, including good clinical practice (“GCP”). The FDA enforces these regulations through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators, CROs and trial sites. If AxoGen or its CROs fail to comply with applicable FDA regulations, the data generated in its clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA may require AxoGen to perform additional clinical trials before approving its applications. AxoGen cannot be certain that, upon inspection, the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities will determine that AxoGen’s clinical trial complies or complied with clinical trial regulations, including GCP. In addition, AxoGen’s clinical trial must be conducted with product produced under applicable current good manufacturing practice regulations. Failure to comply with the clinical trial regulations may require AxoGen to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or regulatory obligations or meet expected deadlines, if these third parties need to be replaced, or if the quality or accuracy of the data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to AxoGen’s clinical protocols or regulatory requirements or for other reasons, AxoGen’s non-clinical development activities or clinical trials may be extended, delayed, suspended or terminated, and it would not be able to obtain regulatory approval for, its products on a timely basis, if at all, and its business, results of operations, financial condition and growth prospects would be adversely affected. Furthermore, AxoGen’s third-party clinical trial investigators may be delayed in conducting its clinical trials for reasons outside of their control.
38
U.S. governmental regulation could restrict the use of AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product, restrict AxoGen’s procurement of tissue or increase costs.
Human tissues intended for transplantation have been regulated by the FDA since 1993. In May 2005, three new comprehensive regulations went into effect that address manufacturing activities associated with HCT/Ps. The first requires that companies that produce and distribute HCT/Ps register with the FDA. The second provides criteria that must be met for donors to be eligible to donate tissues and is referred to as the “Donor Eligibility” rule. The third rule governs the processing and distribution of the tissues and is often referred to as the Current Good Tissue Practices rule. The Current Good Tissue Practices rule covers all stages of allograft processing, from procurement of tissue to distribution of final allografts. Together, they are designed to ensure that sound, high quality practices are followed to reduce the risk of tissue contamination and of communicable disease transmission to recipients. These regulations increased regulatory scrutiny within the industry in which AxoGen operates and have led to increased enforcement action, which affects the conduct of its business. See “Business — Government Regulations.” In addition, these regulations can increase the cost of tissue recovery activities. Additionally, the Avance® Nerve Graft is subjected to certain state and local regulations, as well as compliance to the standards of the tissue bank industry’s accrediting organization, the AATB.
The procurement and transplantation of allograft nerve tissue is also subject to federal law pursuant to the National Organ Transplant Act (“NOTA”), a criminal statute which prohibits the purchase and sale of human organs used in human transplantation, including nerve and related tissue, for “valuable consideration.” NOTA only permits reasonable payments associated with the removal, transportation, processing, preservation, quality control, implantation and storage of human nerve tissue. AxoGen makes payments to certain of its clients and tissue banks for their services related to recovering allograft nerve tissue on its behalf. If NOTA is interpreted or enforced in a manner which prevents AxoGen from receiving payment for services it renders, or which prevents it from paying tissue banks or certain of its clients for the services they render for AxoGen, its business could be materially and adversely affected.
AxoGen is engaged, through its marketing employees, independent sales agents and sales representatives, in ongoing efforts designed to educate the medical community as to the benefits of AxoGen products, and AxoGen intends to continue its educational activities. Although AxoGen believes that NOTA permits payments in connection with these educational efforts as reasonable payments associated with the processing, transportation and implantation of AxoGen products, payments in connection with such education efforts are not exempt from NOTA’s restrictions and AxoGen’s inability to make such payments in connection with its education efforts may prevent it from paying AxoGen sales representatives for their education efforts and could adversely affect AxoGen’s business and prospects. No federal agency or court has determined whether NOTA is, or will be, applicable to every allograft nerve tissue-based material which AxoGen’s processing technologies may generate. Assuming that NOTA applies to AxoGen’s processing of allograft nerve tissue, AxoGen believes that it complies with NOTA, but there can be no assurance that more restrictive interpretations of, or amendments to, NOTA will not be adopted in the future, which would call into question one or more aspects of AxoGen’s method of operations.
Other regulatory entities include state agencies with statutes covering tissue banking. Regulations issued by Florida, New York, California and Maryland, among others, will be particularly relevant to AxoGen’s business. Most states do not currently have tissue banking regulations. However, incidents of allograft related infections in the industry may stimulate the development of regulation in other states. It is possible that others may make allegations against AxoGen or against donor recovery groups or tissue banks about non-compliance with applicable FDA regulations or other relevant statutes or regulations. Allegations like these could cause regulators or other authorities to take investigative or other action, or could cause negative publicity for AxoGen’s business and the industry in which it operates.
Healthcare policy changes may have a material adverse effect on AxoGen.
In March 2010, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act, which substantially changes the
39
way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and encourages improvements in the quality of healthcare items and services. This Act significantly impacts the biotechnology and medical device industries and could have a material adverse impact on numerous aspects of AxoGen’s business.
This Act includes, among other things, the following measures:
| • | a 2.3% excise tax on any entity that manufactures or imports medical devices offered for sale in the U.S., with limited exceptions, beginning in 2013; |
| • | a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research; |
| • | new reporting and disclosure requirements on healthcare manufacturers for any “transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as reporting of certain physician ownership interests, with the first of such reports due March 31, 2013 for calendar year 2012 (“Sunshine Act”); |
| • | payment system reforms including a national pilot program on payment bundling to encourage hospitals, physicians and other providers to improve the coordination, quality and efficiency of certain healthcare services through bundled payment models, beginning on or before January 1, 2013; |
| • | an independent payment advisory board that will submit recommendations to reduce Medicare spending if projected Medicare spending exceeds a specified growth rate; and |
| • | a new abbreviated pathway for the licensure of biologic products that are demonstrated to be biosimilar or interchangeable with a licensed biologic product. |
There are also a number of states (such as Vermont, Massachusetts, Minnesota) with their own Sunshine Acts that implement the reporting and disclosure requirements on healthcare manufacturers for any “transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as reporting of certain physician ownership interests,
In the future, there may continue to be additional proposals relating to the reform of the U.S. healthcare system. Certain of these proposals could limit the prices AxoGen is able to charge for its products or the amounts of reimbursement available for its products and could also limit the acceptance and availability of its products. The adoption of some or all of these proposals could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Additionally, initiatives sponsored by government agencies, legislative bodies and the private sector to limit the growth of healthcare costs, including price regulation and competitive pricing, are ongoing in markets where AxoGen does business. AxoGen could experience an adverse impact on operating results due to increased pricing pressure in the U.S. and in other markets. Governments, hospitals and other third-party payors could reduce the amount of approved reimbursement for AxoGen’s products or deny coverage altogether. Reductions in reimbursement levels or coverage or other cost-containment measures could unfavorably affect AxoGen’s future operating results.
Risks Related to AxoGen’s Intellectual Property
Failure to protect AxoGen’s Intellectual Property rights could result in costly and time consuming litigation and its loss of any potential competitive advantage.
AxoGen’s success will depend, to a large extent, on its ability to successfully obtain and maintain patents, prevent misappropriation or infringement of IP, maintain trade secret protection, and conduct operations without violating or infringing on the IP rights of third parties. See “Business — Intellectual Property.” There can be no assurance that AxoGen’s patented and patent-pending technologies will provide it with a competitive advantage, that AxoGen will be able to develop or acquire additional technology that is patentable, or that third parties will
40
not develop and offer technologies which are similar to AxoGen’s. Moreover, AxoGen can provide no assurance that confidentiality agreements with its employees, consultants and other parties, trade secrecy agreements or similar agreements intended to protect unpatented technology will provide the intended protection. IP litigation is extremely expensive and time-consuming, and it is often difficult, if not impossible, to predict the outcome of such litigation. A failure by AxoGen to protect its IP could have a materially adverse effect on its business and operating results and its ability to successfully compete in its industry.
Future protection for AxoGen’s proprietary rights is uncertain which may impact its ability to successfully compete in its industry.
The degree of future protection for AxoGen’s proprietary rights is uncertain. AxoGen cannot ensure that:
| • | it, or its licensors, were the first to make the inventions covered by each of AxoGen’s patents; |
| • | it, or its licensors, were the first to file patent applications for these inventions; |
| • | others will not independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of AxoGen’s technologies; |
| • | any of AxoGen’s pending patent applications will result in issued patents; |
| • | any of AxoGen’s issued patents or those of its licensors will be valid and enforceable; |
| • | any patents issued to AxoGen or its collaborators will provide any competitive advantages or will not be challenged by third parties; |
| • | it will develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; |
| • | the patents of others will not have a material adverse effect on its business rights; or |
| • | the measures AxoGen relies on to protect its IP underlying their products may not be adequate to prevent third parties from using its technology, all of which could harm its ability to compete in the market. |
AxoGen’s success depends on its ability to avoid infringing on the intellectual property rights of third parties which could expose it to litigation or commercially unfavorable licensing arrangements.
AxoGen’s commercial success depends in part on its ability and the ability of its collaborators and licensors to avoid infringing patents and proprietary rights of third parties. Third parties may accuse AxoGen or collaborators and licensors of employing their proprietary technology in AxoGen products, or in the materials or processes used to research or develop AxoGen products, without authorization. Any legal action against AxoGen collaborators, licensors or it claiming damages and/or seeking to stop AxoGen’s commercial activities relating to the affected products, materials and processes could, in addition to subjecting AxoGen to potential liability for damages, require it or its collaborators and licensors to obtain a license to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes or to manufacture or market the affected products. AxoGen cannot predict whether AxoGen or its collaborators and licensors would prevail in any of these actions or whether any license required under any of these patents would be made available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If AxoGen were unable to obtain such a license, it and its collaborators and licensors may be unable to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes, or manufacture or market the affected products, or AxoGen may be obligated by a court to pay substantial royalties and/or other damages to the patent holder. Even if AxoGen were able to obtain such a license, the terms of such a license could substantially reduce the commercial value of the affected product or products and impair AxoGen’s prospects for profitability. Accordingly, AxoGen cannot predict whether or to what extent the commercial value of the affected product (or products) or AxoGen’s prospects for profitability may be harmed as a result of any of the liabilities discussed above. Furthermore, infringement and other IP claims, with or without merit, can be expensive and time-consuming to litigate and can divert management’s attention from its core business. AxoGen and its licensors may be unable to obtain and enforce IP rights to adequately protect its products and related IP.
41
Others may claim an ownership interest in AxoGen IP which could expose it to litigation and have a significant adverse effect on its prospects.
A third party may claim an ownership interest in one or more of AxoGen’s patents or other IP. A third party could bring legal actions against AxoGen claiming it infringes their patents or proprietary rights, and seek monetary damages and/or enjoin clinical testing, manufacturing and marketing of the affected product or products. While AxoGen believes it owns the right, title and interest in the patents for which it or its licensors have applied and AxoGen’s other IP (including that which is licensed from third parties), and is presently unaware of any claims or assertions by third-parties with respect to AxoGen’s patents or IP, it cannot guarantee that a third-party will not assert a claim or an interest in any of such patents or IP. If AxoGen becomes involved in any litigation, it could consume a substantial portion of AxoGen’s resources, and cause a significant diversion of effort by AxoGen’s technical and management personnel regardless of the outcome of the litigation. If any of these actions were successful, in addition to any potential liability for damages, AxoGen could be required to obtain a license to continue to manufacture or market the affected product, in which case AxoGen may be required to pay substantial royalties or grant cross-licenses to AxoGen’s patents. AxoGen cannot, however, assure you that any such license will be available on acceptable terms, if at all. Ultimately, AxoGen could be prevented from commercializing a product, or be forced to cease some aspect of its business operations as a result of claims of patent infringement or violation of other IP rights, which could have a material and adverse effect on AxoGen’s business, financial condition, and results of operations. Further, the outcome of IP litigation is subject to uncertainties that cannot be adequately quantified in advance, including the demeanor and credibility of witnesses and the identity of the adverse party. This is especially true in IP cases that may turn on the testimony of experts as to technical facts upon which experts may reasonably disagree.
AxoGen depends on maintenance of exclusive licenses.
AxoGen depends fundamentally on keeping and satisfying the terms of exclusive licenses of its nerve repair technologies from UFRF and UTA where the original technologies are purported to be invented. Though AxoGen makes an effort to follow these agreements strictly, a disagreement between AxoGen and either party could have negative impacts on its ability to operate its business effectively. In addition, AxoGen could learn that the technologies it has licensed from UFRF and UTA do not perform as purported, are not efficacious, or are not the property of UFRF or UTA, or some similar problem with the license, any of which would have an immediate and negative impact on AxoGen’s business.
