UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
☒ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended DECEMBER 31, 2017
Or
☐TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from TO
Commission File Number: 001-36046
AXOGEN, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
|
|
|
|
MINNESOTA
|
|
41-1301878
|
|
(State or other jurisdiction of
|
|
(I.R.S. Employer
|
|
incorporation or organization)
|
|
Identification No.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
13631 Progress Blvd., Suite 400 Alachua, FL
|
|
32615
|
|
(Address of principal executive offices)
|
|
(Zip Code)
|
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (386)462-6800
|
|
|
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share
|
|
|
(Title of class)
|
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
|
None
|
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted in its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
|
|
|
|
Large accelerated filer ☐
|
|
Accelerated filer ☒
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-accelerated filer ☐
|
|
Smaller reporting company ☐
|
|
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
|
|
|
|
|
|
Emerging growth company ☐
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of June 30, 2017, the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was approximately $454,058,298 based upon the last reported sale price of our common stock on the NASDAQ Capital Market.
The number of shares outstanding of the Registrant’s common stock as of February 26, 2018 was 34,496,854 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive proxy statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Registrant’s fiscal year are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
From time to time, in reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (including this Form 10-K), in press releases, and in other communications to shareholders or the investment community, AxoGen, Inc. (including AxoGen, Inc.’s wholly owned subsidiaries, AxoGen Corporation and AxoGen Europe GmbH, the “Company”, “AxoGen”, “we”, “our”, or “us”) may provide forward-looking statements, as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, concerning possible or anticipated future results of operations or business developments. Words such as "expects", "anticipates", "intends", "plans", "believes", "seeks", "estimates", "projects", "forecasts", "continue", "may", "should", "will" variations of such words and similar expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements may include, without limitation, statements regarding our assessment on our internal control over financial reporting, our growth, our 2018 guidance, product development, product potential, financial performance, sales growth, product adoption, market awareness of our products, data validation, and our visibility at and sponsorship of conferences and educational events. The forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, which may cause results to differ materially from those set forth in the statements. Forward-looking statements in this Form 10-K should be evaluated together with the many uncertainties that affect the Company’s business and its market, particularly those discussed in the risk factors and cautionary statements in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including as described in “Risk Factors” included in Item 1A of this Form 10-K. Forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance, and actual results may differ materially from those projected. The forward-looking statements are representative only as of the date they are made, and the Company assumes no responsibility to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
General
We are a global leader in developing and marketing surgical solutions for peripheral nerves. We provide products and education to improve surgical treatment algorithms for peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity. Our portfolio of products includes Avance® Nerve Graft, an off-the-shelf processed human nerve allograft for bridging severed peripheral nerves without the comorbidities associated with a second surgical site, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a porcine submucosa extracellular matrix (“ECM”) coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed peripheral nerves, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect damaged peripheral nerves and reinforce the nerve reconstruction while preventing soft tissue attachments and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, a minimally processed human umbilical cord membrane that may be used as a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed. Along with these core surgical products, we also offer the AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System. These evaluation and measurement tools assist healthcare professionals in detecting changes in sensation, assessing return of sensory, grip and pinch function, evaluating effective treatment interventions, and providing feedback to patients on peripheral nerve function. Our portfolio of products is available in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and several European and other international countries.
Peripheral nerves provide the pathways for both motor and sensory signals throughout the body and physical damage to a perripheral nerve or the inability to properly reconnect nerves can result in the loss of muscle function and/or feeling. Nerves can be damaged in a number of ways. When a nerve is cut due to a traumatic injury or surgery, functionality of the nerve may be compromised, causing the nerve to no longer carry the signals to and from the brain to the muscles and skin and reducing or eliminating functionality. Nerve damage or discontinuity of this type generally requires a surgical repair. The traditional gold standard has been to either suture the nerve ends together directly without tension or to bridge the gap between the nerve ends with a less important nerve surgically removed from elsewhere in the patient’s own body, referred to as nerve autograft. Nerves that are not repaired or heal abnormally can form a complication called a neuroma which may send altered signals to the brain resulting in the sensation of pain. This abnormal section of nerve can, under certain circumstances, be surgically cut out and the resulting gap repaired. In addition, compression on a nerve, blunt force trauma or other physical irritations to a nerve can cause nerve damage that may alter the signal conduction of the nerve, result in pain, and may in some instances require surgical intervention to address the resulting nerve compression and inflammation.
In order to improve the options available for the surgical repair and regeneration of peripheral nerves, AxoGen has developed and licensed regenerative medicine technologies. AxoGen’s innovative approach to regenerative medicine has resulted in first-in-class products that it believes are redefining the peripheral nerve repair market. AxoGen’s products are used by surgeons during surgical interventions to repair a wide variety of physical nerve damage or discontinuity throughout the body, which can range from a simple laceration of a finger to a complex brachial plexus injury (an injury to the network of nerves that originate in the neck) as well as nerve injuries caused by dental, orthopedic and other surgical procedures. Avance® Nerve Graft provides surgeons an implant with the micro-architecture of a human nerve. This structure is essential and allows for bridging nerve gaps or discontinuities up to 70mm in length. Additionally, Avance® Nerve Graft has product and distribution synergies with AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. AxoGuard® products provide the unique features of pliability, suturability, and translucence for visualization of the underlying nerve, while also allowing the extracellular matrix to remodel utilizing the patient’s own cells. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is minimally processed human umbilical cord membrane that may be used as a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed.
Regenerative Medical Products Industry
Regenerative medical products enable the repair, restoration, replacement or regeneration of tissue or organ systems of the body. Regenerative medical products are becoming common in various medical arenas because they have been
shown to be effective repairing injured or defective tissues, such as bone, tendons, dermis and other tissues of the body. Surgeons utilize regenerative medical products because they can provide the complex structure required for implant integration and regeneration in the body.
AxoGen believes the primary driver of sustained growth in the regenerative medical product market is continued favorable efficacy as compared to autograft tissue and synthetic medical products, and a wider understanding of this advantage by practitioners. Repair with nerve autograft requires a secondary recovery procedure to remove tissue from another location of the patient’s body to repair the injured area and results in loss of function at the site of donation. Further, nerve autograft may also be costly and time consuming and may result in complications at the second surgical site such as infection. In addition to processed nerve allograft (Avance® Nerve Graft), alternatives to nerve autograft include hollow-tube synthetic or collagen-based medical products that are designed to provide some restoration of function but may be limited by mechanisms of nerve healing and/or biocompatibility with the body. Regenerative medical products often provide more desirable conditions for reconstruction and regeneration of tissue, creating a superior solution for patients and physicians. AxoGen follows this trend, providing regenerative medical products for peripheral nerve repair.
Regenerative medicine products typically consist of and rely on:
|
i.
| |
A scaffold or ECM to support the cells and/or provide the architecture of the tissue; and/or |
|
ii.
| |
Cells to regenerate or remodel the scaffold. |
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector are ECM scaffolds, and utilize the patients’ own cells to remodel or regenerate these scaffolds. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed.
Peripheral Nerves and Their Regeneration
The peripheral nervous system, or PNS, consists of nerves that either extend outside of, or reside outside of, the central nervous system (primarily the brain and spinal cord). Peripheral nerves provide the pathway for signals between the central nervous system and target organs, regulating movement (motor nerves) and touch (sensory nerves). Therefore, if a peripheral nerve is crushed, severed, or otherwise physically damaged, its ability to deliver signals to the target organs is eliminated, or significantly reduced, and could result in a loss of sensation and/or motor functionality. The axon portion of the nerve cell, consisting of cell cytoplasm and resembling a hair-like fiber, carries signals from the cell body to the target organ. Axons can be quite long, even exceeding one meter, but are only a few micrometers in diameter. A typical nerve consists of hundreds of axons that lie within long, thin tubes (endoneurial tubes). Analogous to a wiring cable, these endoneurial tubes are bundled together in groups called fascicles, and each nerve may contain numerous fascicles. This sheath structure provides protection for the axons and support for regeneration in the event of damage or discontinuity. Nerve damage or discontinuity occurs when a sufficient number of axons have been crushed or transected (severed), thereby disrupting signals to the target motor or sensory organ.
Given the right conditions, peripheral nerves have the ability to regenerate. Regenerating axons require the proper environmental conditions including structure and guidance of axons in a tension and compression free environment. In an untreated severe crush injury or transected nerve, errant axons that are not guided by the nerve sheath structure, or other mechanism, can form painful and ineffective nerve proliferation (neuromas). This can then require revision surgery to relieve pain or bring back sensory and/or motor functionality. Therefore, the surgical treatment of peripheral nerves due to damage or discontinuity is typically focused on restoring nerve functionality by providing structural guidance to regenerating axons while protecting the nerve to alleviate compression and tension.
Inflammation can impair tissue regeneration and result in irritation and compression of the nerve. Trauma and surgical interventions can trigger the body’s repair response which can result in inflammation in the surgical arena (nerve and/or surrounding tissue). When this occurs it can compromise the surgical outcomes of nerve repair. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulates inflammation in the surgical bed.
Peripheral Nerve Regeneration Market Overview
Peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity (“PND”) is a major source of physical disability impairing the ability to move muscles or to feel normal sensations. Failure to treat peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity can, in severe cases, lead to full loss of sensation and/or function, pain and, sometimes, amputation. Many peripheral nerve patients who receive treatment do not optimally recover. They may suffer from both reduced, or no, muscle strength, and reduced, or no, sensitivity and pain.
Every day patients suffer traumatic bodily injuries resulting in damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves severe enough to require surgical treatment, including injuries from motor vehicle accidents, power tool injuries, gunshot wounds, dislocations, fractures, lacerations, or other forms of penetrating trauma. The peripheral nerves commonly damaged or discontinued from these traumas include the digital, median, ulnar, radial, facial, spinal accessory and brachial plexus nerves. The “Extremity Trauma” portion of the Market (as defined below) encompases the traumatic PND described above but excludes the OMF, Carpal Tunnel and Breast (as such terms are defined below) portions of the Market.