42
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following information should be read in conjunction with “Selected Financial Data” contained in Item 6 of this Report, our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto contained in Item 8 of this Report, the “Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” contained in Part 1 of this Report, “Risk Factors” contained in Item 1A of this Report, and the other information appearing elsewhere in, or incorporated by reference into, in this Report.
Overview
On September 30, 2011, LecTec completed its business combination with AC in accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement. Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub merged with and into AC, with AC continuing after the Merger as the surviving corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of LecTec. Immediately following the Merger, LecTec changed its name to AxoGen, Inc. In October 2011, AxoGen, Inc. moved its corporate headquarter facilities (principal executive office) from Texarkana, Texas to 13859 Progress Blvd., Suite 100, Alachua, Florida 32615.
For accounting purposes, AC was identified as the acquiring entity and LecTec as the acquired entity. The Merger was accounted for using the purchase method of accounting for financial reporting purposes. The purchase method requires the identification of the acquiring entity, based on the criteria of Accounting Standards Codification 805-10-55-12, Accounting for Business Combinations. Under purchase accounting, the assets and liabilities of an acquired company (LecTec) as of the effective date of the acquisition were recorded at their respective estimated fair values and added to those of the acquiring company. Accordingly, the consolidated financial statements and related footnote disclosures presented for periods prior to the Merger are those of AC alone. The consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 include the operations and cash flows of AC through September 30, 2011 and the combined operations and cash flows of the Company subsequent to the Merger. The common stock of AC has been retrospectively adjusted to reflect the exchange ratio of one share of AC common stock for 0.03727336 share of the Company’s common shares as established in the Merger Agreement. Historical results for LecTec prior to the Merger are not included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
AxoGen is a leading regenerative medicine company dedicated to advancing the science and commercialization of peripheral nerve repair solutions. Peripheral nerves provide the pathways for both motor and sensory signals throughout the body and their damage can result in the loss of function and feeling. In order to improve surgical reconstruction and regeneration of peripheral nerves, AxoGen has developed and licensed patented and patent pending technologies. AxoGen’s innovative approach to regenerative medicine has resulted in first-in-class products that will define their product categories. AxoGen’s products offer a full suite of surgical nerve reconstruction solutions including Avance® Nerve Graft, the only commercially available processed nerve allograft for bridging severed nerves without the comorbidities associated with a second surgical site, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a porcine submucosa ExtraCellular Matrix (“ECM”) coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed nerves, and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect injured peripheral nerves and reinforce coaptation sites while preventing soft tissue attachments.
Revenue from the distribution of these products is the main contributor to AxoGen’s total reported sales and has been the key component of its growth to date. AxoGen revenues increased in the fourth quarter and the twelve months of 2012 compared to the fourth quarter and the twelve months of 2011, respectively, as a result of increased usage in the number of accounts utilizing our products. AxoGen has continued to broaden its sales and marketing focus which is expected to have a positive contribution to its revenue growth in the long term, even though in the near term revenue growth may lag behind expense increase.
From May 2009 to December 2010, AxoGen temporarily stopped the manufacturing of Avance® Nerve Graft due to adequate inventory. In December 2010, AxoGen resumed the manufacturing of Avance® Nerve Graft, and as a result incurred higher processing and testing fees, travel costs and temporary labor costs in 2011
43
compared to 2012. In 2011 AxoGen reviewed inventory expiration and wrote off inventory for products manufactured in early 2009. Additionally AxoGen reviewed and adjusted inventories and established reserves to adequately reflect inventory value in 2011. AxoGen believes that such actions will not be required in the future and that it has the necessary inventories, inventory reserves and manufacturing capabilities for its anticipated sales growth.
Results of Operations
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations is based upon the Company’s consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and reported amount of expenses during the period reported. Management bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience, observance of trends in the industry, information provided by outside sources and on various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Our significant accounting policies are described in Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements contained in Item 8 of this Report. The most significant estimates include allowance for doubtful accounts, valuation of goodwill, effective interest rate on the note payable, and the provision for income taxes.
Effective Interest Rate on Note Payable
The PDL Royalty Contract is accounted for as long-term debt. The Company records interest using its best estimate of the effective interest rate. This estimate takes into account both the internal rate of return (IRR) of the PDL agreement and the rate of return as the result of exercise of the Put option. The IRR of the PDL Royalty Contract is based on the actual payments to date, projected future revenues and required minimum payments, and is calculated at 19.81%. The PDL Royalty Contract Put option provides PDL a 20% return, if exercised. As a result of the return of the Put option being higher than the IRR of the PDL agreement, management believes the best estimate of the effective interest rate on this instrument would be the Put rate. As a result, the Company is accruing interest using the specified internal rate of return for the Put which is 20%. We currently have no knowledge of PDL’s intent to exercise the Put, but will monitor this on an ongoing basis. From time to time, the Company will reevaluate the expected cash flows and may adjust the effective interest rate. Since inception of the Royalty Contract, if the interest rate utilized were to change by 1% the effect on interest expense through December 31, 2012 would increase or decrease by approximately $51,000. Determining the effective interest rate requires judgment and is based on significant assumptions related to estimates of the amounts and timing of future revenue streams and PDL’s ultimate decision to exercise the Put. Determination of these assumptions is highly subjective and different assumptions could lead to materially different outcomes.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2012 and 2011
Revenues
Revenues for the year ended December 31, 2012 increased 59% to approximately $7,692,000 as compared to approximately $4,849,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011 principally due to a greater number of customers utilizing AxoGen products.
Gross Profit
Gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2012 increased 136% to approximately $5,730,000 as compared to approximately $2,423,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. This increase was primarily attributable to the increased revenues and gross margin in 2012 and not incurring inventory write-offs such as that of $614,000 for expiring inventory and $214,000 for raw material obsolescence in 2011 or higher processing and testing fees, travel costs and temporary labor costs due to the resumption of the manufacturing of Avance® Nerve Graft in 2011.
Costs and Expenses
Total cost and expenses increased 44% to approximately $13,532,000 for the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $9,392,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. These increases were primarily due to increasing sales and marketing activities, increases in research and development in preparation for the Company’s Investigational New Drug (IND) Application with the FDA and subsequent start of its phase 3 trial and increases in salaries as AxoGen hires to meet growth needs, offset by decreases in certain professional services and financing costs.
As a percentage of revenues, total operating expenses were 175.9% for the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to 193.7% for the year ended December 31, 2011. Such lower total costs and expenses as a percentage of revenue were a result of increased expenses in 2012 being absorbed by increased revenues.
44
Sales and marketing expenses increased 57.2% to approximately $6,884,000 for the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $4,379,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. This increase was primarily due to an increase in sales and marketing activity as the Company expands support for both its direct sales force and independent distributors and increasing the number of its direct sales representatives. As a percentage of revenues, sales and marketing expenses were 89.4% for the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to 90.3% for the year ended December 31, 2011. Sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of revenue remaining flat between periods was primarily a result of 2012 revenue increases being offset by increased costs associated with new sales representatives and marketing and educational resources in 2012.
General and administrative expenses increased 21.0% to approximately $5,221,000 for the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $4,316,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. As a percentage of revenues, general and administrative expenses were 67.9% for the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to 89.0% the year ended December 31, 2011. The increase in aggregate dollars spent were a result of hiring and costs related to being a public company, offset by a savings in certain professional fees and finance costs. As a percentage of revenue, general and administrative expenses decreased as the increase in aggregate dollars spent were absorbed by the increase in revenues.
Research and development expenses increased 104.7% to approximately $1,427,000 in the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $697,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. Development includes AxoGen’s clinical efforts and a large portion of the increase in research and development expenses from 2011 to 2012 related to expenditures for such clinical activity. Because AxoGen’s products are developed for sale in their current use, it conducts limited direct research and product development, but intends to pursue new products and new applications for existing products in the future that may result in increased spending.
Other Income and Expenses
Interest expense increased 27% to approximately $1,391,000 for the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $1,095,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. This increase was a result of the interest expense related to the PDL transaction. As a result of the accounting treatment for the PDL transaction, interest expense included approximately $780,000 of non-cash expense that is expected to be paid in the future based upon the terms of the PDL transaction and increases in AxoGen revenues. The $780,000 of non cash expense was derived from taking the total amount of imputed interest for the year ended December 31, 2012 on the PDL agreement less the actual cash payment made to PDL for that period. Excluding this non-cash component, cash paid for interest decreased in 2012 by approximately $381,000 compared to 2011 as a result of accrued interest on convertible debt and an increased interest rate on borrowed money in 2011 not recurring in 2012.
Interest expense — deferred financing costs decreased 19.3% to approximately $987,000 for the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $1,223,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. This decrease is primarily due to certain deferred financing costs associated with warrants issued as consideration for several amendments executed during 2010 related to the Loan and Security agreement originally entered into in April 2008 becoming fully amortized by March 31, 2011.
Change in fair value of warrant liability decreased 100% to $0 in the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to approximately $62,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011.
Income Taxes
Income tax benefit of approximately $738,000 for 2012 was the result of the Company’s ability to utilize net operating losses and franchise tax adjustments which resulted in tax refunds. The company had no income tax expense or income tax benefit for 2011 due to incurrence of net operating losses. The Company does not believe there are any additional tax refund opportunities currently available.
45
Effect of Inflation
Inflation has not had a significant impact on the Company’s operations or cash flows.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Long-Term Debt / Note Payable
On October 5, 2012, AxoGen entered into the Royalty Contract with PDL. Proceeds from the PDL transaction were used to fully repay the MidCap Loan, as defined below, and extinguish AxoGen’s long-term debt obligations thereunder. The Royalty Contract has a term of eight years. Under the Royalty Contract, PDL is to receive royalty payments currently paid weekly based on a 9.95% royalty rate of certain of the Company’s Net Revenues (the “Assigned Interests”), subject to certain guaranteed quarterly payment amounts of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter that commence in the quarter ending December 31, 2014. The minimum annual payment amounts are as follows: 2014 - $1,250,805, 2015 - $6,781,440, 2016 - $9,232,642, 2017 and 2018 - $9,000,000, 2019 - $9,063,000 and 2020 - $6,939,000. The royalty payment is based on only that portion of Company Net Revenue that is generated by the sale, distribution or other use of the Company’s products Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector (the “Acquired Revenues”), which at this time represents all of the Company’s Net Revenue with the exception of shipping and handling fees which represent less than 2.3% of total revenues. Future revenue, if any, from other products or services will not be subject to the PDL royalty payment. Further, on October 5, 2016, or in the event of the occurrence of a material adverse event, our transfer of revenue interest or substantially all of our interest in the products or AxoGen’s bankruptcy or material breach of the Royalty Contract, PDL may require AxoGen to repurchase the Assigned Interests at the Put Price. The Put Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a 20% internal rate of return to PDL on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by AxoGen, and (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment AxoGen owed to PDL. Although we have no knowledge of PDL’s intent to exercise the Put, based on actual payments to date, projected future revenues and the required minimum payments, we currently believe the Put Rate is the best estimate of the effective interest rate of the Royalty Contract. Finally, in the event of a Change of Control, AxoGen must repurchase the Assigned Interests from PDL for a repurchase price equal to the Change of Control Price on or prior to the third business day after the occurrence of the Change of Control. The Change of Control Price is the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate an internal rate of return to PDL of thirty-two and one half percent (32.5%) on all payments made by PDL pursuant to the Royalty Contract as of the date of the Change of Control Payment, taking into account the amount and timing of all payments made by AxoGen to PDL (and retained by PDL) prior to and as of the date of payment of the Change of Control Payment, plus (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment owed. The total consideration PDL paid to the Company was $20,800,000 (the “Funded Amount”), including $19,050,000 PDL paid to the Company on October 5, 2012, and $1,750,000 PDL paid to the Company on August 14, 2012 pursuant to the Interim Royalty Contract. Upon the closing of PDL’s purchase of the specified royalties described above, which was concurrent with the execution of the Royalty Contract, the Interim Royalty Contract was terminated. There are no financial covenants or other restrictions on the use of capital by AxoGen as a result of the Royalty Contract, however, PDL has a first perfected security interest in the Assigned Interests.
On September 30, 2011, the Company, entered into the Loan and Security Agreement with MidCap Financial SBIC, LP (“MidCap”), as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (the “MidCap Loan”). The MidCap Loan had a principal amount of $5.0 million and a term of 42 months, and was subject to prepayment penalties. Under this agreement, AxoGen was required to make interest only payments for the first 12 months, and payments of both interest and straight line amortization of principal for the remaining 30 months. The interest rate was 9.9% per annum, and interest was computed on the basis of a 360-day year and the actual number of days elapsed during which such interest accrues.
The MidCap Loan contained customary affirmative and negative covenants, including, without limitation, (i) covenants requiring AxoGen to comply with applicable laws, provide to MidCap copies of AxoGen’s financial statements, maintain appropriate levels of insurance and protect, defend and maintain the validity and enforceability of AxoGen’s material intellectual property, (ii) covenants restricting AxoGen’s ability to dispose of all or any part of its assets (subject to certain exceptions), engage in other lines of business, changes in its senior management, enter into merger or consolidation transactions, incur or assume additional indebtedness, or incur liens on its assets, and (iii) covenants requiring the Company to meet certain minimum Net Invoiced Revenue, as defined in the agreement, or maintain a cash balance of 80% of the loan principal amount.
The MidCap Loan was secured by all of AxoGen’s assets. The Lenders also received a ten-year warrant to purchase 89,686 shares of AxoGen’s common stock at $2.23 per share. Proceeds from the PDL transaction were used to fully repay the MidCap Loan and extinguish AxoGen’s obligations thereunder.
On April 21, 2008, AxoGen entered into a Loan and Security Agreement with Oxford Finance Corporation and ATEL Ventures, Inc., as subsequently amended (the “2008 Loan and Security Agreement”), which provided for a loan with an aggregate principal amount of $7.5 million. The loan’s maturity date was October 1, 2011. The loan boar interest at a rate of 18% per month and was secured by all of AxoGen’s assets. On September 30, 2011, AxoGen paid in full the entire outstanding balance of the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement, using the proceeds from the MidCap Loan.
On June 11, 2010, AxoGen entered into Convertible Debt Agreements for an aggregate principal amount of $3.7 million with 8% interest and principal and interest payable in full on June 30, 2013, as amended. The Convertible Debt Agreements were collateralized by a third lien on certain property and were subordinated to the
46
2008 Loan and Security Agreement. Immediately prior to the closing of the Merger, the Convertible Debt Agreements pursuant to their terms automatically converted into AC common stock which was then exchanged for Company common stock pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement.
On May 3, 2011, AxoGen issued an 8% Convertible Note Payable to LecTec Corporation for $500,000. On May 31, 2011, AxoGen issued additional convertible notes payable under the same terms of which $2,000,000 was issued to LecTec and $500,000 was issued to certain AC shareholders. On August 29, 2011, AxoGen issued an additional subordinated secured convertible promissory note in the principal amount of $2,000,000 to LecTec and $500,000 to certain AC shareholders. These notes were collateralized by all of AxoGen’s assets and subordinated to the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement. Immediately prior to the closing of the Merger, the notes held by investors other than LecTec automatically converted into AC’s common stock which was then exchanged for LecTec common stock pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement. Immediately after to the closing of the Merger, the notes held by LecTec were retired.
The Company had no material commitments for capital expenditures at December 31, 2012 or 2011. Under the Royalty Contract, the Company sold to PDL the Acquired Revenues and PDL is to receive for eight years the Assigned Interests, i.e., a royalty payment based on a 9.95% royalty rate of the Company’s Net Revenues, subject to certain agreed upon minimum payments of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter, and was provided the Put and receives certain payments in the event of a Change of Control. The total consideration PDL paid to the Company was $20,800,000, including $19,050,000 PDL paid to the Company on October 5, 2012, and $1,750,000 PDL paid to the Company on August 14, 2012, pursuant to the Interim Royalty Contract. Upon the closing of PDL’s purchase of the specified royalties under the Royalty contract, which was concurrent with its execution, the Interim Royalty Contract was terminated. Proceeds from the PDL Royalty Contract transaction where used to fully repay the MidCap Loan and extinguish AxoGen’s obligations thereunder. There are no financial covenants or other restrictions on the use of capital by AxoGen as a result of the Royalty Contract, however, PDL has a first perfected security interest in the Assigned Interests. In the event that the Company is unable to generate revenue in excess of its PDL Assigned Interests payments and other expenses, or PDL were to exercise the Put at a time when the Company did not have sufficient capital to pay the Put Price, AxoGen would need to raise additional capital. There is no assurance that if AxoGen is required to secure funding it can do so on terms acceptable to it, or at all, and its liquidity would be severely compromised.
Cash Flow Information
On October 5, 2012, AxoGen entered into the Royalty Contract with PDL. Proceeds from the PDL transaction were used to fully repay the MidCap Loan, and extinguish AxoGen’s long-term debt obligations thereunder. The Royalty Contract has a term of eight years. Under the Royalty Contract, PDL is to receive royalty payments currently paid weekly based on a 9.95% royalty rate of certain of the Company’s Net Revenues (the “Assigned Interests”), subject to certain guaranteed quarterly payment amounts of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter that commence in the quarter ending December 31, 2014. The minimum annual payment amounts are as follows: 2014 - $1,250,805, 2015 - $6,781,440, 2016 - $9,232,642, 2017 and 2018 - $9,000,000, 2019 - $9,063,000 and 2020 - $6,939,000. The royalty payment is based on only that portion of Company Net Revenue that is generated by the sale, distribution or other use of the Company’s products Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector (the “Acquired Revenues”), which at this time represents all of the Company’s Net Revenue with the exception of shipping and handling fees which represent less than 2.3% of total revenues. Future revenue, if any, from other products or services will not be subject to the PDL royalty payment. Further, on October 5, 2016, or in the event of the occurrence of a material adverse event, our transfer of revenue interest or substantially all of our interest in the products or AxoGen’s bankruptcy or material breach of the Royalty Contract, PDL may require AxoGen to repurchase the Assigned Interests at the Put Price. The Put Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a 20% internal rate of return to PDL on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by AxoGen, and (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment AxoGen owed to PDL. Although we have no knowledge of PDL’s intent to exercise the Put, based on actual payments to date, projected future revenues and the required minimum payments, we currently believe the Put Rate is the best estimate of the effective interest rate of the Royalty Contract. Finally, in the event of a Change of Control, AxoGen must repurchase the Assigned Interests from PDL for a repurchase price equal to the Change of Control Price on or prior to the third business day after the occurrence of the Change of Control. The Change of Control Price is the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate an internal rate of return to PDL of thirty-two and one half percent (32.5%) on all payments made by PDL pursuant to the Royalty Contract as of the date of the Change of Control Payment, taking into account the amount and timing of all payments made by AxoGen to PDL (and retained by PDL) prior to and as of the date of payment of the Change of Control Payment, plus (ii) any Delinquent Assigned Interests Payment owed. The total consideration PDL paid to the Company was $20,800,000 (the “Funded Amount”), including $19,050,000 PDL paid to the Company on October 5, 2012, and $1,750,000 PDL paid to the Company on August 14, 2012 pursuant to the Interim Royalty Contract. Upon the closing of PDL’s purchase of the specified royalties described above, which was concurrent with the execution of the Royalty Contract, the Interim Royalty Contract was terminated. There are no financial covenants or other restrictions on the use of capital by AxoGen as a result of the Royalty Contract, however, PDL has a first perfected security interest in the Assigned Interests.
47
The Company currently has sufficient capital to maintain its operations for more than 12 months. If future capital is necessary, the Company may raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or from other sources. The sale of additional equity may result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that, if necessary, AxoGen will be able to secure additional funding on terms acceptable to it, or at all. Should additional capital not become available to AxoGen, if needed, AxoGen may be required to take certain action, such as, slowing sales and marketing expansion, delaying certain regulatory activities or reducing headcount.
AxoGen had working capital of approximately $16.8 million and a current ratio of 12.4 at December 31, 2012, compared to a working capital of $8.8 and a current ratio of 5.4 at December 31, 2011. The increase in working capital and the current ratio at December 31, 2012, compared to December 31, 2011, was primarily due to the Royalty Contract with PDL. The Company believes it has sufficient cash resources to meet its liquidity requirements for the next 12 months. AxoGen’s future capital requirements depend on a number of factors, including, without limitation, revenue increases consistent with its business plan, and the corresponding royalty payments of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter due to PDL and pursuant to AxoGen’s licensing agreements in connection with Avance® Nerve Graft, cost of products and acquisition and/or development of new products. In particular, if revenue does not increase by fourth quarter 2014 to a level whereby the 9.95% royalty owed to PDL on AxoGen’s gross revenues exceeds the PDL minimum royalty payments at such time of approximately $1.3 million, and such differential continues, or grows larger as the PDL minimum royalty payments increase, AxoGen would face increasing capital needs. Such capital needs could be substantial depending on the extent to which AxoGen is unable to increase revenue. If the Company requires additional capital it could seek to raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or from other sources. The sale of additional equity may result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that AxoGen will be able to secure funding on terms acceptable to it, or at all. The increasing need for capital as the PDL transaction matures could also make it more difficult to obtain funding through either equity or debt. Should additional capital not become available to AxoGen, as needed, AxoGen may be required to take certain action, such as, slowing sales and marketing expansion, delaying regulatory approvals or reducing headcount.
During 2012, the Company had a net increase in cash and cash equivalents of $5,717,000 as compared to a net increase of cash and cash equivalents of $6,392,000 in 2011. The Company’s principal sources and uses of funds are explained below:
Net Cash used in operating activities
The Company used approximately $8,662,000 of cash for operating activities in 2012, as compared to using approximately $7,079,000 of cash for operating activities in 2011. This increase in cash used in operating activities is primarily attributed to the increase in net loss before income taxes in 2012, as well as cash used for inventory purchases.
Net Cash provided by for investing activities
Investing activities for 2012 used approximately $127,000 of cash as compared to 2011 which provided approximately $7,112,000. This decrease in cash provided is attributable to cash acquired in 2011 as a result of the Merger.