Beyond the physical damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves resulting from traumatic bodily injury described above, peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity also occurs due to surgical intervention. Nerve damage or discontinuity can occur during dental and oral surgery procedures such as third molar extractions, placement of dental implants and removal of tumors during which one or more sections of the trigeminal nerve can be damaged or discontinued (“OMF”). This can result in numbness in certain areas of the face and mouth.
Breast reconstruction neurotization (“Breast”) is another portion of the Market. Currently, when a woman undergoes autologous breast reconstruction after a mastectomy, she receives the shape of a natural breast, but oftentimes without experiencing any sensory feeling. This forfeiture of sensation can have a profound effect contributing to quality of life issues such as depression and other emotional challenges. In certain cases sensation can be returned to the breast area with the use of the Company’s products through an innovative surgical technique called ReSensation™. The Company believes that the ideal Breast Reconstruction should restore Size, Shape, Symmetry, Softness and now, Sensation – without the potential risks and co-morbidity associated with autograft. The ReSensation™ technique incorporates the Company’s vision into a reproducible and efficient solution for reconstructive plastic surgeons.
Finally, peripheral nerves are also damaged due to compression injuries. For instance, severe and recurrent carpal tunnel cases may result in complications and damage to the peripheral nerve that requires surgical intervention and protection of the peripheral nerve. PND caused by recurrent carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome constitutes the “Carpal Tunnel” portion of the Market.
In the cases where a peripheral nerve is severed and the gap between its two ends is extremely small, the surgeon may be able to reconnect the peripheral nerve without tension through direct suturing using a coaptation aid (“Primary Repair”). When the gap in the nerve tissue is more than a few millimeters in length, the surgeon typically needs to use material to bridge the gap between the peripheral nerve ends to ensure a tension-free repair (“Gap Repair”). Historically for a Gap Repair surgeons have relied on a nerve autotransplantation (autologous nerve grafting or nerve autograft). In nerve autograft procedures, surgeons remove peripheral nerve from another part of the patient’s body, frequently the sural nerve from the back of the lower leg, to repair the damaged nerve. Nerve autografting is often effective in repairing a damaged peripheral nerve, but it presents a tradeoff — the surgeon can attempt to fix the damaged nerve but must create an additional nerve deficit at another location in the body. For example, a patient may opt to get movement and feeling back in their finger while losing some sensation in their foot. Additionally, the secondary surgery to obtain the needed nerve autograft also: (1) increases operating time, in a large hospital by potentially as much as 30 to 90 minutes, and thus medical expenses, we estimate by $3,200 to $9,500 per procedure, and (2) is estimated to result in a 27% complication rate due to surgical site infection, wound healing and chronic pain. In the case of extreme trauma where multiple peripheral nerves need to be repaired, it may not be possible to recover enough nerve from the patient to complete the Gap Repair. Further, nerve autograft tissue may not provide an appropriate diameter match with the diameter of the injured nerve stump, an important factor in a successful repair outcome.
Drawbacks of repair with autograft nerve eventually led to the development of hollow tube conduits, or hollow tube nerve cuffs for Primary Repair and Gap Repair made of, for instance, bovine collagen or polyglycolic acid. The nerve cuff is typically an absorbable hollow tube that, unlike natural peripheral nerve, does not have internal microarchitecture and endoneurial tubes to support regenerating axons; as a result, it is deficient in the qualities that natural peripheral nerve possesses to support nerve regeneration across a gap. Hollow-tubes may also lack pliability and structural integrity needed when used around joints and may be difficult to use in a confined space. Clinical data has demonstrated that hollow tubes are most effective when used in very short gaps, what AxoGen defines as Primary Repair, and the reliability of successful nerve recovery diminishes as gap length increases with a 34% to 57% failure rate for hollow tube conduits in repairs with a greater than 5mm gap. We aslo believe that the use of AxoGuard® Nerve Connector by surgeons could reduce surgery repair time by up to 40%, as compared to sucturing.
The shortcomings of hollow-tubes for peripheral nerve repair limit where they may be used effectively. Thus, AxoGen believes the peripheral nerve repair market needs an alternative off-the-shelf product that offer other features such as a natural ECM scaffold and three-dimensional structure of a typical nerve for bridging nerve discontinuities without the comorbidities of an additional surgical site required for harvest of autograft nerve tissue. AxoGen believes its Avance® Nerve Graft and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector products address the market needs for both Gap Repair and Primary Repair.
Compression on a peripheral nerve or blunt force trauma can also cause nerve damage that may require surgical intervention. In these cases, the peripheral nerve is not severed and thus does not create the need for a Primary or Gap Repair. However, the surgeon may want to protect and isolate the peripheral nerve during the healing process. In these situations peripheral nerve protection is provided by wrapping the nerve (“Nerve Protection”).
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is a porcine submucosa extracellular matrix used for Nerve Protection. Other Nerve Protection products are usually made from bovine collagen or polyglycolic acid and are typically absorbable. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector provides the unique features of pliability, suturability, and translucence for visualization of the underlying peripheral nerve, while also allowing the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and separate the peripheral nerve from the surrounding tissue.
Inflammation can impair tissue regeneration and result irritation and compression of the peripheral nerve. Trauma and surgical interventions can trigger the body’s repair response which can result in inflammation in the peripheral nerve and/or the surrounding tissue. When this occurs it can compromise the surgical outcomes of peripheral nerve repair. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane can be proactively used in these surgical applications (“Proaction”). Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane has been specifically designed as a soft tissue covering to modulate inflammation, provide a longer resorption profile to separate the tissue layers for at least 16 weeks and to provide the handling and suturability features the Company believes is favored by peripheral nerve surgeons.
We estimate the United States PND market for our current product portfolio for Extremity Trauma, OMF, Breast and Carpal Tunnel is $2.2 billion (the “Market”). From a product prospective as to these targeted markets, we estimate that Avance® Nerve Graft represents $976 million, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector $391 million, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector $433 million and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane $439 million.
We estimate that the Extremity Trauma portion of the Market is approximately $1.5 billion. The estimated size of the Extremity Trauma portion of the market is based upon epidemiological studies regarding the general number of trauma patients, physician interviews and incidence of PND in the population. We believe that each year in the U.S., more than 1.4 million people suffer damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves resulting in over 700,000 extremity nerve repair procedures (“Health”, United States, 2011, Publication of U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; Noble, et al. J of Trauma Injury Infection and Critical Care 1998; Kurt Brattain, MD, Magellan Medical Technology Consultants, Inc., Minneapolis, Minnesota 2013). We have estimated the portion of these extremity nerve repair procedures that would be addressed by our Gap Repair, Primary Repair, Nerve Protection and Proaction products and applied the average sales price of the appropriate product (Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, respectively) to determine that the probable market sizes. Within the Extremity Trauma portion of the Market, our Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector,
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane products are approximately $668 million, $161 million, $238 million and $439 million, respectively.
We estimate that the OMF portion of the Market is approximately $293 million, based upon research that has indicated approximately 80,350 PND occur in the U.S. each year that are related to benign tumor resections, third molar surgeries, anesthetic injections and dental implants. (The Prophylactic Extraction of Third Molars: A Public Health Hazard: Jay W. Friedman, DDS, Health Policy and Ethics; Peer Reviewed; Friedman American Journal of Public Health; September 2007, Vol 97, No. 9, pp 1554 — 1559 — Journal of Oral Implantology, Vol. XXXVI/No. Five/2010; “Inferior Alveolar Nerve Injury in Implant Dentistry: Diagnosis, Causes, Prevention, and Management”; Ahmed Ali Alhassani, BDS - “Nerve Injuries after Dental Injection: A Review of the Literature”; Clinical Practice, July/August 2006, Vol. 72, No. 6, Miller H. Smith, BMedSc, DDS; Kevin E. Lung, BSc, DDS, MSc, FRCD(C). McClary, et al., Ameloblastoma: a clinical review and trends in management. EurArch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jul;273(7):1649-61. Ruggiero, et al., American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons Position Paper on Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw-2014 Update. J Oral MaxillofacSurg72:1938-1956, 2014. Agbaje, et al., Systematic review of the incidence of inferior alveolar nerve injury in bilateral sagittal split osteotomy and the assessment of neurosensory disturbances. IntJ Oral MaxillofacSurg. 2015 Apr;44(4):447-51). We have applied the average sales price of the Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector that address such PND in order to derive the OMF portion of the Market.
According to market data, there are annually 307,660 breast cancer patients of which 113,834 result in a mastectomy. Of those mastectomy patients, every year more than 20,000 women choose autologous flap reconstruction as compared to implant based reconstructions. (2016 ASPS Plastic Surgery Statistics Reports from 2012 -2016 ASPS. Includes reconstructive revisions and reconstructions of large, breast-conserving surgeries (lumpectomy)). Removing those procedures that are not appropriate for neurotization, and based upon the Company’s assumption that 65% of women will elect to have a bilateral procedure, we estimate that the Breast portion of the Market is approximately $250 million. (2016 ASPS Plastic Surgery Statistics Reports, Includes TRAM, DIEP, and "Other Flaps", Distribution based on 2016 ASPS Data).