Net Cash provided by financing activities
Financing activities in 2012 provided approximately $14,506,000 of cash as compared to approximately $6,359,000 of cash in 2011. This increase in cash provided is primarily attributed to issuance of $20,800,000 of additional debt, partially offset by the repayment of approximately $5,000,000 of debt (of which approximately $4.8 million is non-cash proceeds and payments) during 2012 and fees associated therewith.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
AxoGen does not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Not applicable
48
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
CONTENTS
49
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and
Board of Directors of
AxoGen, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of AxoGen, Inc. as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for the years then ended. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall consolidated financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of AxoGen, Inc. as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ LURIE BESIKOF LAPIDUS & COMPANY, LLP
Minneapolis, Minnesota
March 12, 2013
50
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2012 and 2011
| December 31, 2012 |
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 13,907,401 | $ | 8,190,781 | ||||
| Accounts receivable |
1,050,089 | 797,654 | ||||||
| Inventory |
3,151,109 | 1,760,540 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other |
187,256 | 133,500 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
18,295,855 | 10,882,475 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
108,534 | 247,824 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
— | 169,987 | ||||||
| Intangible assets |
573,731 | 899,480 | ||||||
| Deferred financing costs |
1,252,443 | 295,276 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 20,230,563 | $ | 12,495,042 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
$ | 1,479,752 | $ | 1,585,100 | ||||
| Current portion of long-term debt |
— | 434,734 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
1,479,752 | 2,019,834 | ||||||
| Long-term debt |
— | 4,403,737 | ||||||
| Note Payable — Revenue Interest Purchase Agreement |
21,580,252 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
23,060,004 | 6,423,571 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Shareholders’ equity (deficit): |
||||||||
| Common stock, $.01 par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 11,122,573 and 11,062,188 shares issued and outstanding |
111,226 | 110,622 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
54,908,226 | 54,391,784 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(57,848,893 | ) | (48,430,935 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total shareholders’ equity (deficit) |
(2,829,441 | ) | 6,071,471 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 20,230,563 | $ | 12,495,042 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
51
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 7,691,704 | $ | 4,849,470 | ||||
| Cost of goods sold |
1,961,877 | 2,426,544 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Gross profit |
5,729,827 | 2,422,926 | ||||||
| Costs and expenses: |
||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
6,883,953 | 4,378,694 | ||||||
| Research and development |
1,427,211 | 697,355 | ||||||
| General and administrative |
5,220,599 | 4,315,604 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total costs and expenses |
13,531,763 | 9,391,653 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loss from operations |
(7,801,936 | ) | (6,968,727 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||
| Interest expense |
(1,391,342 | ) | (1,094,657 | ) | ||||
| Interest expense — deferred financing costs |
(986,844 | ) | (1,223,126 | ) | ||||
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
— | 62,305 | ||||||
| Other income |
23,972 | 4,985 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other income (expense) |
(2,354,214 | ) | (2,250,493 | ) | ||||
| Loss before income taxes |
(10,156,150 | ) | (9,219,220 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Income tax benefit |
738,192 | — | ||||||
| Net Loss |
(9,417,958 | ) | (9,219,220 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Preferred Stock dividends (assumes all paid) |
— | (1,028,351 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss available to common shareholders |
$ | (9,417,958 | ) | $ | (10,247,571 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Weighted Average Common Shares outstanding — basic and diluted |
11,089,425 | 3,697,390 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loss Per Common share — basic and diluted |
$ | (0.85 | ) | $ | (2.77 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
52
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
Years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Total Stockholders’ Deficit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2010 |
2,544,750 | $ | 1,125,000 | 1,205,624 | $ | 12,056 | 9,934,980 | $ | (38,183,364 | ) | $ | (27,111,328 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | 250,044 | — | 250,044 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
— | — | 98,700 | 987 | 25,493 | — | 26,480 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Director Stock Compensation |
— | — | 27,275 | 273 | 74,727 | — | 75,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of preferred stock, debt, and accrued interest into Common Stock and shares exchange in Merger |
(2,544,750 | ) | (1,125,000 | ) | 5,001,854 | 50,019 | 21,447,936 | — | 20,372,955 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred Stock dividend payable forfeited |
— | — | — | — | 7,076,729 | — | 7,076,729 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrant Liability forfeited |
— | — | — | — | 2,607,510 | — | 2,607,510 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Merger Closing — LecTec shares |
— | — | 4,305,026 | 43,050 | 11,804,866 | — | 11,847,916 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
— | — | 423,709 | 4,237 | 995,763 | — | 1,000,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrants |
— | — | — | — | 173,736 | — | 173,736 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Series B preferred stock dividends |
— | — | — | — | — | (292,330 | ) | (292,330 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Series C preferred stock dividends |
— | — | — | — | — | (515,577 | ) | (515,577 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Series D preferred stock dividends |
— | — | — | — | — | (220,444 | ) | (220,444 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | (9,219,220 | ) | (9,219,220 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2011 |
— | — | 11,062,188 | $ | 110,622 | $ | 54,391,784 | $ | (48,430,935 | ) | $ | 6,071,471 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | 495,077 | — | 495,077 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
— | — | 58,340 | 583 | 15,069 | — | 15,652 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock Grant for Services |
— | — | 7,500 | 75 | 21,300 | — | 21,375 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancellation of shares |
— | — | (5,455 | ) | (54 | ) | (14,946 | ) | — | (14,999 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Merger Closing — Fractional shares |
— | — | — | — | (58 | ) | — | (58 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | (9,417,958 | ) | (9,417,958 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2012 |
— | — | 11,122,573 | $ | 111,226 | $ | 54,908,226 | $ | (57,848,893 | ) | $ | (2,829,441 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
53
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (9,417,958 | ) | $ | (9,219,220 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used for operating activities: |
||||||||
| Depreciation |
187,749 | 273,528 | ||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
127,080 | 67,147 | ||||||
| Loss on impairment |
299,654 | — | ||||||
| Loss on abandonment of license |
147,826 | — | ||||||
| Amortization of deferred financing costs |
352,667 | 1,223,126 | ||||||
| Amortization of debt discount |
161,529 | 23,643 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
495,077 | 250,044 | ||||||
| Directors Stock Compensation |
— | 15,000 | ||||||
| Stock grant for service |
21,375 | — | ||||||
| Cancellation of shares |
(14,999 | ) | — | |||||
| Change in fair value of warrant liability |
— | (62,305 | ) | |||||
| Interest added to note payable |
780,252 | 55,562 | ||||||
| Change in assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts receivable |
(252,435 | ) | (368,954 | ) | ||||
| Inventory |
(1,390,570 | ) | 142,249 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other |
(53,757 | ) | 20,070 | |||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(105,348 | ) | 500,820 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used for operating activities |
(8,661,858 | ) | (7,079,290 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(48,459 | ) | (20,610 | ) | ||||
| Acquisition of intangible assets |
(78,825 | ) | (68,856 | ) | ||||
| Cash acquired with Merger |
— | 7,201,638 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash (used for) provided by investing activities |
(127,284 | ) | 7,112,172 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt |
— | 10,500,000 | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of note payable |
15,961,294 | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
— | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Repayments of long-term debt |
(161,292 | ) | (4,732,857 | ) | ||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(1,309,834 | ) | (434,772 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
15,652 | 26,480 | ||||||
| Merger |
(58 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
14,505,762 | 6,358,851 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents |
5,716,620 | 6,391,733 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
8,190,781 | 1,799,048 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
$ | 13,907,401 | $ | 8,190,781 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow activity: |
||||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | 649,108 | $ | 1,029,753 | ||||
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: |
||||||||
| Payments of long term debt with proceeds from note payable (this amount represents a payment made by PDL directly to MidCap Financial SBIC, LP) |
$ | 4,838,706 | $ | — | ||||
| Conversion of preferred stock, convertible debt and accrued interest into common stock |
21,497,955 | |||||||
| Accretion of dividends of Series B preferred stock |
— | 292,330 | ||||||
| Accretion of dividends of Series C preferred stock |
— | 515,577 | ||||||
| Accretion of dividends of Series D preferred stock |
— | 220,444 | ||||||
| Preferred stock dividend payable forfeited with the Merger |
— | 7,076,729 | ||||||
| Warrant Liability forfeited with the Merger |
— | 2,607,510 | ||||||
| Debt discount related to warrants issued with debt |
— | 173,736 | ||||||
| Net assets acquired on Merger |
— | 11,847,916 | ||||||
| Note and accrued interest retired with the Merger |
— | 4,555,562 | ||||||
| Directors stock compensation included in prepaid expenses |
— | 60,000 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
54
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2012 and 2011
| 1. | Basis of Presentation |
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of AxoGen, Inc. (the “Company” or “AxoGen”) and its wholly owned subsidiary AxoGen Corporation (“AC”) as of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011 and the years then ended. The Company’s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
| 2. | Organization and Business |
Business Summary
On September 30, 2011, LecTec Corporation (“LecTec”) completed its business combination with AC in accordance with the terms of an Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 31, 2011, by and among LecTec, Nerve Merger Sub Corp., a subsidiary of LecTec (“Merger Sub”), and AC, which the parties amended on September 30, 2011 and August 9, 2011 (as amended, the “Merger Agreement”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub merged with and into AC, with AC continuing after the merger as the surviving corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of LecTec (the “Merger”). Immediately following the Merger, LecTec changed its name to AxoGen, Inc. In October 2011, the Company moved its corporate headquarter facilities (principal executive office) from Texarkana, Texas to 13859 Progress Blvd., Suite 100, Alachua, Florida 32615.
In connection with the Merger,
| • | all outstanding AC convertible securities were converted into shares of AC common stock and exchanged for shares of AxoGen, Inc. common stock; |
| • | all outstanding AC warrants expired unexercised; |
| • | all outstanding shares of AC common stock, including those issued upon conversion of AC convertible securities, were exchanged for shares of AxoGen, Inc. common stock at a ratio of one share of AC common stock for 0.03727336 share of AxoGen, Inc. common stock; |
| • | all outstanding options to purchase shares of AC common stock were exchanged for options to purchase shares of AxoGen, Inc. common stock at a ratio of one option to purchase shares of AC common stock for an option to purchase 0.03727336 share of AxoGen, Inc. common stock. |
A total of 6,221,077 shares of the Company’s common stock were issued in share exchange, and an additional 558,267 shares of the Company’s common stock were reserved for issuance upon exercise of AC stock options which were converted into the Company’s stock options. Upon completion of the Merger, all AC securities were cancelled.
Immediately following the completion of the Merger, former AC shareholders owned approximately 56.8% of the outstanding common stock of the Company, LecTec shareholders owned approximately 39.4% of the outstanding common stock of the Company, and certain investors owned the remaining 3.8% of the outstanding common stock of the Company.
For accounting purposes, AC was identified as the acquiring entity and LecTec as the acquired entity. The merger was accounted for using the purchase method of accounting for financial reporting purposes. The purchase method requires the identification of the acquiring entity, based on the criteria of Accounting Standards Codification 805-10-55-12, Accounting for Business Combinations. Under purchase accounting, the assets and
55
liabilities of an acquired company (LecTec) as of the effective date of the acquisition were recorded at their respective estimated fair values and added to those of the acquiring company. Accordingly, the consolidated financial statements and related footnote disclosures presented for periods prior to the Merger are those of AC alone. The consolidated Statement of Operations for the year ended December 31, 2011 includes the operations and cash flows of AC through September 30, 2011 and the combined operations and cash flows of AC and LecTec subsequent to the Merger.
The common stock of AC has been retrospectively adjusted to reflect the exchange ratio of one share of AC common stock for 0.03727336 share of the Company’s common shares as established in the Merger Agreement.
The Company is a regenerative medicine company with a portfolio of proprietary products and technologies for peripheral nerve reconstruction and regeneration. Peripheral nerves provide the pathways for both motor and sensory signals throughout the body and their damage can result in the loss of function and feeling. In order to improve surgical reconstruction and regeneration of peripheral nerves, the Company has developed and licensed technologies which are used in its products. Its product portfolio includes Avance® Nerve Graft, which the Company believes is the first and only commercially available allograft nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities (a gap created when the nerve is severed), AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a coaptation aid allowing for close approximation of severed nerves, and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector that protects nerves during the body’s healing process after surgery.
| 3. | Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed and determinable, delivery has occurred and there is a reasonable assurance of collection of the sales proceeds. Revenues for products are recognized when the tissue is delivered to the customer, at which time title passes to the customer. Once product is delivered, the Company has no further performance obligations. Delivery is defined as delivery to a customer location or segregation of product into a contracted distribution location. At such time, this product cannot be sold to any other customer. Fees charged to customers for storage and shipping of products are recognized as revenues when processed tissue is shipped to the customer or end user.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Concentration
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are maintained at financial institutions and, at times, balances may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has never experienced any losses related to these balances and does not believe it is not exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable and Concentration of Credit Risk
Accounts receivable are carried at the original invoice amount less an estimate made for doubtful accounts based on a review of all outstanding amounts on a monthly basis. Management determines the allowance for doubtful accounts by regularly evaluating individual customer receivables and considering a customer’s financial condition, credit history and current economic conditions. Accounts receivable are written off when deemed uncollectible. Recoveries of accounts receivable previously written off are recorded when received. As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, there were no amounts deemed uncollectible and there was no allowance for doubtful accounts recorded.
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to accounts receivable are limited because a large number of geographically diverse customers make up the Company’s customer base, thus spreading the trade credit risk. The Company also controls credit risk through credit approvals, credit limits and monitoring procedures.
56
Inventories
Inventories are comprised of implantable tissue, nerve grafts, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, and supplies that are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or market and consist of the following:
| December 31, 2012 |
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| Finished goods |
$ | 2,143,176 | $ | 1,374,817 | ||||
| Work in process |
145,156 | 145,300 | ||||||
| Raw materials |
862,777 | 240,423 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 3,151,109 | $ | 1,760,540 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Inventories are net of reserve of $537,798 and $433,706 at December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively
Property and Equipment
Depreciation and amortization is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
| Furniture and equipment |
2-5 years | |
| Leasehold improvements |
5 years (or lease term if less) | |
| Processing equipment |
5-7 years |
Major additions and improvements are capitalized, while replacements, maintenance and repairs, which do not improve or extend the life of the respective assets, are expensed as incurred. When assets are retired or otherwise disposed of, related costs and accumulated depreciation and amortization are removed and any gain or loss is reported as other income or expense.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets consist primarily of license agreements for exclusive rights to use various patented and patent-pending technologies described in Note 6 and other costs related to the license agreements, including patent prosecution and protection costs. Such costs are capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over the underlying terms of the license agreements or estimated useful life of patents, ranging from 5 to 20 years.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets, Including License Agreements
The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. For the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company recorded an impairment loss of $129,667; there was no impairment for the year ended December 31, 2011.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized, but is tested for impairment annually. The Company utilizes the income approach in estimating fair value. The Company’s 2012 annual goodwill impairment analysis indicated a significant decrease in the carrying value of goodwill, due to declines in the associated revenues, resulting in a $169,887 impairment loss being recorded for the year ended December 31, 2012; there was no impairment for the year ended December 31, 2011.
57
Deferred Financing Costs
The Company capitalizes all third-party costs incurred, including equity-based payments, associated with the issuance of long-term debt. The costs are amortized to interest expense over the term of the debt using the effective interest method.
Advertising
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising costs were approximately $56,000 and $17,000 for 2012 and 2011, respectively, and are included in sales and marketing expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Research and Development Costs
Research and Development costs are expensed as incurred.
Income Taxes
The Company has not recorded current income tax expense due to the generation of net operating losses. Deferred income taxes are accounted for using the balance sheet approach which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will not be realized. A full valuation allowance has been established on the deferred tax asset as it is more likely than not that future tax benefit will not be realized. In addition, future utilization of the available net operating loss carryforward may be limited under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 as a result of changes in ownership.
The Company identifies and evaluates uncertain tax positions, if any, and recognizes the impact of uncertain tax positions for which there is a less than more-likely-than-not probability of the position being upheld when reviewed by the relevant taxing authority. Such positions are deemed to be unrecognized tax benefits and a corresponding liability is established on the balance sheet. The Company has not recognized a liability for uncertain tax positions. If there were an unrecognized tax benefit, the Company would recognize interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in interest expense and penalties in operating expenses. The Company’s remaining open tax years subject to examination by the Internal Revenue Service include the years ended December 31, 2009 through 2012; there currently are no examinations in process.
Preferred Stock
The Company accounted for its preferred stock under the provisions of Accounting Standards Codification on Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, which sets forth the standards for how an issuer classifies and measures certain financial instruments with characteristics of both liabilities and equity. This standard requires an issuer to classify a financial instrument that is within the scope of the standard as a liability or temporary equity if such financial instrument embodies an unconditional obligation to redeem the instrument at a specified date and/or upon an event certain to occur.
Prior to conversion in connection with the Merger, all or any number of the Series B, Series C, and Series D preferred stock was originally redeemable by a majority of preferred shareholder approval at any time after January 7, 2015 at a redemption price determined in accordance with the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation, plus accrued and unpaid dividends. The Company has determined that its Series B, Series C, and Series D preferred stock required temporary equity classification as its obligation to redeem these instruments were outside the control of the Company. Permanent equity classification was not currently applicable as the preferred stock was not currently redeemable but may become so in the future.
58
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The respective carrying value of certain on-balance-sheet financial instruments approximated their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. These financial instruments include cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt approximates its carrying value based upon current rates available to the Company.
Stock-Based Compensation
Stock-based compensation cost related to stock options granted under the AC 2002 Stock Option Plan and AxoGen 2010 Stock Incentive Plan (see Note 10) is measured at grant date, based on the fair value of the award, and is recognized as an expense over the employee’s requisite service period. The Company estimates the fair value of each option award issued under the Plan on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model that uses the assumptions noted in the table below. The Company estimates the volatility of its common stock at the date of grant based on the volatility of comparable peer companies which are publicly traded, for the periods prior to the merger, and based on the Company’s common stock for periods subsequent to the merger. The Company determines the expected life based on historical experience with similar awards, giving consideration to the contractual terms, vesting schedules and post-vesting forfeitures. The Company uses the risk-free interest rate on the implied yield currently available on U.S. Treasury issues with an equivalent remaining term approximately equal to the expected life of the award. The Company has never paid any cash dividends on its common stock and does not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. The Company used the following weighted-average assumptions for options granted during the year ended December 31:
| Years ended December 31, |
2012 | 2011 | ||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
4.0 | 4.0 | ||||||
| Expected volatility |
117.2 | % | 90.9 | % | ||||
| Risk free rate |
0.61 | % | 1.27 | % | ||||
| Expected dividends |
0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
The Company estimates forfeitures when recognizing compensation expense and this estimate of forfeitures is adjusted over the requisite service period based on the extent to which actual forfeitures differ, or are expected to differ, from such estimates. Changes in estimated forfeitures are recognized through a cumulative catch-up adjustment, which is recognized in the period of change, and also impact the amount of unamortized compensation expense to be recognized in future periods. The Company did not apply a forfeiture allocation to its unvested options outstanding during the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 as they were deemed insignificant.
Earnings (Loss) Per Common Share
Earnings (loss) per common share (EPS) is calculated for basic EPS by dividing net income (loss) available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period.
The basic loss attributable to common stockholders was computed as follows:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (9,417,958 | ) | $ | (9,219,220 | ) | ||
| Less preferred dividends |
(— | ) | (1,028,351 | ) | ||||
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (9,417,958 | ) | $ | (10,247,571 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
There were no dilutive instruments as of December 31, 2012 and 2011. The basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding were 11,089,425 and 3,697,390 for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011.
59
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
The Company’s management has reviewed and considered all recent accounting pronouncements and believe there are none that could potentially have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial condition, results of operations, or disclosures.
| 4. | Merger |
On September 30, 2011, LecTec completed its business combination with AC pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement (see Note 2).
The following table summarizes the estimated fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition. The total acquisition price of $11,847,916 has been allocated as follows:
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7,201,638 | ||
| Other current assets |
40,483 | |||
| Notes and accrued interest receivable |
4,555,562 | |||
| Goodwill |
169,987 | |||
| Intangible assets |
260,000 | |||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(379,754 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total purchase price |
$ | 11,847,916 |
The following table sets forth the unaudited pro forma results of the Company as if the Merger had taken place on the first day of the period presented. These combined results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may have been achieved had the companies always been combined.
| Year
Ended December 31, 2011 |
||||
| Revenues |
$ | 4,914,938 | ||
| Net Loss |
$ | (8,610,775 | ) | |
| Basic and diluted net loss per common share |
$ | (0.79 | ) | |
| Weighted average shares — basic and diluted |
10,957,705 | |||
60
| 5. | Property and Equipment |
Property and equipment consist of the following:
| December 31, 2012 |
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| Furniture and equipment |
$ | 572,459 | $ | 535,183 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
42,564 | 42,564 | ||||||
| Processing equipment |
995,815 | 988,716 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(1,502,304 | ) | (1,318,639 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property and equipment |
$ | 108,534 | $ | 247,824 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 6. | Intangible Assets |
The Company’s intangible assets consist of the following:
| December 31, 2012 |
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| License agreements |
$ | 772,230 | $ | 899,231 | ||||
| Patents |
63,429 | 291,907 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization |
(261,928 | ) | (291,658 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Intangible assets, net |
$ | 573,731 | $ | 899,480 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
License agreements are being amortized over periods ranging from 17-20 years. Patent costs are being amortized over three years. Pending patent costs are not amortizable. Amortization expense for 2012 and 2011 was approximately $127,000 and $67,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2012, future amortization of license and patent agreements is expected to be $58,400 for 2013 $55,300 for 2014, $46,000 for 2015, 2016 and 2017.
In 2012 the Company determined that the carrying value of certain patents were not recoverable and exceeded their estimated fair value. As a result, the Company recorded an impairment loss of $129,667 to reduce these patents to their estimated fair value.
License Agreements
The Company has entered into license agreements (the “License Agreements”) with the University of Florida Research Foundation (“UFRF”) and University of Texas at Austin (“UTA”) and Emory University (“Emory”). Under the terms of the License Agreements, the Company acquired exclusive worldwide licenses for underlying technology used in repairing and regenerating nerves. The licensed technologies include the rights to issued patents and patents pending in the United States and international markets. The effective term of the License Agreements extends through the term of the related patents and the agreements may be terminated by the Company with 60 days prior written notice. Additionally, in the event of default, licensors may terminate an agreement if the Company fails to cure a breach after written notice. The License Agreements contain the key terms listed below:
| • | AxoGen pays royalty fees ranging from 1% to 3% under the License Agreements based on net sales of licensed products. One of the agreements also contains a minimum royalty of $12,500 per quarter, which may include a credit in future quarters in the same calendar year for the amount the minimum royalty exceeds the royalty fees. Also, when AxoGen pays royalties to more than one licensor for sales of the same product, a royalty stack cap applies, capping total royalties at 3.75%; |
| • | Under one of the agreements, if AxoGen does not achieve certain regulatory milestones, which AxoGen has not achieved, AxoGen would owe an annual license maintenance fee starting on August 31, 2012 of $120,000, escalating to $240,000 on August 31, 2013 and August 31, 2014. In 2012, AxoGen decided to abandon the license and as a result recorded a $147,826 loss on abandonment of license. |
61
| • | If AxoGen sublicenses technologies covered by the License Agreements to third parties, AxoGen would pay a percentage of sublicense fees received from the third party to the licensor. Currently, AxoGen does not sublicense any technologies covered by License Agreements. The Company is not considered a sub-licensee under the License Agreements and does not owe any sublicensee fees for its own use of the technologies; |
| • | AxoGen reimburses the licensors for certain legal expenses incurred for patent prosecution and defense of the technologies covered by the License Agreements; and |
| • | Currently, under one of the License Agreements, AxoGen would owe a $15,000 milestone fee upon receiving a Phase II Small Business Innovation Research or Phase II Small Business Technology Transfer grant involving the licensed technology. The Company has not received either grant and does not owe such a milestone fee. Other milestone fees are due if AxoGen develops certain pharmaceutical or medical device products under the License Agreements. No such products are currently under development. |
Royalty fees were approximately $167,000 and $115,000 during 2012 and 2011 and are included in sales and marketing expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
| 7. | Long-Term Debt / Note Payable |
Long-term debt / note payable consists of the following:
| December 31, 2012 |
December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| Loan and Security Agreement with financial institutions for aggregate of $5,000,000 with 9.9% interest payable monthly through September 2012; principal and interest payable monthly for the 30 months thereafter maturing on April 1, 2015, collateralized by all the assets of the Company and subject to certain financial covenant restrictions including minimum revenue requirements |
$ | — | $ | 5,000,000 | ||||
| Revenue Interest Purchase Agreement with PDL for aggregate of $20,800,000 with amounts payable monthly at 9.95% of Net Revenues through September 2014; and the greater of (i) 9.95% of product revenue or (ii) specific quarterly amounts varying from approximately $1.3 million to $2.5 million per quarter through September 2020. The minimum annual payment amounts are as follows: 2014 — $1,250,805, 2015 — $6,781,440, 2016 — $9,232,642, 2017 and 2018 — $9,000,000, 2019 — $9,063,000 and 2020 — $6,939,000. |
21,580,252 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total debt |
21,580,252 | 5,000,000 | ||||||
| Less unamortized debt discount |
— | (161,529 | ) | |||||
| Less current portion |
— | (434,734 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Long-term portion |
$ | 21,580,252 | $ | 4,403,737 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Note Payable
On October 5, 2012, AxoGen entered into a Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement (the “Royalty Contract”) with PDL, pursuant to which the Company sold to PDL the right to receive specified royalties of 9.95% on the Company’s Net Revenues (as defined in the Royalty Contract) generated by the sale, distribution or other use of AxoGen’s products Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector. The Royalty Contract has a term of eight years. Under the Royalty Contract, PDL is to receive royalty payments based on a royalty rate of 9.95% of the Company’s Net Revenues, subject to certain agreed upon minimum payment requirements of approximately $1.3 to $2.5 million per quarter which begin in the fourth quarter of 2014 through the third quarter of 2020 as provided in the Royalty Contract. The total consideration PDL paid to the Company was $20,800,000 (the “Funded Amount”), including $19,050,000 PDL paid to the Company on October 5, 2012, and $1,750,000 PDL paid to the Company on August 14, 2012 pursuant to an Interim Revenue Interest Purchase Agreement between the Company and PDL, dated August 14, 2012 (the “Interim Royalty Contract”). Upon the closing (the “Closing”) of PDL’s purchase of the specified royalties described above, which was concurrent with the execution of the Royalty Contract, the Interim Royalty Contract was terminated.