We estimate that the Carpal Tunnel portion of the Market is approximately $188 million, or 118,000 procedures. According to literature, there are approximately 500,000 primary carpal tunnel and 53,000 primary cubital tunnel relief surgeries performed annually in the U.S. For carpal tunnel, we estimate that our addressable market is the 20% of carpal tunnel surgeries that require revision procedures to address the recurrence of symptoms. From the 53,000 primary cubital tunnel surgeries, we estimate that our addressable market is 18,000 of such surgeries comprised of revision and primary interventions. As a result, we estimate that approximately 100,000 carpal tunnel revision surgeries and 18,000 total cubital tunnel procedures are addressable each year in the U.S. to mitigate the recurrence of symptoms. These revision and primary surgeries are required due to compression of the peripheral nerve due to soft tissue attachments from the surrounding tissue or tissue infiltration entrapping the nerve. To prevent additional recurrences, surgeons will opt to use a Nerve Protection product such as the AxoGuard® Nerve Protector. In order to derive the Carpal Tunnel portion of the Market, we multiplied the average sales price of our AxoGuard® Nerve Protector by the number of estimated procedures.
Although distribution and sales of products in the Extremity Trauma, OMF, Breast and Carpal Tunnel portions of the Market constitute our prime revenue sources today, market expansion opportunities in lower extremity surgery, head and neck surgery, urology and the surgical intervention for pain offer us new and expanded revenue opportunities. For example, we have developed the AxoGuard® NerveCap which is designed to protect a peripheral nerve end and separate the nerve from the surrounding environment to reduce the development of asymptomatic or painful neuromas (“Neuroma Management”). A neuroma is a tangled mass of disorganized nerve and fibrous tissue which, if not properly diagnosed and addressed, can require long term pharmacologic treatment and pain management. An example of the use of the AxoGuard® Nerve Cap is in the situation of a digital amputation whereby the nerves that are cut in the amputation may form a neuroma if the nerve end is not properly terminated or capped. We intend in 2018 to conduct clinical evaluation and user preference studies of the AxoGuard® Nerve Cap and define our marketing plan for Neuroma Management.
Lower limb/total join replacement (“TJR”) is another market opportunity. In the United states there are approximately 700,000 total knee replacements (“TKR”) per year and 310,000 total hip replacements (“THR”) per year.
We estimate that 6% of patients have neuropathic pain with TKR and THR and more than 60,000 have neuropathic pain post joint replacement. We believe if we proceed with entering this area in the future it would increase the Market for our products by approximately $125 million.
AxoGen’s Product Portfolio
Overview of AxoGen’s Products
AxoGen’s proprietary products and technologies are designed to overcome fundamental challenges in peripheral nerve repair. AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft is the alternative to autografts and other off-the-shelf peripheral nerve repair products for nerve gaps up to 70mm in length. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is a coaptation aid for transected peripheral nerve. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is a protective wrap for peripheral nerves damaged by compression, or where the surgeon wants to protect and isolate the peripheral nerve during the healing process after surgery. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane expands the surgical repair portion of the product portfolio and offers a resorbable covering to keep tissue structures apart while providing the known beneficial properties of placental membrane.
The AxoGen surgical solution product portfolio provides surgeons off-the-shelf products for a wide variety of peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity.
Functional measurements play an important role in the evaluation of peripheral nerve function by assisting the healthcare professionals in detecting changes in sensation or muscle strength, assessing return of sensory or motor function, establishing effective treatment interventions, and providing feedback to the patients Standardized evaluation and measurement of peripheral nerve function is also an important part of identifying nerve damage or discontinuity and determining treatment outcomes. AxoGen’s functional measurement products include the AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator tool (for sensory function) and the AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System (for sensory and motor function).
Avance® Nerve Graft
Avance® Nerve Graft is intended for the surgical repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities to support regeneration across the defect (a gap created when the nerve is severed). It is intended to act as a bridge in order to guide and structurally support axonal regeneration across a peripheral nerve gap caused by traumatic injury or surgical intervention. Avance® Nerve Graft is decellularized and sterile extracellular matrix (ECM) processed from human peripheral nerve tissue. AxoGen developed the Avance® Nerve Graft by following the guiding principle that the human body created the optimal peripheral nerve structure. AxoGen, through its licensing efforts and research, developed the Avance® process, a proprietary method for processing recovered human peripheral nerve tissue in a manner that preserves the essential structure of the ECM while cleansing away cellular and noncellular debris. Avance® Nerve Graft provides the natural peripheral nerve structure of an autograft and the ease and availability of an off-the-shelf product. AxoGen believes that Avance® Nerve Graft is the first off-the-shelf human nerve allograft for bridging nerve discontinuities. Avance® Nerve Graft is comprised of bundles of small diameter endoneurial tubes that are held together by an outer sheath called the epineurium. Avance® Nerve Graft has been processed to remove cellular and noncellular factors such as cells, fat, blood, axonal debris and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (“CSPG”), while preserving the three-dimensional laminin lined tubular bioscaffold (i.e. microarchitecture), epineurium and microvasculature of the peripheral nerve. After processing, Avance® Nerve Graft is flexible and pliable, and its epineurium can be sutured in place allowing for tension-free approximation of the proximal and distal peripheral nerve stumps. The design results in a product that has clean and clear pathways for the regenerating axons to grow through. During the healing process, the body revascularizes and gradually remodels the graft into the patient’s own tissue while allowing the processed peripheral nerve allograft to physically support axonal regeneration across the peripheral nerve discontinuity.
With lengths up to 70 mm and diameters up to 5 mm, the Avance® Nerve Graft allows surgeons to choose the correct length for repairing the relevant peripheral nerve gap, as well as to match the diameter to the proximal and distal end of the severed peripheral nerve. The Avance® Nerve Graft is stored frozen and utilizes packaging that maintains the graft in a sterile condition. The packaging is typical for medical products so the surgical staff is familiar with opening
the package for transfer of the Avance® Nerve Graft into the sterile surgical field. Such packaging also provides protection during shipment and storage and a reservoir for the addition of sterile fluid to aid in thawing the product. The Avance® Nerve Graft thaws in less than 10 minutes, and once thawed, it is ready for implantation.
The Avance® Nerve Graft provides the following key advantages:
|
·
| |
A three-dimensional bioscaffold for bridging a peripheral nerve gap; |
|
·
| |
No patient donor-nerve surgery, therefore no comorbidities associated with a secondary surgical site; |
|
·
| |
Available in a variety of diameters up to 5mm to meet a range of anatomical needs; |
|
·
| |
Available in a variety of lengths up to 70mm, to meet a range of gap lengths; |
|
·
| |
Decellularized and cleansed extracellular matrix that remodels into patient’s own tissue; |
|
·
| |
Structurally supports the body’s own regeneration process; |
|
·
| |
Handles similar to an autograft, and is flexible and pliable; |
|
·
| |
Alleviates tension at the repair site; |
|
·
| |
Three-year shelf life; and |
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is a coaptation aid used to align and connect severed peripheral nerve ends in a tensionless repair. The product is in a tubular shape with an open lumen on each end where the severed peripheral nerve ends are placed. It is typically used when the gap between the peripheral nerve ends is less than 5mm in length. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is made from a minimally processed porcine ECM which allows the body’s natural healing process to repair the peripheral nerve while its tube shape isolates and protects the discontinued nerves during the healing process. During healing, the patient’s own cells incorporate into the extracellular matrix product to remodel and form a tissue similar to the outermost layer of the peripheral nerve (nerve epineurium). AxoGuard® Nerve Connector is provided sterile, for single use only, and in a variety of sizes to meet the surgeon’s needs.
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector can be used:
|
·
| |
As an alternative to direct suture repair; |
|
·
| |
As a peripheral nerve coaptation; Connnector Assisted Repair™ |
|
·
| |
To aid coaptation in direct repair, grafting, or cable grafting repairs; and |
|
·
| |
To reinforce the coaptation site. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Connector has the following advantages:
|
·
| |
Minimally processed porcine submucosa extra-cellular matrix product used to repair severed peripheral nerve tissue; |
|
·
| |
Alleviates tension at the repair site; |
|
·
| |
Remodels into the patient’s own tissue instead of degrading; |
|
·
| |
Reduces the number of required sutures (versus direct repair with suture) allowing for up to 40% reduced surgery time (Boechstyns, Jhand Surg. 2013;38:2405-2411); |
|
·
| |
Moves location of sutures away from the coaptation face; |
|
·
| |
Reduces potential for fascicular mismatch; |
|
·
| |
Allows visualization of underlying peripheral nerve ends; |
|
·
| |
Provides a physical barrier preventing infiltraton of surrounding tissues into the coaptation site and the potential for axonal sprouting outside the coaptation site; |
|
·
| |
Available in seven different diameters and two different lengths to address a variety of nerve repair situations; |
|
·
| |
Strong and flexible, easy to suture; and |
|
·
| |
Stored at room temperature with a minimum of 18-month shelf life. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is a product used to protect and wrap damaged peripheral nerves and reinforce reconstructed nerve gaps while preventing soft tissue attachments. It is designed to protect and isolate the peripheral nerve during the healing process after surgery by creating a barrier between the nerve tissue and the surrounding tissue bed. The product is delivered in a slit tube format allowing it to be wrapped around peripheral nerve structures. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is made from a minimally processed porcine ECM. During healing, the ECM remodels allowing the protector to separate the peripheral nerve from the surrounding tissue. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector competes against off-the-shelf biomaterials such as reconstituted collagen as well as the use of the patients own tissue such as vein and hypothenar fat pad wrapping. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector is provided sterile, for single use only, and in a variety of sizes to meet the surgeon’s needs.