62
The Company records interest using its best estimate of the effective interest rate, currently the Company is accruing interest using the specified internal rate of return of the put option of 20%. From time to time, the Company will reevaluate the expected cash flows and may adjust the effective interest rate. Determining the effective interest rate requires judgment and is based on significant assumptions related to estimates of the amounts and timing of future revenue streams. Payments made to PDL consist of interest and principal. Based on current calculations of repayments, using actual payments to date, an estimate of future revenue streams and an estimated effective rate of 20% (calculated using the put rate in the agreement), principal payments are scheduled to begin in April 2015. All payments made prior to this date are interest only payments.
Put Option
Under the Royalty Contract, on October 5, 2016, or in the event of the occurrence of a material adverse event, our transfer of revenue interest or substantially all of our interest in the products or AxoGen’s bankruptcy or material breach of the Royalty Contract, PDL may require AxoGen to repurchase the Assigned Interests at the “Put Price.” The Put Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a specified internal rate of return to PDL of 20% on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by the Company, and (ii) any “Delinquent Assigned Interest Payment” (as defined in the Royalty Contract) the Company owed to PDL.
Change of Control; Call Option
In addition, in the event of a “Change of Control” (as defined in the Royalty Contract), the Company must repurchase the assigned Interests from PDL for a repurchase price equal to the “Change of Control Price” on or prior to the third business day after the occurrence of the Change of Control. The Change of Control Price is equal to the sum of (i) an amount that, when paid to PDL, would generate a specified internal rate of return to PDL of thirty-two and one half percent (32.5%) on the Funded Amount, taking into consideration payments made to PDL by the Company, and (ii) any “Delinquent Assigned Interest Payment” (as defined in the Royalty Contract) the Company owed to PDL. In addition, at any time after October 5, 2016, the Company, at its option, can call the Royalty Contract for a price equal to the Change of Control Price.
Board Designee
Under the Royalty Contract, during the term of the Royalty Contract, PDL is entitled to designate, and AxoGen shall appoint an individual designated by PDL, who shall serve on the Board of Directors of the Company (the “Board”) until the Company’s 2013 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the “2013 Annual Meeting”). For the 2013 Annual Meeting and each annual meeting thereafter during the term of the Royalty Contract, the Board shall nominate and recommend the PDL designee as a director nominee to serve on the Board until the next annual meeting and shall include such nomination in AxoGen’s proxy statement for the 2013 Annual Meeting and each annual meeting thereafter, provided that the election of the PDL designee is subject to shareholders’ approval. Should at any time there become a vacancy on the Board as a result of (i) the resignation, death or removal of the PDL designee or (ii) such PDL designee failing to obtain the requisite approval of the Company’s shareholders at any annual or special meeting of the Company’s shareholders and where no other individual is elected to such vacancy, PDL shall have the right to designate an individual to fill such vacancy, and AxoGen shall take such actions necessary to appoint, such individual to the Board.
Preemptive Rights
Under the Royalty Contract, PDL has preemptive rights with respect to certain new issuances of AxoGen’s equity securities and securities convertible, exchangeable or exercisable into such equity securities.
63
Restriction on Dividends
Under the Royalty Contract, during the period from the October 5, 2012 to December 4, 2016 (or the payment of the Put Price in the event PDL exercises its put option on or prior to December 4, 2016), AxoGen shall not, nor shall it permit any subsidiary to, declare, pay or make any dividend or distribution on any shares of the common stock or preferred stock of such entity (other than dividends or distributions payable in its stock, or split-ups or reclassifications of its stock) or apply any of its funds, property or assets to the purchase, redemption or other retirement of any common or preferred stock, or of any options to purchase or acquire any such shares of common or preferred stock of any such entity (collectively, “Restricted Payments”), except that: (i) each subsidiary may make direct or indirect Restricted Payments to the Company; and (ii) the Company and each subsidiary may purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire Equity Interests issued by it solely with the proceeds received from the substantially concurrent issue of new shares of its common stock or other common Equity Interests. For purposes of the Royalty Contract, “Equity Interests” of any person means any and all shares, rights to purchase, options, warrants, general, limited or limited liability partnership interests, member interests, participation or other equivalents of or interest in (regardless of how designated) equity of such entity, whether voting or nonvoting, including common stock, preferred stock, convertible securities or any other “equity security” (as such term is defined in Rule 3a11-1under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended).
Guarantee and Collateral Agreement
In connection with the Royalty Contract, on October 5, 2012, AxoGen and AC, entered into a Guarantee and Collateral Agreement (the “Guarantee and Collateral Agreement”) with PDL, pursuant to which (i) AC unconditionally and irrevocably guarantees to PDL the prompt and complete payment and performance by AxoGen when due of the “Secured Obligations,” which include the Company’s obligations under the Royalty Contract, and any other obligations that AxoGen may owe to PDL under the Royalty Contract and other transaction documents; and (ii) each of the Company and AC grants to PDL a security interest in certain collateral as specified in the Guarantee and Collateral Agreement for the prompt and complete payment and performance when due of the Secured Obligations.
Long-Term Debt
On September 30, 2011, the Company entered into the Loan and Security Agreement with MidCap Financial SBIC, LP (“MidCap”), as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (the “MidCap Loan”). The credit facility under the MidCap loan had a principal amount of $5.0 million and a term of 42 months, and is subject to prepayment penalties. Under the MidCap Loan, AxoGen was required to make interest only payments for the first 12 months, and payments of both interest and straight line amortization of principal for the remaining 30 months. The interest rate was 9.9% per annum, and interest was computed on the basis of a 360-day year and the actual number of days elapsed during which such interest accrues.
The agreement contained customary affirmative and negative covenants, including, without limitation, (i) covenants requiring AxoGen to comply with applicable laws, provide to MidCap copies of AxoGen’s financial statements, maintain appropriate levels of insurance, protect, defend and maintain the validity and enforceability of AxoGen’s material intellectual property, (ii) covenants restricting AxoGen’s ability to dispose of all or any part of its assets (subject to certain exceptions), engage in other lines of business, change its senior management, enter into merger or consolidation transactions, incur or assume additional indebtedness, or incur liens on its assets, and (iii) covenants requiring the Company to meet certain minimum Net Invoiced Revenue as defined in the agreement, or maintain a cash balance of 80% of the loan principal amount.
The MidCap Loan was secured by all of AxoGen’s assets. The lenders also received a ten-year warrant to purchase 89,686 shares of AxoGen’s common stock at $2.23 per share. The fair value of the warrant was $173,736 and was recorded as debt discount and was being amortized through interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the debt. Amortization of debt discount was $12,207 for 2011. The Company also recorded $317,990 in deferred financing costs which were being amortized over the term of the loan. Amortization of the deferred financing cost was $22,714 for 2011.
64
On April 21, 2008, the Company entered into a Loan and Security Agreement with two different lenders, as subsequently amended (the “2008 Loan and Security Agreement”), which provided for a loan with an aggregate principal amount of $7.5 million. The loan’s maturity date was October 1, 2011. The loan bore interest at a rate of 18% per month, as amended, and was secured by all of the Company’s assets. Upon the execution of the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement, the Company recorded $155,556 in deferred financing costs which were being amortized through interest expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations over the life of the term note. Amortization of the deferred financing costs was $12,963 for 2011.
In conjunction with the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement, the Company also issued warrants to purchase a combined 280,803 shares of the Company’s Series C Preferred Stock, immediately exercisable at $0.7345 per share, expiring on May 1, 2018. The fair value of the warrants was recorded as debt discount and was being amortized through interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the debt. Amortization of this debt discount was $11,436 during 2011.
During 2010, the Company executed six amendments to the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement, resulting in the issuance of a total of 28,561,272 additional warrants for the purchase of the Company’s Series D preferred stock, immediately exercisable at $0.1198 per share, expiring on varying dates during the year 2020. The total fair value of the warrants of $2,160,879 was recorded as deferred financing costs during 2010 and was being amortized through interest expense — deferred financing costs on the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. The Company recognized $990,792 in amortization of these costs for 2011. See additional discussion related to the accounting for the warrants at Note 9.
On April 11, 2011, the Company entered into a waiver and seventh amendment (the “Amendment”) to the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement. The Amendment waived the event of default resulting from the failure to pay the balance due under the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement by March 31, 2011, increased the annual interest rate to 18% beginning April 1, 2011, and extended the maturity to the earlier of an acquisition event (including the Merger discussed in Note 4), or October 1, 2011. In connection with the Amendment, an event of default would occur if the Company fails to receive proceeds from equity and/or convertible subordinated debt financings of at least $2.5 million by May 31, 2011 and an additional $2.5 million by August 31, 2011.
On September 30, 2011, the Company paid the entire outstanding loan balance under the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement. The Company also paid a loan pay off fee of $109,436 which is included in the amortization of deferred financing costs for 2011. The warrants issued to the holders of the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement (see Note 9) expired upon the effective date of the Merger.
2010 Convertible Debt and Warrants
The 2010 Convertible Debt is convertible automatically into shares of conversion stock, defined in the agreement as a future “qualified next equity financing”, or its Series C preferred stock. The debt is also convertible at the option of the Company in the event of a future equity financing which is not considered a “qualified next equity financing”. The conversion price is 65% of the price per share paid at the next equity financing, as defined in the agreement.
Upon issuance of the 2010 Convertible Debt, the Company recorded a total of $122,900 in deferred financing costs which were being amortized through interest expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations over the debt term. Amortization of the deferred financing costs was $87,221 for 2011.
In connection with the Merger on September 30, 2011, the 2010 convertible debt of $1,338,455 and $2,359,091 and accrued interest of $263,371 were converted into 2,581,963 shares of AC common stock using a conversion price of $0.0572 (65% of price per share paid at the next equity financing or $0.088) and 0.03727336 exchange ratio.
65
2011 Convertible Debt
On May 3, 2011, the Company issued an 8% convertible note payable for $500,000 to LecTec related to the Merger. On May 31, 2011, the Company issued additional convertible notes payable under the same terms of which $2,000,000 was issued to LecTec and $500,000 was issued to certain AC shareholders. The notes were collateralized by all assets of the Company and subordinated to the Company’s 2008 Loan and Security Agreement. Principal and interest accrued under the note was due upon the earlier of June 30, 2013 or a change in control other than in connection with the Merger.
On August 29, 2011, the Company issued an additional subordinated secured convertible promissory note in the principal amount of $2,000,000 to LecTec and $500,000 to certain AC shareholders on the same terms as the $3,000,000 notes issued by the Company in May 2011.
The $4,500,000 notes to LecTec were retired on September 30, 2011 after the closing of the Merger. The $1,000,000 notes to certain AC shareholders were converted into 423,709 shares of AxoGen, Inc.’s common stock using the $0.088 conversion price and 0.03727336 exchange ratio.
| 8. | Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) and Temporary Equity |
AxoGen, Inc. Classes of Stock
AxoGen, Inc.’s authorized capital stock consists of 50,000,000 shares, par value $0.01 per share. The authorized capital stock is divisible into the classes and series, has the designation, voting rights, and other rights and preferences and is subject to the restrictions that the AxoGen Board of Directors may from time to time establish. Unless otherwise designated by the AxoGen Board of Directors, all shares are common stock. AxoGen has not designated any shares other than common stock.
In connection with the Merger, 32,709,676 shares of AC common stock were converted into 1,219,199 shares of AxoGen, Inc.’s common stock using the 0.03727336 exchange ratio.
On September 30, 2011, AxoGen sold to certain investors in a private placement 423,709 shares of common stock at $2.36 per share.
On October 10, 2011, each non-employee director of AxoGen was granted 5,455 shares of AxoGen common stock, valued at $2.75 per share, in lieu of a cash retainer payment for the director’s services through December 31, 2012. The Company recorded $15,000 of directors fee included in general and administrative expenses and $60,000 in prepaid expenses related to issuance of 27,275 shares of common stock to five directors.
AC Classes of Stock
General
AC had authorized 133,000,000 shares of common stock with a $.00001 par value.
AC had authorized 103,408,891 shares of preferred stock with a $.00001 par value which the Board of Directors is empowered to designate and issue in different series. At December 31, 2010, the Board of Directors had designated and issued 2,544,750 shares of Series A Preferred Stock; 17,065,217 shares of Series B Preferred Stock; 16,798,924 shares of Series C Preferred Stock and 67,000,000 shares of Series D Preferred Stock.