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector can be used to:
|
·
| |
Protect damaged peripheral nerves or nerve repair sites from surrounding tissue; |
|
·
| |
Minimize risk of soft tissue attachments and entrapment in compressed peripheral nerves; |
|
·
| |
Protect peripheral nerves in a traumatized wound bed; and |
|
·
| |
Reinforce a coaptation site. |
AxoGuard® Nerve Protector has the following advantages:
|
·
| |
Minimally processed Porcine submucosa bioscaffold used to reinforce a coaptation site, wrap a partially severed peripheral nerve or protect peripheral nerve tissue; |
|
·
| |
Creates a protective layer that isolates and protects the peripheral nerve in a traumatized wound bed; |
|
·
| |
Remodels into the patient’s own tissue instead of degrading; |
|
·
| |
Easily conforms and provides 360 degree wrapping of damaged peripheral nerve tissue; |
|
·
| |
Supports the body’s own natural wound healing; |
|
·
| |
Minimizes the potential for soft tissue attachments and peripheral nerve entrapment by physically isolating the nerve during the healing process; |
|
·
| |
Allows peripheral nerve gliding; |
|
·
| |
Strong and flexible, plus easy to suture; |
|
·
| |
Is available in five different widths and two different lengths to address a variety of peripheral nerve repair situations; and |
|
·
| |
Stored at room temperature with a minimum of 18-month shelf life. |
Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane
Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is minimally processed human umbilical cord membrane that may be used as a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed. Inflammation can impair tissue regeneration and result in irritation and compression of the nerve. Trauma and surgical interventions can trigger the body’s repair response which can result in inflammation in the surgical arena (peripheral nerve and/or surrounding tissue). When this occurs it can compromise the surgical outcomes of peripheral nerve repair.
For decades, the medical community has realized the beneficial qualities of human amniotic membrane and continues to utilize this natural tissue in applications across the body. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane offers a resorbable anatomical covering to keep tissue surfaces apart. Avive®Soft Tissue Membrane is provided sterile and in a variety of sizes to meet the surgeon’s surgical needs.
Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane:
|
·
| |
Serves as a permeable membrane to separate tissues in the surgical bed; and |
|
·
| |
Modulates inflammation in the surgical bed. |
Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane has the following advantages:
|
·
| |
Amniotic membrane that is naturally resorbable; |
|
·
| |
Minimally processed to preserve the natural properties of umbilical cord amniotic membrane; |
|
·
| |
Comprised of umbilical cord amniotic membrane which is up to eight times thicker than amniotic membrane alone; |
|
·
| |
Long lasting (in animal studies, stays in place for at least 16 weeks); |
|
·
| |
Easy to handle, suture or secure during a surgical procedure; |
|
·
| |
Conforms and stays in place at the application site; |
|
·
| |
Chorion Free (reducing the likelihood of immune response); and |
|
·
| |
Room temperature storage with a two-year shelf life. |
AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System
AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System is a device for evaluating patients with peripheral nerve conditions. We believe that an important step for improving patient outcomes is to support the standardized evaluation and measurement of peripheral nerve function. Today there is little consistency of measurement protocols. With the AcroVal® system examiners will have digital, less subjective results for their patients with conditions like peripheral neuropathy, peripheral nerve compression syndromes, and transected peripheral nerves. Ultimately, we believe that standardization of evaluation and measurement techniques will facilitate comparison and interpretation of clinical results leading to better understanding and care for patients with peripheral nerve conditions.
Dr. A. Lee Dellon, a world-renowned peripheral nerve expert, developed the peripheral nerve functional evaluation and measurement system over 25 years ago. We acquired the rights to his device in 2015 and launched the product in March 2016. The AcroVal® consists of three different devices designed to evaluate hand strength and neurosensory function:
|
·
| |
AcroGrip® - hand grip strength measurement; |
|
·
| |
AcroPinch® – pinch strength measurement; and |
|
·
| |
Pressure-Specified Sensory Device® (PSSD) – somatosensory evaluation and measurement device. |
AcroVal® can be used to assist healthcare professionals:
|
·
| |
In detecting changes in sensation, pinch strength or grip strength; |
|
·
| |
Assessing return of sensory or motor function; |
|
·
| |
Establishing effective treatment interventions; and |
|
·
| |
Providing feedback to patients. |
AcroVal® has the following advantages:
|
·
| |
Quantitative, electronic pre and post-intervention results; |
|
·
| |
Flexible format to allow for additional measurement devices; |
|
·
| |
Assessment of severity of nerve entrapment syndromes; |
|
·
| |
Reference database to provide baseline standards and support patient education. |
AxoTouch® Two Point Discriminator
The AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator tool can be used to measure the innervation density of any surface area of the skin. The discs are useful for determining sensation after damage to a peripheral nerve , following the progression of a repaired peripheral nerve, and during the evaluation of a person with possible peripheral nerve damage, such as division or compression.
The AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator tool is a set of two aluminum discs each containing a series of prongs spaced between two to 15 millimeters apart. Additionally, 20 and 25 millimeter spacing is provided. A circular depression on either side of the disc allows ease of rotation. The discs can be rotated between a single prong for testing one-point and any of the other spaced prongs for testing two-point intervals.
AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator has the following advantages:
|
·
| |
Capable of measuring the innervation density of any skin surface; |
|
·
| |
Portable and easy to use; |
|
·
| |
Strong aluminum design is resistant to bending; |
|
·
| |
Bright colors allow for clear discrimination between discs; |
|
·
| |
Clear numbering allows users to interpret results; and |
|
·
| |
Reusable carry case protects discs. |
Tissue Recovery and Processing for Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane
Avance® Nerve Graft Processing Overview
Over several years, AxoGen has developed the Avance® Process, an advanced and proprietary technique to process the Avance® Nerve Graft from donated human peripheral nerve tissue. The Avance® Process requires special training over several months for each manufacturing associate who processes Avance® Nerve Grafts. The processing and manufacturing system for Avance® Nerve Graft has required significant capital investment, and we plan to make additional investments to continually improve our manufacturing and quality assurance processes and systems. AxoGen’s Avance® Process is depicted as follows:
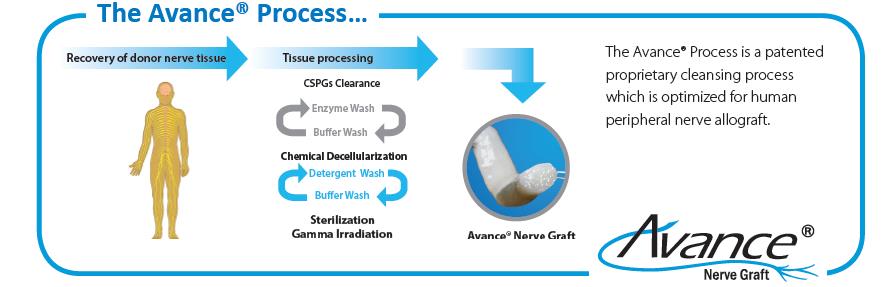
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane Processing
The AxoGen’s Avance® Process and SMART processing of Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane consists of several steps, including peripheral nerve tissue, in the case of Avance®, and umbilical cord, in case of Avive®, recovery and testing, donor medical review and release, processing, packaging, and sterilization to meet or exceed all applicable U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”), state, and international regulations and American Association of Tissue Banks (“AATB”) standards. We have a number of contracts with recovery agencies to supply peripheral nerve tissue and umbilical cord and believe these contracts, and the ability to enter into additional contracts, will provide us with the
tissues we require for our Avance® and Avive® products. As an FDA registered tissue establishment, AxoGen utilizes both its own personnel and a variety of subcontractors for recovery, storage, testing, processing and sterilization of the donated peripheral nerve and umbilical cord tissue. Additionally, independent certified laboratories have been contracted by AxoGen and its subcontractors to perform testing. The safety of Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is supported by donor screening, process validation, process controls, and validated terminal sterilization methods. The AxoGen Quality System has built in redundancies so that each product released for implantation meets our stringent quality control and product requirements.
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane Tissue Recovery and Processing Facility
AxoGen partners with FDA registered tissue establishments and AATB accredited recovery agencies or recovery agencies in compliance with AATB standards for human tissue recovery. After consent for donation is obtained, donations are screened and tested in detail for safety in compliance with the federal regulations and AATB standards on communicable disease transmission. AxoGen processes and packages Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane using its employees and equipment. From 2009 until February 2016 Avance® Nerve Graft processing and packaging was performed in a clean room facility at LifeNet Health, Virginia Beach, Virginia (“LifeNet Health”). Business requirements of LifeNet Health led to their need for additional space and they notified AxoGen that AxoGen would need to transition out of the Virginia Beach facility on or before February 27, 2016. On August 6, 2015 AxoGen entered into a License and Services Agreement (the “CTS Agreement”) with Community Blood Center (d/b/a Community Tissue Services) (“CTS”), Dayton, Ohio, an FDA registered tissue establishment. Processing of the Avance® Nerve Graft in the clean room facility pursuant to the CTS Agreement began in February 2016. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is now processed at CTS under the CTS Agreement.
The CTS Agreement is for a five-year term, subject to earlier termination by either party at any time for cause (subject to the non-terminating party’s right to cure, in certain circumstances), or without cause upon 18 months prior notice. Under the CTS Agreement AxoGen pays CTS a facility fee for clean room/manufacturing, storage and office space. CTS also provides services in support of AxoGen’s manufacturing such as routine sterilization of daily supplies, providing disposable supplies, microbial services and office support. The service fee is based on a per donor batch rate. The CTS facility provides a cost effective, quality controlled and licensed facility. However, AxoGen could reproduce a manufacturing space that would meet its needs if it no longer continued its relationship with CTS. AxoGen’s processing methods and process controls have been developed and validated to ensure product uniformity and quality. Pursuant to the CTS Agreement, AxoGen pays license fees on a monthly basis to CTS which total an annual amount of approximately $1.4 million.
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane Packaging
After processing, each Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is visually inspected and organized by size into finished product codes. It is then packaged in primary packaging. The outer pouch is the primary sterility and moisture barrier. The packaging operation is performed in a controlled environment at CTS.
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane Sterilization and Labeling
After being processed and packaged, Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane are then terminally sterilized and shipped to AxoGen’s Burleson, Texas distribution facility (the “Distribution Facility”). There the products receive their final labels and are released following a final stringent technical and quality review. Orders for Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane are placed with AxoGen’s customer care team and the products are packaged and shipped from the Distribution Facility.
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane Product Release
The AxoGen Quality System meets the requirements set forth under 21 CFR Part 1271 for Human Cells, Tissues and Cellular and Tissue-Based Products, including Good Tissue Practices (“GTP”) and is compliant with the 21 CFR Part 820 Quality System Regulations (“QSR”). AxoGen has established quality procedures for review of tissue recovery, relevant donor medical record review and release to processing that meet or exceed FDA requirements as
defined in 21 CFR Part 1271, state regulations, international regulations and AATB standards. Furthermore, AxoGen utilizes validated processes for the handling of raw material components, environmental control, processing, packaging and terminal sterilization. In addition to ongoing monitoring activities for product conformity to specifications and sterility, shipping methods have been validated in accordance with applicable industry standards.
Manufacturing of AxoGen Products Other Than Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane
Manufacturing for the AxoGuard® Product Line
AxoGuard® is manufactured by Cook Biotech Incorporated, West Lafayette, Indiana (“Cook Biotech”), which was established in 1995 to develop and manufacture tissue grafts utilizing porcine extracellular matrix technology. AxoGen decided to expand its portfolio of products and felt that the unique ECM material offered by Cook Biotech provided the combination of properties needed in nerve reconstruction. Cook Biotech’s ECM material is pliable, capable of being sutured, translucent and allows the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel and form a tissue similar to the nerve’s epineurium. Cook has its own source of the raw material for the ECM material and manufactures AxoGuard® products from such source. In August 2008, Cook Biotech entered into an agreement, amended in March 2012, with AxoGen to distribute its product worldwide in the field of the peripheral and central nervous system, but excluding use of the AxoGuard® product in the oral cavity for endodontic and periodontal applications and OMF surgery solely as they relate to dental, soft or hard tissue repair or reconstruction. We believe the exclusion does not limit our identified OMF market, but expansion into certain additional OMF market areas could be limited to the Avance® Nerve Graft.
The Cook Biotech agreement was amended on February 26, 2018 to run through June 30, 2027. It requires certain minimum purchases, although through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforced such provision, and establishes a formula for the transfer cost of the AxoGuard® products. Under the agreement, AxoGen provides purchase orders to Cook Biotech, and Cook Biotech fulfills the purchase orders.
Manufacturing for the AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System and AxoTouch®Two Point Discriminator
The AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System and AxoTouch® Two Point Discriminator are contract manufactured by Viron Technologies, doing business as Cybernetics Research Laboratories (“CRL”), Tucson, Arizona. CRL provides the AcroVal® to the Company’s Distribution Facility and AxoGen performs final inspection and packaging for customer shipment. CRL provides warranty service on behalf of the Company for the AcroVal® and maintains certain levels of spare parts inventory for manufacturing and fulfillment of warranty work. CRL supplies the AxoTouch unpackaged and it is packaged at the Distribution Facility.
We believe CRL has capacity to support any future volumes of AcroVal® and AxoTouch®.
Sales and Marketing
Overview
AxoGen is focused on the developing market of peripheral nerve repair and regeneration, is committed to improving awareness of new surgical peripheral nerve repair options and is advancing evaluation capabilities for nerve issues, as well as building additional scientific and clinical data to assist surgeons and patients in making informed choices with respect to treatment of peripheral nerve injuries. AxoGen believes that there is an opportunity to rethink current approaches to peripheral nerve repair and that its approach will solidify its position as a leader in the field of peripheral nerve repair products. The following provides the key elements of AxoGen’s sales and marketing strategy.
Increase Awareness of AxoGen’s Products
Prior to the introduction of AxoGen’s portfolio of peripheral nerve repair products, surgeons had a limited number of options available for the surgical repair of damaged or discontinued peripheral nerves. AxoGen entered the market to
improve the standard of care for patients. AxoGen intends to increase market share by improving awareness and adoption of nerve repair techniques and AxoGen’s products through the continued use of educational conferences and presentations, surgical resident and fellow training, scientific publications, and a knowledgeable and professional sales team. AxoGen works to increase usage within active accounts as well as expand the overall customer base by adding new active accounts. AxoGen defines an “active account” as an account that has ordered one or more of AxoGen’s surgical products six or more times in the last twelve months. AxoGen is focused on plastic reconstructive surgeons and orthopedic and plastic hand surgeons who perform surgeries on patients suffering traumatic nerve damage or discontinuity and who perform hand reconstructive surgeries, certain OMF surgeons who repair damaged oral nerve and certain surgeons who perform autologous flap breast reconstruction.
Expand Clinical and Scientific Data Regarding the Performance of AxoGen Products
Generating clinical data is an important component of AxoGen’s marketing strategy. To date AxoGen has fifty-three peer reviewed clinical papers. Forty-five of such clinical papers relate to our Avance® Nerve Graft and eighteen to our AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector products. Certain of these publications contain data on multiple products. AxoGen will continue to accept patients, for which there are more than 1,300 Avance® nerve repairs enrolled to date, in its RANGER® clinical study (defined below in “Government Regulations”), a utilization registry of Avance® Nerve Graft. Five of the above mentioned publications and more than 50 scientific conference presentations have been generated to date from the registry. A multicenter prospective randomized comparative pilot study of hollow tube conduits and Avance® Nerve Graft has completed subject enrollment and outcome follow-up. A pivotal multicenter prospective randomized comparative pilot study of hollow tube conduits and Avance® Nerve Graft to support the transition to a BLA is currently enrolling. Case series in digital nerve repair have been published from the Mayo Clinic, Georgetown University Medical Center and Philadelphia Hand Center and a case series in OMF have been published from UT Southwestern and University of Illinois-Chicago. A number of additional investigator initiated case reports, studies and publications have been completed. A pilot study on the repair of the cavernous nerves in prostate cancer patients has completed enrollment, follow-up and data analysis . Case series in brachial plexus, military trauma, neurotization of breast reconstruction and compressive neuropathy are also being developed. AxoGen also supports outside research and will continue to work with investigators working on grants with a translational focus.
Commitment to the Education of Best Practices in Peripheral Nerve Repair
AxoGen has established educational conferences and presentations and surgical resident and fellow training that we believe is positioning us as a leader in providing peripheral nerve repair best practices. In 2018, we expect to train two-thirds of hand surgeon fellows through such courses and training. The Company provides education on peripheral nerve repair through its “Best Practices in Nerve Repair” national programs (“National Programs”) as well as local and regional educational events. In calendar years 2015, 2016 and 2017, we conducted 9, 13 and 15 National Programs, respectively, and we expect to conduct 18 National Programs in 2018. These are supported by on-line tools and discussion forums such as Nerve Matters, an on-line community of peripheral nerve surgeons where the surgeons can ask questions, present cases and share findings in the area of peripheral nerve repair.
Execute the Sales Process and Expand the AxoGen Sales Team
AxoGen provides full sales and distribution services through both a direct sales force and a team of independent distributors. As of December 31, 2017, AxoGen had 60 direct sales professionals and 20 independent distributors in the U.S. By the end of 2018, AxoGen anticipates the number of direct sales professionals in the U.S. will be more than 75. AxoGen’s products are available in eleven countries outside the U.S. through nine independent distributors. AxoGen provides support and resources for independent distributors both within and outside the United States and is increasing its direct sales force in selected United States territories. AxoGen provides its products to hospitals, surgery centers and military hospitals, calling on plastic reconstructive surgeons and orthopedic and plastic hand surgeons and certain OMF surgeons to review the benefits of the AxoGen products. While surgeons make the decision to implant the products in appropriate patients, hospitals make the decision to buy the products from AxoGen. In today’s budget constrained environment, hospital committees review new technologies for cost effectiveness as well as quality. AxoGen believes that it has been successful in meeting the needs of these hospital committees by demonstrating the cost/benefit of its products and providing a fair value to the hospital.
Expand the Product Pipeline and Applications in Peripheral Nerve Repair
AxoGen has developed line extensions and additional products to support surgeons in their needs for repairing damaged or discontinued peripheral nerves. AxoGen believes additional opportunities exist to develop or acquire complementary products in peripheral nerve repair. In addition, there exists opportunities to expand the existing portfolio of products in new applications of peripheral nerve repair in lower extremity surgery, head and neck surgery, urology and the surgical intervention for pain.
AxoGen Strengths
AxoGen believes that it has the following strengths in the field of peripheral nerve repair and regeneration:
Established Peripheral Nerve Repair Expertise
AxoGen has made a significant investment in understanding peripheral nerve anatomy and surgical peripheral nerve repair and regeneration. This has been accomplished through interaction with leading academic centers throughout the United States and by striving to build an outstanding internal team of technical and clinical experts.
Commitment to the Promotion and Education of Best Practices in Peripheral Nerve Repair
AxoGen has established educational conferences and presentations and surgical resident and fellow training that we believe is positioning us as a leader in providing peripheral nerve repair best practices. AxoGen has developed the programs and speakers to train surgeons currently in practice as well as surgical fellows.
Surgical Implant Commercialization Experience
The AxoGen commercialization team consists of sales, marketing, and customer care professionals with backgrounds in the medical device and biotechnology industries. The team has strong experience in the introduction of technologies and has been instrumental in beginning to establish the Avance® Nerve Graft and the AxoGuard® product lines as a new standard of care for the surgical treatment of peripheral nerve damage or discontinuities in our core markets. AxoGen believes it can leverage these capabilities in expanding the commercial success of the current AxoGen products and future product opportunities such as the Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane and in new surgical applications.