In connection with the Merger, on September 30, 2011 each share of Series A, B, C and D convertible preferred stock, for a total of 53,555,857 shares, were converted into shares of AC common stock and exchanged for 1,996,206 shares of AxoGen, Inc. common stock using the 0.03727336 exchange ratio.
66
Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
In 2004, AC issued 2,544,750 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A”) at $0.4421 per share for an aggregate price of $1,125,000. No dividends accrued or were payable on the Series A, except upon the declaration of dividends on AC’s common stock, payable at a rate per share of Series A equal to the amount the holder would be entitled to receive had all of the Series A been converted to AC common stock. Upon liquidation, Series A holders have preference to any distribution of any of the assets of AC to the holders of AC Common Stock after Series B, Series C, and Series D preferences have been paid. Series A has no redemption option. Each share of Series A is convertible into AC common stock at any time at the option of the holder by dividing the Preferred Original Issue Price by the Conversion Price at the time of conversion, which as of December 31, 2010 is equal to the purchase price of $0.4421. The conversion price is subject to adjustment, as defined. The only election right for Series A is to vote along with AC common shareholders to elect two directors to the Board. Each share of Series A has voting rights equal to the number of AC common shares as if converted.
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock
In 2006, AC issued 16,847,826 shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series B”) at $0.46 per share for an aggregate price of $7,750,000. The holders of the Series B are entitled to receive a cash dividend in preference over shares of AC common stock and Series A shareholders of AC at a rate of 8% of the issued price, per annum. Upon liquidation, the Series B holders have preference to any distributions of any of AC’s assets equal to the Preferred Original Issue Price plus any unpaid dividends after Series C and Series D preferences have been paid. At any time on or after January 7, 2015, the Series B shareholders have the right to redeem shares equal to the redemption price upon written request of at least 55% of the holders of Series B. Each share of Series B is convertible into AC common stock at any time at the option of the holder by dividing the Preferred Original Issue Price by the Conversion Price at the time of conversion, which as of December 31, 2010 is equal to the purchase price of $0.46. The conversion price is subject to adjustment, as defined. The holders of a majority of the Series B, C and D Preferred Stock have the right to elect three directors to the Board. Also, Series B, C and D will vote together with Series A and AC common shareholders to elect two directors to the Board. Each share of Series B, C and D has voting rights equal to the number of AC common shares as if converted.
AC is accreting dividends on the Series B, based on the stated dividend rate of 8% per annum. The Series B dividends accreted for the year ended December 31, 2011 was $292,329. A total of $3,152,603 in Series B dividends had been accreted as of September 30, 2011 and were forfeited in accordance with the Merger.
On June 11, 2010, 7,065,217 shares of Series B, representing $3,250,000, were converted into 263,344 shares of AC’s common stock at the election of the shareholder.
Series C Convertible Preferred Stock
In 2007, AC issued 16,518,121 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series C”) at $0.7345 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $12,132,559. The holders of the Series C are entitled to receive a cash dividend in preference over shares of AC common stock, Series A and Series B shareholders of AC at a rate of 8% of the issued price, per annum. Upon liquidation, the Series C holders have preference to any distributions of any of AC’s assets equal to the Preferred Original Issue Price plus any unpaid dividends after Series D preferences have been paid. At any time on or after January 7, 2015, the Series C shareholders have the right to redeem shares equal to the redemption price upon written request of at least 60% of the holders of Series C. Each share of Series C is convertible into AC common stock at any time at the option of the holder by dividing the Preferred Original Issue Price by the Conversion Price at the time of conversion, which as of December 31, 2010 is equal to the purchase price of $0.7345. The conversion price is subject to adjustment, as defined. The holders of a majority of the Series B, C and D have the right to elect three directors to the Board. Also, Series B, C and D will vote together with Series A and AC common shareholders to elect two directors to the Board. Each share of Series B, C and D has voting rights equal to the number of AC common shares as if converted.
67
AC is accreting dividends on the Series C, based on the stated dividend rate of 8% per annum. The dividends accreted for the year ended December 31, 2011 was $515,577. A total of $3,403,651 in Series C dividends had been accreted as of September 30, 2011 and were forfeited in accordance with the Merger.
On June 11, 2010, 5,445,882 shares of Series C, representing $4,000,000, were converted into 202,986 shares of AC’s common stock at the election of the shareholder.
Series D Convertible Preferred Stock and Warrants
On January 7, 2010, AC issued 39,156,876 shares of Series D Preferred Stock (“Series D”) at $0.1198 per share for an aggregate price of $4,661,326, net of issuance costs of $29,667. Of the total shares issued, 16,694,489 shares were issued for $2,000,000 in cash. The remaining 22,462,387 shares were issued in conjunction with the conversion of $2,617,000 of principal and $73,994 of accrued and unpaid interest under the 2009 Convertible Debt (see Note 7). The holders of the Series D are entitled to receive a cash dividend in preference over all other shareholders of AC at a rate of 8% of the issued price, per annum. Upon liquidation, the Series D holders have preference to any distributions of any of AC’s assets equal to the Preferred Original Issue Price plus any unpaid dividends. At any time on or after January 7, 2015, the Series D shareholders have the right to redeem shares equal to the redemption price upon written request of at least 66 2/3% of the holders of Series D. Each share of Series D is convertible into AC common stock at any time at the option of the holder by dividing the Preferred Original Issue Price by the Conversion Price at the time of conversion, which as of December 31, 2010 is equal to the purchase price of $0.1198. The conversion price is subject to adjustment, as defined. The holders of a majority of the Series B, C and D have the right to elect three directors to the Board. Also, Series B, C and D will vote together with Series A and AC common shareholders to elect two directors to the Board. Each share of Series B, C and D has voting rights equal to the number of AC common shares as if converted.
AC is accreting dividends on the Series D, based on the stated dividend rate of 8% per annum. Dividends accreted during the year ended December 31, 2011 were $220,444. A total of $518,426 in Series D dividends had been accreted as of September 30, 2011 and were forfeited in accordance with the Merger.
On September 11, 2010, 9,000,617 shares of Series D, representing $1,078,274, were converted into 335,483 of AC’s common stock at the election of the shareholder.
In conjunction with the issuance of the Series D, AC also issued warrants for the purchase of 8,347,236 shares of AC’s Series D Preferred Stock, immediately exercisable at $0.1198 per share, expiring on January 7, 2015. The investors paid additional consideration totaling $10,000 for the purchase of the warrants. The warrants are considered offering costs related to the Series D issuance and their fair value of $517,529 was recorded net against proceeds on the issuance of the stock during 2010.
68
| 9. | Preferred Stock Warrants and Warrant Liability |
Preferred Stock Warrants
At September 30, 2011, the outstanding warrants to purchase the Company’s Series C and Series D preferred stock which were issued in connection with certain financing arrangements and amendments to existing financing arrangements were expired unexercised in connection with the Merger. Information relating to these warrants at December 31, 2010 is summarized as follows:
| Warrants |
Remaining Number Outstanding |
Exercise Price | ||||||
| Series C Warrants-2008 Loan and Security Agreement |
280,803 | $ | 0.7345 | |||||
| Series D Warrants-2009 Convertible Debt |
4,368,948 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| Series D Warrants-Series D Preferred Stock Issuance |
8,347,236 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| *Series D Warrants-1st Amendment |
6,243,362 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| *Series D Warrants-2nd Amendment |
8,694,558 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| *Series D Warrants-3rd Amendment |
4,462,227 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| *Series D Warrants-5th Amendment |
2,260,440 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
| *Series D Warrants-6th Amendment |
6,900,685 | $ | 0.1198 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
41,558,259 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| * | Warrants issued to lenders in conjunction with amendments to 2008 Loan and Security Agreement (see Note 7). |
Warrant Liability
The warrants issued in conjunction with the 2008 Loan and Security Agreement (see Note 7) are issuable for Series C preferred stock. The warrants issued in connection with the 2009 Convertible Debt (see Note 7) and the Series D Preferred Stock (see Note 8) are issuable for Series D preferred stock. Both the Series C and Series D preferred stock are considered contingently redeemable based on the shareholders’ right to redeem the shares on or after January 7, 2015. In accordance with Accounting Standards Codification on Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, since the warrants are indexed to contingently redeemable securities of the Company, they are classified as liabilities upon issuance. As liability classified derivative financial instruments, the warrants are initially and subsequently required to be measured at their fair values as defined in Accounting Standards Codification on Fair Value Measurement.
The change in fair value of the warrants between each reporting period is recorded in the statements of operations and was estimated by the Company using a binomial lattice valuation model. The following assumptions were incorporated into the valuations for 2011 and 2010:
| 2011 | ||
| Exercise price |
$0.1198 – $0.7345 | |
| Market value of stock at end of period |
$0.01 | |
| Expected dividend rate |
0.00% | |
| Expected volatility |
33.47% – 62.86% | |
| Risk-free interest rate |
0.03% – 3.18% | |
| Expected life in years |
3.40 – 9.90 | |
| Shares underlying warrants outstanding classified as liabilities |
41,558,259 |
The Company recorded income of $62,305 for 2011, as a result of the change in the fair value of warrant liability between reporting periods which was recorded in other income (expense) on the consolidated statements of operations. The total balance of the warrant liability as of September 30, 2011 of $2,607,510 was forfeited in accordance with the Merger.
69
| 10. | Stock Options |
AC has a 2002 Stock Option Plan (“the AC Plan”), which allows for issuance of incentive stock options and non-qualified stock options to employees, directors and consultants at an exercise price equal to or greater than fair market value. Under the provisions of the AC Plan, AC authorized for issuance 18,144,658 shares for purchase pursuant to options.
AxoGen, Inc. has a AxoGen 2010 Stock Incentive Plan (the “AxoGen Plan”), which allows for issuance of incentive stock options and non-qualified stock options to employees, directors and consultants at an exercise price equal to or greater than fair market value. On September 27, 2011, LecTec amended and restated the AxoGen Plan to, among other things, increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the plan by 2,300,000 shares. The total number of shares authorized for issuance under the AxoGen Plan is 2,750,000 shares. As a result of the Merger, options granted under the AC Plan were assumed by the Company so that each stock option pursuant to the AC Plan so assumed continued to have, and be subject to, the same terms and conditions of such stock option immediately prior to the Merger, except that (i) each AC Plan stock option is exercisable for that number of shares of Company common stock equal to the product of the number of shares of AC common stock that were issuable upon exercise of such stock option immediately prior to the Merger multiplied by the Closing Ratio (“as defined in the Merger Agreement”) and (ii) the per share exercise price for the shares of Company common stock issuable upon the exercise of such assumed stock option will be equal to the quotient determined by dividing the exercise price per share of AC common stock at which such stock option was exercisable immediately prior to the Merger by the Closing Ratio. The options to employees typically vest 12.5% every six months over a four-year period and those to directors and certain executive officers have vested 25% per quarter over one year or had no vesting period. Options issued to consultants vest over the service period ranging from three to ten years. Options have terms ranging from seven to ten years.
Stock-based compensation expense was $495,077 and $250,044 for 2012 and 2011, respectively.
The following is a summary of stock option activity:
| Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term(Years) |
||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2010: |
447,659 | $ | 0.27 | 8.62 | ||||||||
| Granted |
1,141,952 | 2.61 | ||||||||||
| LecTec stock option from Merger |
464,000 | 3.48 | ||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(9,223 | ) | (0.06 | ) | ||||||||
| Exercised |
(98,700 | ) | (0.27 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2011: |
1,945,688 | 2.41 | 7.35 | |||||||||
| Granted |
267,576 | 2.99 | ||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(354,932 | ) | (2.48 | ) | ||||||||
| Exercised |
(58,341 | ) | (0.27 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 |
1,799,991 | 2.54 | 7.66 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2012 |
941,876 | 2.71 | 7.11 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
The average fair value of options granted at market during 2012 and 2011 was $2.99 and $0.42 per option, respectively.
The intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $173,000 and $190,000, respectively. The intrinsic value of options outstanding at December 31, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $288,000 and $1,126,000, respectively. The intrinsic value of options exercisable at December 31, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $0 and $391,000, respectively.
70
In connection with the Merger, all outstanding options to purchase shares of AC Common Stock were exchanged for options to purchase shares of AxoGen, Inc. common stock at a ratio of one to 0.03727336. The Company recorded $19,769 and $38,521 incremental cost in 2012 and 2011, respectively, related to this modification.