Avance® Nerve Graft Performance
AxoGen has worked with leading institutions, researchers and surgeons to support innovation in the field of surgical peripheral nerve repair. We believe AxoGen’s RANGER® study (defined below in the section entitled “Government Regulations”) is the largest multi-center clinical study conducted in peripheral nerve gap repair. AxoGen is also conducting a Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Subject and Evaluator Blinded Comparative Study of Nerve Cuffs and Avance® Nerve Graft Evaluating Recovery Outcomes for the Repair of Nerve Discontinuities (“RECON”). This study is the phase 3 trial to support its Biologics License Application (“BLA”) for the Avance® Nerve Graft. (See “Government Regulations”). The January, 2012 edition of Microsurgery and November 2012 edition of The Journal of Hand Surgery, June 2015 edition of Journal of Reconstructive Microsurgery and January 2017 edition of HAND each contain an article summarizing the RANGER® study results. The Brooks et al. publication reported on 55 Avance® Nerve Graft nerve repairs and resulted in meaningful motor and sensory recovery in 87% of nerve discontinuities between 5 and 50 mm. Additionally, no implant related adverse events were reported. (Brooks, D. N., Weber, R. V., Chao, J. D., Rinker, B. D., Zoldos, J., Robichaux, M. R., Ruggeri, S. B., Anderson, K. A., Bonatz, E. E., Wisotsky, S. M., Cho, M. S., Wilson, C., Cooper, E. O., Ingari, J. V., Safa, B., Parrett, B. M. and Buncke, G. M. (2012), Processed nerve allografts for peripheral nerve reconstruction: A multicenter study of utilization and outcomes in sensory, mixed, and motor nerve reconstructions. Microsurgery, 32: 1—14. doi: 10.1002/micr.20975 and Cho, et al. 2012, J Hand Surg Am 37(11):2340-9). A meta-analysis of available clinical outcomes data from published papers on the leading synthetic collagen conduit showed meaningful improvement in only 40-74% of cases bridging a gap in the nerve. This data was further verified in a review of autograft alternative in the 2016 edition of Hand Clinics. A similar meta-analysis for
nerve autograft reported meaningful improvement in 60-88% of nerve repairs. Finally, the Company expanded RANGER® to include an additional study arm called Sensation-NOW™ for breast neurotization.
International Opportunity for Revenue
AxoGen currently focuses on the U.S. market, with additional foreign distribution and sales in Canada, United Kingdom and certain other countries. The need for the surgical repair of damaged or discontinued nerves is a global issue. Through its ex-U.S. revenue, AxoGen has shown the capability to take its current peripheral nerve repair product offering into new geographical markets. AxoGen does not currently have European Union (“E.U.”) wide approval for Avance® Nerve Graft, but the AxoGuard® products currently have a CE Mark and can be sold in the E.U. and affiliated countries. The Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System and AxoTouch® Two Point Discriminator are only available in the United States, but AxoGen is taking action to introduce them internationally, which introduction is subject to meeting the appropriate regulatory standards of a particular country. To date, revenue from international distribution and sales have not been material, there are no material risks associated with foreign operations and we do not have dependencies as to international revenue. See Risk Factors - AxoGen’s operations must comply with FDA and other governmental requirements.
Research and Development
AxoGen believes it provides the most extensive product portfolio for peripheral nerve repair available. Our current development focus is to expand clinical data in both traumatic peripheral nerve repair and other surgical applications. Additional product line extensions of the Avance® and AxoGuard® products and other peripheral nerve repair products may be developed. In this regard, AxoGen introduced: (1) an AxoGuard® Connector line extension in winter 2014 by providing a new longer 15mm product; (2) AxoTouch® in the fall of 2014; (3) AcroVal® in March 2016 and (4) Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane launched in November 2016. AxoGuard® Nerve Cap has been developed and the Company has obtained 510(k) premarket clearance from the FDA. Future user handling and clinical work will be completed prior to the full introduction of the product.
AxoGen works with academic institutions in the expansion of treatments for peripheral nerve and is involved in a number of grants from government agencies related to nerve repair or use of our products and/or technologies. For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, AxoGen spent approximately $6.7 million, $4.2 million and $3.2 million, respectively, on research and development expenses and recognized grant revenue of approximately $56,000 $290,000 and $433,000, respectively.
Competition
The medical device and biotechnology industries are characterized by rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition and a strong emphasis on proprietary products. As such, AxoGen cannot predict what products may be offered in the future that may compete with AxoGen’s products. With regard to peripheral nerve function evaluation and measurement there are a number of methods and techniques with little consistency of measurement protocols. Currently as to peripheral nerve repair products, AxoGen competes primarily against all transected and non-transected peripheral nerve repair approaches including direct suture repair, autograft and hollow-tube nerve conduits and materials used to wrap and protect damaged peripheral nerve tissue. Finally, there are numerous companies that offer amnion products in a variety of formats, primarily in the area of wound care, which could be competitive with AxoGen’s Avive® product.
Because the requirements of the biomaterials used in peripheral nerve repair can vary based on the severity and location of the damaged nerve, the size and function of the nerve, surgical technique and patient preference, AxoGen’s peripheral nerve repair products compete against both autograft materials (nerve in the case of a bridging repair and vein or fat in the case of a nerve protection repair), and a limited number of off-the-shelf alternatives for grafting and protecting. Competitive aspects of our products focus on the overall value proposition of our products and their suitability for specific applications and can include composition and structure of the material, ease of use, clinical evidence, handling, and price. AxoGen’s major competitors for off-the-shelf repair options in hollow-tube conduits and bio-absorbable wraps are the following companies:
|
·
| |
Integra LifeSciences Holding Corporation (NASDAQ: IART) (“Integra”). Integra offers NeuraGen®, a hollow tube product made from reconstituted bovine collagen and NeuraWrapTM, a reconstituted bovine collagen biomaterial used for nerve wrapping; |
|
·
| |
Baxter International, Inc. (NYSE: BAX) (“Baxter”). Baxter acquired Synovis which offers Neurotube, a hollow tube made of polyglycolic acid; and |
|
·
| |
Stryker Corporation (NYSE: SYK) (“Stryker”). Stryker offers the NeuroMatrix and Neuroflex products, both of which are hollow tubes derived from reconstituted bovine collagen and NeuroMend, a reconstituted bovine collagen biomaterial used for nerve wrapping. |
AxoGen believes that surgeons use Avance® Nerve Graft because it provides them with the natural three-dimensional structure and familiar handling characteristics of a typical peripheral nerve for bridging peripheral nerve discontinuities (severed peripheral nerves) without the comorbidities and additional surgical site of an autograft as well as confidence in the performance of the product as a result of the growing body of clinical literature. AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector provide the unique features of pliability, suturability, and translucence for visualization of the underlying nerve while also allowing the patient’s own cells to incorporate into the extracellular matrix to remodel. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane expands the surgical repair portion of the product portfolio and is a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed. The AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System is a continuation of AxoGen’s commitment to improving patient outcomes. AxoGen believes that the standardization of evaluation and measurement techniques will facilitate comparison and interpretation of clinical results leading to better understanding and care for patients with peripheral nerve damage.
AxoGen believes any current or future competitors face the following important barriers to entry as it relates to the market for its peripheral nerve repair products. AxoGen’s intellectual property (“IP”), and that of its partners, including patents, patents-pending and know how, is believed to be an important barrier for its Avance® Nerve Graft and AxoGuard® products. AxoGen has developed knowledge and experience in understanding and meeting FDA regulatory requirements for Avance® Nerve Graft, including having made a substantial investment in conducting the preclinical and clinical testing necessary to support a submission for a FDA BLA. Additionally, AxoGen believes the ability to offer a portfolio of products focused on peripheral nerve repair and evaluation provides a unique competitive position as to other entities that do not have this breath of product offering. However, due to its limited resources, its smaller size and its relatively early stage, AxoGen believes it may face competitive challenges from larger entities and barriers that are difficult to overcome and could negatively impact its growth, including introduction of new products and bundling of products to achieve pricing benefits by our competitors.
Intellectual Property
Overview
AxoGen relies on a combination of patent, trademark, trade secret, and copyright, as well as other IP laws, to protect its IP rights. In addition, AxoGen utilizes license, non-disclosure, and assignment agreements to protect these IP rights. Specifically, AxoGen requires vendors, contract organizations, consultants, advisors and employees to execute nondisclosure agreements. AxoGen also requires consultants, advisors and employees who develop IP to assign to AxoGen any of their rights to all IP conceived in connection with their relationship with AxoGen.
License Agreements
AxoGen has entered into license agreements with University of Florida Research Foundation (the “UFRF”) and the University of Texas at Austin (“UTA”). Under the terms of these license agreements, AxoGen has exclusive worldwide licenses for the underlying technologies used by AxoGen in its Avance® Nerve Graft. The license agreements include both the right to issued patents and patents pending in the U.S. and international markets. The effective term of the license agreements extends through the term of the related patents. In the event of default, licensors may also terminate an agreement (after written notice) if AxoGen fails to cure a breach. The license agreements contain the following key terms:
|
·
| |
Payment of annual license maintenance fees, some of which may be credited against future royalty payments; |
|
·
| |
Payment of royalty fees of 1%-3% based on net revenue of the licensed products, the level depending on the agreement, which may include a minimum quarterly royalty payment with discounts off royalty rates when royalty stacking applies; |
|
·
| |
Payment of a percentage of sublicense fees received; |
|
·
| |
Reimbursement of certain legal expenses incurred for patent prosecution and defense; and |
|
·
| |
Other payments of various amounts based on achieving certain milestones. |
Currently, AxoGen pays royalties to UFRF and UTA specific to the licensed technologies related to the Avance® Nerve Graft.