Total future compensation expense related to nonvested awards is expected to be approximately $1,405,000 at December 31, 2012 which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 3.04 years. The following table represents non-vested share-based payment activity with employees for the year ended December 31, 2012 and 2011:
| Number of Options |
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||||
| Nonvested options — December 31, 2010: |
325,575 | 0.27 | ||||||
| Granted |
1,141,952 | 0.42 | ||||||
| Vested |
(195,099 | ) | (0.87 | ) | ||||
| Forfeited |
(9,223 | ) | (0.004 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Nonvested options — December 31, 2011: |
1,263,205 | 1.41 | ||||||
| Granted |
267,576 | 2.99 | ||||||
| Vested |
(317,734 | ) | (1.92 | ) | ||||
| Forfeited |
(354,932 | ) | (2.48 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Nonvested options — December 31, 2012 |
858,115 | 2.36 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 11. | Income Taxes |
The Company has temporary differences between the carrying amount of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and their respective income tax basis, as measured by enacted state and federal rates as follows:
| December 31 | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards |
18,182,000 | 15,065,000 | ||||||
| Charitable contributions |
2,800 | 3,000 | ||||||
| Inventory Reserves |
365,600 | 163,000 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
52,300 | 361,000 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
18,602,700 | 15,592,000 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Depreciation |
(154,900 | ) | (160,000 | ) | ||||
| Amortization |
(51,700 | ) | (51,000 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
(206,600 | ) | (211,000 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax assets |
18,396,100 | 15,381,000 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Valuation allowance |
(18,396,100 | ) | (15,381,000 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
As of December 31, 2012, the Company had net operating loss carry forwards of approximately $48.3 million to offset future taxable income which expire in various years through 2031. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce the deferred tax assets reported if, based on the weight of the evidence, it is more likely than not that a portion or none of the deferred tax assets will be realized. After consideration of all the evidence, including reversal of deferred tax liabilities, future taxable income and other factors, management has determined that a full valuation allowance is necessary as of December 31, 2012 and 2011. The valuation allowance increased by $3,015,100 and $3,572,000 during 2012 and 2011, respectively.
71
The net income tax benefit of approximately $738,000 for 2012 was the result of the Company’s ability to utilize net operating losses and franchise tax adjustments which resulted in tax refunds. The Company had no income tax expense or income tax benefit for 2011 due to incurrence of net operating losses. The Company does not believe there are any additional tax refund opportunities currently available.
| 12. | Employee Benefit Plan |
The Company adopted the AxoGen Simple IRA plan in 2007. All full-time employees who have attained the age of 18 are eligible to participate in the Plan. Eligibility is immediate upon employment and enrollment is available any time during employment. Participating employees may make annual pretax contributions to their accounts up to a maximum amount as limited by law. The simple IRA plan requires the Company to make matching contributions of between 1% and 3% of the employee’s annual salary as long as the employee participates in the Plan. Additionally, the matching has to be at least 3% for three of the first five years of the Plan. Both employee contributions and Company contributions vest immediately. In 2012 and 2011, the Company match was 3% of the participating employee’s annual salary. The Company contributed $102,189 and $66,687 in matching funds during 2012 and 2011, respectively.
| 13. | Commitments and Contingencies Operating Leases |
Operating Leases
The Company leases its lab space under one-year lease agreements, currently expiring in September 2013.
Its corporate office space lease agreement expires in April 2014. Estimated future minimum rental payments on the leases are as follows:
| Year ending December 31 |
||||
| 2013 |
$ | 145,964 | ||
| 2014 |
34,015 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| TOTAL |
$ | 179,979 | ||
|
|
|
Total rent expense for the Company’s leased office and lab space for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $176,000 and $171,000, respectively.
Service Agreements
In 2008, the Company entered into a biostorage and management services agreement with a vendor. The agreement specifies monthly administration fees, storage fees based on volume, and retrieval fees per specimen based on lead times. The agreement can be terminated with 90 days written notice.
In 2009, the Company also entered into a two-year tissue processing agreement with another vendor. Tissue processing fees are based on a per donor batch rate. The agreement requires minimum annual purchases of $160,000 and either party may terminate this agreement with six month written notice. In 2011 and 2012, the parties agreed to an extension for an additional twelve months and amended the agreement to provide for automatic twelve month renewals.
In August 2008, the Company entered into an agreement to distribute the AxoGuard® product worldwide in the field of peripheral nerve repair, and the parties subsequently amended the agreement in March, 2012. The agreement has an initial seven-year term from the date of the original agreement and following such initial term, the agreement automatically renews for an additional seven (7) year period provided that the parties agree to meet at least ninety (90) days before the end of such initial term to review whether the purchase price of the products obtained from Cook Biotech need to be adjusted and reasonably agree to such adjustment in writing, where such agreement shall not be unreasonably withheld. The Cook Biotech agreement also requires certain minimum purchases, although through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforce such provision, and establishes a formula for the transfer cost of the AxoGuard® products.
72
In December 2011, the Company also entered into a Master Services Agreement for Clinical Research and Related Services. The Company was required to pay $151,318 upon execution of this agreement and $20,416 per month for 42 months starting in January 2012 through August 2015.
Certain executive officers of the Company are parties to employment contracts. All such contracts have severance payments in the event of a Company change of control, provided certain conditions are met. One contract has a severance provision in the event of termination without cause.
73
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) Documents filed as part of this Report
(1) The following financial statements are filed herewith in Item 8 of Part II of this annual report on Form 10-K:
| (i) | Consolidated Balance Sheets |
| (ii) | Consolidated Statement of Operations |
| (iii) | Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity |
| (iv) | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows |
| (v) | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
(3) Exhibits
| Exhibit Number |
Description | |
| 2.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 31, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to LecTec Corporation’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 2, 2011) | |
| 2.2 | Amendment No. 1 to Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of June 30, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Appendix A2 to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 2.3 | Amendment No. 2 to Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of August 9, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Appendix A3 to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 3.2 | AxoGen, Inc. Amended and Restated Bylaws. (incorporated by reference to Appendix C to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| **10.1 | Patent License Agreement, dated as of August 3, 2005, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Texas System (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.2 | Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement with Sublicensing Terms, dated as of February 21, 2006, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.3 | Sid Martin Biotechnology Development Institute Incubator License Agreement, dated as of September 26, 2006, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.4.1 | Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of February 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
74
| **10.4.2 | Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of August 9, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.5.1 | Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.5.2 | Amendment dated March 14, 2012 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
| +10.6.1 | Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2012, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and PDL BioPharma, Inc. | |
| +10.6.2 | Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2012, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation and PDL BioPharma, Inc. | |
| 10.6.3 | Interim Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and PDL BioPharma, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 10.7 | LecTec Corporation 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, Amended and Restated on September 27, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Appendix E to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| ***10.8.1 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 15, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.8.2 | Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.9.1 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of May 6, 2003, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.9.2 | Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.10 | Lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC, its successors and assigns (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 14, 2011) | |
| ***10.15 | Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2007) | |
| 10.16 | Settlement Agreement and Mutual Release, dated May 29, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and The Mentholatum Company (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 6, 2009) | |
| *10.17 | Supply and License Agreement, entered into as of January 1, 2004, by and between Novartis Consumer Health, Inc. and LecTec Corporation (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2009) | |
| 10.18 | Term Sheet between Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. and LecTec Corporation (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 12, 2009) | |
75
| 10.19 | Settlement and License Agreement, dated November 11, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 12, 2009) | |
| *10.20 | Settlement Agreement and Mutual Release, dated December 18, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and Johnson & Johnson Consumer Companies, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010) | |
| ***10.21 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 1, 2011, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Gregory G. Freitag (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
| ***10.22 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of February 27, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Jill Schiaparelli (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
| 10.23 | Second Amendment dated February 27, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC, its successors and assigns (Previously filed) | |
| 10.24.1 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2011, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation, as borrower, Midcap Financial SBIC, LP, as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.24.2 | First Amendment to Loan and Security Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Midcap Financial SBIC, LP. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 10.24.3 | Subordination and Intercreditor Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc., PDL BioPharma, Inc. and Midcap Financial SBIC, LP. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiary of the Registrant (Previously filed) | |
| +23.1 | Consent of Lurie Besikof Lapidus & Company, LLP | |
| 24.1 | Power of Attorney (Previously filed) | |
| +31.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer | |
| +31.2 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer | |
| +32.1 | Certification pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 99.1 | AxoGen, Inc. press release, dated March 12, 2013 (Previously filed) | |
| +101 | Interactive Data File | |
| * | Confidential treatment has been requested as to certain portions, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| ** | Confidential treatment has been granted for portions of this Exhibit pursuant to Rule 24b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended. The confidential portions have been deleted and filed separately with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| *** | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| + | Filed herewith. |
76
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on August 6, 2013.
| AXOGEN, INC |
| /s/ KAREN ZADEREJ |
| Karen Zaderej |
| Chief Executive Officer |
77
| Exhibit Number |
Description | |
| 2.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 31, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to LecTec Corporation’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 2, 2011) | |
| 2.2 | Amendment No. 1 to Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of June 30, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Appendix A2 to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 2.3 | Amendment No. 2 to Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of August 9, 2011, among LecTec Corporation, Nerve Merger Sub Corp. and AxoGen Corporation (incorporated by reference to Appendix A3 to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| 3.2 | AxoGen, Inc. Amended and Restated Bylaws. (incorporated by reference to Appendix C to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| **10.1 | Patent License Agreement, dated as of August 3, 2005, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Texas System (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.2 | Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement with Sublicensing Terms, dated as of February 21, 2006, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.3 | Sid Martin Biotechnology Development Institute Incubator License Agreement, dated as of September 26, 2006, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.4.1 | Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of February 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.4.2 | Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of August 9, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| **10.5.1 | Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.5.2 | Amendment dated March 14, 2012 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
| +10.6.1 | Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2012, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and PDL BioPharma, Inc. | |
| +10.6.2 | Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2012, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation and PDL BioPharma, Inc. | |
78
| 10.6.3 | Interim Revenue Interests Purchase Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and PDL BioPharma, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 10.7 | LecTec Corporation 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, Amended and Restated on September 27, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Appendix E to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011) | |
| ***10.8.1 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 15, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.8.2 | Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.9.1 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of May 6, 2003, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| ***10.9.2 | Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.10 | Lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC, its successors and assigns (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 14, 2011) | |
| ***10.15 | Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2007) | |
| 10.16 | Settlement Agreement and Mutual Release, dated May 29, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and The Mentholatum Company (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 6, 2009) | |
| *10.17 | Supply and License Agreement, entered into as of January 1, 2004, by and between Novartis Consumer Health, Inc. and LecTec Corporation (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2009) | |
| 10.18 | Term Sheet between Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. and LecTec Corporation (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 12, 2009) | |
| 10.19 | Settlement and License Agreement, dated November 11, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and Endo Pharmaceuticals Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 12, 2009) | |
| *10.20 | Settlement Agreement and Mutual Release, dated December 18, 2009, by and between LecTec Corporation and Johnson & Johnson Consumer Companies, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010) | |
| ***10.21 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 1, 2011, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Gregory G. Freitag (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
| ***10.22 | Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of February 27, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Jill Schiaparelli (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011) | |
79
| 10.23 | Second Amendment dated February 27, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC, its successors and assigns (Previously filed) | |
| 10.24.1 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2011, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation, as borrower, Midcap Financial SBIC, LP, as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011) | |
| 10.24.2 | First Amendment to Loan and Security Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Midcap Financial SBIC, LP. (incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 10.24.3 | Subordination and Intercreditor Agreement dated August 14, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc., PDL BioPharma, Inc. and Midcap Financial SBIC, LP. (Incorporated by reference to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012) | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiary of the Registrant (Previously filed) | |
| +23.1 | Consent of Lurie Besikof Lapidus & Company, LLP | |
| 24.1 | Power of Attorney (Previously filed) | |
| +31.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer | |
| +31.2 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer | |
| +32.1 | Certification pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 99.1 | AxoGen, Inc. press release, dated March 12, 2013 (Previously filed) | |
| +101 | Interactive Data File | |
| * | Confidential treatment has been requested as to certain portions, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| ** | Confidential treatment has been granted for portions of this Exhibit pursuant to Rule 24b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended. The confidential portions have been deleted and filed separately with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| *** | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| + | Filed herewith. |
80