Patents
As of the date of this Form 10-K, AxoGen owned or was the exclusive licensee of nine issued U.S. patents, six pending U.S. patent applications and multiple international patents and patent applications with regard to its peripheral nerve products. The granted European Patent No. EP1425390 has been validated in France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom. The following table illustrates the issued U.S. patents owned or licensed by AxoGen with regard to its peripheral nerve products, including the patent number, a description of each patent, and the estimated expiration date of each patent.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Patent No.
|
|
Description
|
|
Estimated expiration date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 6,972,168
|
|
Materials and Methods for Nerve Grafting, Selection of Nerve Grafts, and in vitro Nerve Tissue Culture
|
|
August 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 7,402,319
|
|
Cell Free Tissue Replacement for Tissue Engineering
|
|
September 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 7,732,200
|
|
Materials and Methods for Nerve Grafting, Selection of Nerve Grafts, and in vitro Nerve Tissue Culture
|
|
December 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 6,696,575
|
|
Biodegradable, electrically conducting polymer for tissue engineering applications
|
|
March 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 7,851,447
|
|
Materials and Methods for Nerve Repair
|
|
November 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 8,545,485
|
|
Nerve Elevator and Method of Use
|
|
May 2032
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 8,758,794
|
|
Cell Free Tissue Replacement for Tissue Engineering
|
|
September 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 8,986,733
|
|
Materials and Methods for Nerve Repair
|
|
August 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US D777,917
|
|
Two Point Discriminator Sensory Measurement Device
|
|
January 2032
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 9,690,975
|
|
Quantitative Structural Assay of a Nerve Graft
|
|
July 2035
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 9,572,911
|
|
Method for Decellularization of Tissue Grafts
|
|
March 2034
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
US 9,629,997
|
|
Materials and Methods for Protecting Against Neuromas
|
|
December 2033
|
With respect to our Avance® Nerve Graft we have patent protection through September 2023 in the United States. In addition we also expect it will receive Biosimilar Protection that could provide an additional 12 years of exclusivity. Finally, AxoGen has Enforcement Discretion from FDA allowing continued sales under controls applicable to Human Cellular and Tissue-based Products (“HCT/P”) with an agreed transition plan to a Biologic Product under a Biologic License Application (“BLA”). We believe a competitive processed peripheral nerve allograft would need to complete a BLA Phase I, II and III clinical study prior to clinical release which we believe would take approximately 8 years.
Additionally, AxoGen entered into an exclusive distribution agreement with Cook Biotech in August 2008, as subsequently amended in February 2018, to distribute its ECM technology in the form of the Surgisis® Nerve Cuff, the form of a nerve wrap or patch, or the form of any other mutually agreed to configuration in the field of peripheral nervous system and central nervous system use, but excluding use of the AxoGuard® product in the oral cavity for endodontic and periodontal applications and OMF surgery solely as they relate to dental, soft or hard, tissue repair or reconstruction. AxoGen has subsequently rebranded the Surgisis products under the AxoGuard® name. Cook Biotech believes it has know-how and trade secrets with respect to the ECM technology that provides certain competitive obstacles.
Because of the length of time and expense associated with bringing new products through development and the governmental approval process, medical technology companies have traditionally placed considerable importance on obtaining and maintaining patent protection for significant new technologies, products and processes. AxoGen intends to seek patent protection for appropriate proprietary technologies by filing patent applications when possible in the U.S. and selected other jurisdictions. AxoGen’s policy is to seek patent protection for the inventions that it considers important to the development of its business. However, in some cases patent protection is not possible, but product value to AxoGen’s portfolio can still be derived. AxoGen also intends to use its scientific expertise to pursue and file patent
applications on new developments with respect to uses, methods, and compositions to enhance its IP position in the areas that are important to the development of its business.
Trademarks, Trade Secrets, Copyrights and Domain Names
AxoGen has registered and filed numerous trademark applications with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and appropriate offices in foreign countries in order to distinguish its products from competitors’ products. It possesses trade secrets and material know-how in the following general subject matters: nerve and tissue processing, nerve repair, product testing methods, and pre-clinical and clinical expertise. AxoGen has registered copyrights for training tools and artistic renderings. It has entered into an agreement with an independent artistic creator, under which the artistic director retains copyright rights to any copyrighted material under agreement with AxoGen and provides AxoGen a license to such copyrights.
Government Regulations
U.S. Government Regulation Overview
AxoGen’s products are subject to regulation by the FDA, as well as other federal and state regulatory bodies in the U.S. and comparable authorities in other countries. In addition, its Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane must comply with the standards of the tissue bank industry’s accrediting organization, the AATB.
AxoGen distributes for Cook Biotech the AxoGuard® product line. Cook Biotech is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the AxoGuard® product line. AxoGuard® products are regulated as medical devices and subject to premarket notification requirements under section 510(k) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FD&C Act”), 21 CFR Part 820 (“Quality System Regulation”) and related laws and regulations. Cook Biotech has obtained a 510(k) premarket clearance from the FDA for the use of porcine (pig) small intestine submucosa for the repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities where gap closure can be achieved by flexion of the extremity. Cook Biotech has also obtained a 510(k) premarket clearance for the AxoGuard® Nerve Protector for the repair of peripheral nerve damage in which there is no gap or where a gap closure is achieved by flexion of the extremity. We sell the 510(k) cleared device under the trade name AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector.
AxoGen is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. The Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is processed and distributed in accordance with FDA requirements for Human Cellular and Tissue-based Products (HCT/P) under 21 CFR Part 1271 regulations, US State regulations and the guidelines of the AATB.
AxoGen also distributes the AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator. This device that is manufactured for AxoGen and distributed from the Burleson Facility is a Class I device (general controls) that is exempt from premarket notification and the Quality System Regulation requirements except for the Recordkeeping and Complaint file requirements. It is classified by FDA under 21 CFR 882.1200 (Two-point discriminator, product code: GWI).
The AcroVal® line of devices is manufactured for AxoGen and distributed from the Burleson Facility. The AcroVal® devices are regulated as medical devices and are subject to premarket notification requirements under section 510(k) of the FD&C Act. The AcroVal® line of devices includes the AcroGrip®, AcroPinch® and PSSD®, all of which received 510(k) clearance by the FDA in the 1990’s. The AcroGrip® was cleared under the name Digi-Grip Sensor, the AcroPinch®was cleared as Pinch Sensor and PSSD® as the NK Pressure-Specified Sensory Device.
In 2007, AxoGen began to process and distribute its Avance® Nerve Graft pursuant to Section 361 of the PHS Act and 21 CFR Part 1271 Human Cells, Tissues, and Cellular and Tissue Based Products controls. Such action was based on AxoGen’s good faith belief that the Avance® Nerve Graft product was a HCT/P tissue product regulated solely under Section 361. From October 2008 through early 2010, AxoGen was in communication with the FDA concerning the regulatory status of the Avance® Nerve Graft product. In April 2010, in response to a Request For Designation filed by AxoGen, the FDA determined that the Avance® Nerve Graft was a biologic product that would be reviewed and regulated by CBER under the requirements of Section 351 of the PHS Act. Section 351 requires, among other things, an approved license to market a biological product.
AxoGen met with CBER in July 2010 and, between July 2010 and November 2010, provided information to CBER that resulted in the FDA issuing a letter stating the agency’s intent to exercise enforcement discretion with respect to the introduction or delivery for introduction into interstate commerce of the Avance® Nerve Graft assuming that certain conditions are met relating to the transition of the Avance® Nerve Graft from regulation as a HCT/P to a biological product under section 351 of the PHS Act. Specifically, the FDA is permitting the Avance® Nerve Graft to be distributed, subject to FDA enforcement discretion, provided that:
|
·
| |
AxoGen transitions to compliance with Section 501(a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act, the current Good Manufacturing Practice, or cGMP, regulations in 21 CFR Parts 210 and 211 and the applicable regulations and standards in 21 CFR Parts 600-610 prior to initiation of a phase 3 clinical trial; designed to demonstrate the safety, purity, and potency of the Avance® Nerve Graft. |
|
·
| |
AxoGen has performed several gap analyses of its quality system for compliance with 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 regulations. The gap analyses have identified areas in which our quality system could improve with respect to compliance to the regulations. The transition is in process and we periodically review the 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 regulations to ensure that we create and implement appropriate changes, including new quality procedures. Through our internal auditing process, we periodically assess our compliance to the regulations. As AxoGen initiates the phase 3 clinical trial and eventual BLA submission, we will retain an external audit firm with experience in auditing to 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 regulations to verify quality system compliance to the regulations. The associated costs for these activities are not material and the Company believes it can appropriately implement all necessary changes. |
|
·
| |
AxoGen conducts a phase 3 clinical trial to demonstrate safety, purity and potency of the Avance® Nerve Graft under a Special Protocol Assessment (“SPA”). |
|
·
| |
AxoGen and the FDA agreed to the SPA in August 2011 and in accordance with FDA regulations in 21CFR § Part 312, AxoGen submitted an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”) to the FDA in April 2013. The IND became effective in March 2015 and the phase 3 clinical trial was initiated in the second quarter of 2015. |
|
·
| |
AxoGen continues to comply with the regulations and standard for 21 CFR Part 1271. |
|
·
| |
AxoGen was audited by the FDA at its processing facility in March 2013, March 2015 and October 2016 and its Distribution Facility in October 2015. The quality system was found to be in compliance with 21 CFR Part 1271 and no FDA Form 483 observations were issued. |
|
·
| |
In February 2018. AxoGen was audited by the FDA with respect to its Medical Device Quality System under 21 CFR Part 820 and its Human Tissue Quality System under 21 CFR Part 1271. Such audit resulted in two Form 483 observations on general procedures on the Medical Device regulations and no Form 483 observations as to the Human Tissue Quality System. AxoGen is taking necessary action to correct these observations and does not anticipate any issues with respect to such corrections. |
|
·
| |
AxoGen continues to exercise due diligence in executing its requirements under the transition program. |
|
·
| |
In February 2018 AxoGen conducted a periodic review of applicable state-based permits, licenses and registrations that could be applicable to its operations at its Dayton, Ohio and Burleson, Texas facilities. The Company has determined that its Burleson distribution facility should be appropriately registered as such with respect to the Company’s AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector Products in Washington, D.C., Montana, New York and Utah. The Company is taking the necessary action to complete these registrations and does not anticipate any issues with respect to such registrations. |
AxoGen is working to ensure compliance with the applicable regulations through ongoing discussions with the FDA regarding the transition of the quality system to 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 regulations with the FDA and through audits for compliance to 21 CFR Part 1271 and amendments to the IND providing updates to the phase III clinical trial. The final determination of regulatory compliance will be made by the FDA during the pre-license inspection as part of the BLA review. If the FDA does not find AxoGen to be in compliance, or if AxoGen is unable to meet the required standards for preclinical studies, clinical studies and Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls, the approval of the BLA would become impossible or delayed.
The FDA will end the period of enforcement discretion upon a final determination of AxoGen’s future BLA submission or if the FDA finds that AxoGen does not meet the conditions for the transition plan, or is not exercising due diligence in executing the transition (e.g., study completion, or BLA submission is neither timely nor adequate). If final action on the BLA is negative or AxoGen is found to not meet the conditions for the transition plan or its execution, AxoGen will not be able to continue to distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft. AxoGen continues to work diligently with the FDA and, in this context, continues to distribute Avance® Nerve Graft.
The BLA application of Avance® Nerve Graft, if approved, will require a potentially substantial user fee payment to the FDA, although certain exemptions, waivers and discounts of the user fees may apply, including certain waivers or discounts for small businesses.
The Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act, referred to herein as FDASIA (Public Law 112-144), which was signed into law on July 9, 2012, amended the FD&C Act. FDASIA includes the Prescription Drug User Fee Amendments of 2012 which authorizes the FDA to continue to collect the following user fees from applicants who submit certain new drug and biological product applications and supplements:
|
·
| |
Application Fee: Each new BLA has a fee required upon submission. For AxoGen’s fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, this fee for a BLA requiring clinical data is $2,421,495. The fee is adjusted each year so we cannot provide an accurate estimate of what our fee will be upon submission of our BLA. For small companies (fewer than 500 employees and no other approved biologic product on the market) submitting its first application, a waiver of the application fee is available. AxoGen may be able to apply for this waiver for the Avance® Nerve Graft BLA. |
|
·
| |
Establishment Fee: Establishment fees (for the place of business where the biologic product is manufactured) are based on the FDA budget divided by the total number of establishments. For AxoGen’s fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, the Establishment Fee is $512,200. This fee is adjusted each year so we cannot provide an accurate estimate of what our fee will be upon approval of our BLA. AxoGen will have to pay an establishment fee after BLA approval and then pay such fee annually thereafter. |
|
·
| |
Product Fee: A product fee is assessed for each strength or potency in which the approved (non-revoked, non-suspended) product is manufactured in final dosage form. The product fee is based on an estimate of the number of products that would be subject to, and for which the companies would pay, product fees. The product fee is determined by dividing the adjusted total fee revenue from product fees by the number of estimated products (based on previous year’s product fees) subject to the product fee (excluding product fee waivers and reductions granted by the FDA). For AxoGen’s fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, the product fee has been established at $97,750. AxoGen may have to pay a Product Fee after BLA approval. AxoGen expects to apply for a product fee waiver for the Avance® Nerve Graft. |
FDA — General
FDA regulations govern nearly all the activities that AxoGen performs, or that are performed on its behalf, to ensure that medical products distributed domestically or exported internationally are safe and effective for their intended uses. The activities the FDA regulates include the following:
|
·
| |
product design, development and manufacture; |
|
·
| |
product safety, testing, labeling and storage; |
|
·
| |
pre-clinical testing in animals and in the laboratory; |
|
·
| |
clinical investigations in humans; |
|
·
| |
premarketing clearance or approval and licensing; |
|
·
| |
record-keeping and document-retention procedures; |
|
·
| |
advertising and promotion; |
|
·
| |
the import and export of products; |
|
·
| |
product marketing, sales and distribution; |
|
·
| |
post-marketing surveillance and medical device reporting, including reporting of deaths, serious injuries, communicable diseases, device malfunctions or other adverse events; and |
|
·
| |
corrective actions, removals and recalls. |
Failure to comply with applicable FDA regulatory requirements may subject AxoGen to a variety of administrative or judicially-imposed penalties or sanctions and/or prevent it from obtaining or maintaining required approvals, clearances or licenses to manufacture and market its products. Such failure to comply with the applicable FDA requirements may subject AxoGen to stringent administrative or judicial actions or sanctions, such as agency refusal to approve pending applications, warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution of products, injunctions, or civil or criminal prosecution.
FDA’s Premarket Clearance and Approval Requirements - Medical Devices
Unless an exemption applies, each medical device distributed commercially in the U.S. requires either a 510(k) premarket notification submission or a Pre-Market Approval (“PMA”) Application to the FDA. Medical devices are classified into one of three classes—Class I, Class II, or Class III—depending on the degree of risk, the level of control necessary to assure the safety and effectiveness of each medical device and how much is known about the type of device. For devices first intended for marketing after May 28, 1976, pre-market review and clearance by the FDA for Class I and II medical devices is accomplished through the 510(k) pre-market notification procedure by finding a device substantially equivalent to a legally marketed Class I or II device, unless the device is exempt. The majority of Class I medical devices are exempt from the 510(k) premarket notification requirement. Devices deemed by the FDA to pose the greatest risk, such as life-sustaining, life-supporting or implantable devices for which Class II controls are inadequate to assure safety or effectiveness, and novel devices, including devices deemed not substantially equivalent to a previously cleared 510(k) device, are placed in Class III. Class III devices generally require an approved PMA prior to marketing.
A PMA must be supported by extensive data, including, but not limited to, technical, preclinical, clinical trials, manufacturing and labeling to demonstrate to the FDA’s satisfaction, the safety and effectiveness of the device.
FDA’s Premarket Approval Requirements - Biologic Products
Biological Product License Application (BLA) Pathway
Biological products subject to BLA requirements are approved under the Public Health Service Act. Biological products require FDA approval of a BLA to be marketed. In order to be approved, a BLA must demonstrate the safety, purity and potency of the product candidate based on results of preclinical studies and clinical trials. A BLA must also contain extensive CMC and other manufacturing information, and the applicant must pass an FDA pre-approval inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which the biologic product is produced to assess compliance with the FDA’s cGMP. Satisfaction of FDA approval requirements for biologics typically takes several years and the actual time required may vary substantially based on the type, complexity and novelty of the product. AxoGen cannot be certain that any BLA approvals for its products will be granted on a timely basis, or at all.
The steps for obtaining FDA approval of a BLA to market a biologic product in the U.S. include:
|
·
| |
completion of preclinical laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies under the FDA’s good laboratory practices regulations; |
|
·
| |
submission to the FDA of an IND, for human clinical testing, which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin and which must include independent Institutional Review Board, or IRB, approval at each clinical site before the trials may be initiated; |
|
·
| |
performance of an adequate and well-controlled clinical trial in accordance with Good Clinical Practices to establish the safety and efficacy of the product for each indication; |
|
·
| |
submission to the FDA of a BLA, which contains detailed information about the CMC for the product, reports of the outcomes and full data sets of the clinical trials, and proposed labeling and packaging for the product; |
|
·
| |
satisfactory review of the contents of the BLA by the FDA, including the satisfactory resolution of any questions raised during the review; |
|
·
| |
satisfactory completion of an FDA Advisory Committee review, if applicable; |
|
·
| |
satisfactory completion of an FDA inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which the product is produced to assess compliance with cGMP regulations, to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to ensure the product’s identity, strength, quality and purity; and |
|
·
| |
FDA approval of the BLA including agreement on post-marketing commitments, if applicable. |
Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluations of product chemistry, toxicity and formulation, as well as animal studies. An IND sponsor must submit the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information and analytical data, to the FDA as part of the IND. Some preclinical testing may continue after the IND is submitted. The IND must become effective before human clinical trials may begin. An IND will automatically become effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions about issues such as the conduct of the trials and or supporting preclinical data as outlined in the IND. In that case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding FDA concerns or questions before clinical trials can proceed. In other words, submission of an IND may not result in the FDA allowing clinical trials to commence.
Biosimilar Biological Products
A regulatory approval pathway for biosimilars was established by The Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (“BPCIA”), as part of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010. An important component of the legislation specified that a manufacturer of a reference biological product would be granted 12 years of exclusive, non-patent market exclusivity before a biosimilar could be approved for marketing in the US. An application for a biosimilar product may not be submitted to FDA until four years after the approval date of the BLA for the reference biological product. BPCIA provides for an abbreviated licensure process for a biosimilar, i.e., a biological product that is highly similar to an FDA-approved biological product, known as a reference product, and has no clinically meaningful differences compared to the reference product in terms of safety, purity and potency. At its discretion, the FDA can waive a requirement for any required element in an application for a biosimilar product. In addition, the legislation distinguished approval of a biosimilar from approval of such a product as a substitute for the reference biological products. Where a product is approved as a substitute for the reference biologic, it is considered an interchangeable product. Approval as interchangeable requires that the product is biosimilar and can be expected to produce the same clinical results as the reference product in any given patient, and if intended for repeat dosing, a demonstration that the risk in terms of safety or diminished efficacy of alternating or switching between the use of the interchangeable and reference product is not greater than the risk of using the reference product without such alternating or switching. Interchangeable products can be substituted for a reference product without intervention of the prescribing healthcare provider. Several states are enacting or are considering laws that regulated the use and substitution of biosimilar and interchangeable products. For example, Virginia requires licensure as interchangeable by the FDA for a pharmacist to dispense a biosimilar in place of a prescribed biological product (Virginia § 54.1-3408.04).
FDA’s Pre-Approval and Pre-Licensing Requirements
Before approving a BLA, the FDA generally inspects the facility or the facilities at which the product is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the product if it finds that the facility does not appear to be in cGMP compliance. If the FDA determines the application, manufacturing process or manufacturing facilities are not acceptable, it will either not approve the application or issue a complete response letter to indicate that the review cycle for an application is complete and that the application is not ready for approval. The letter will describe specific deficiencies
and, when possible, will outline recommended actions the applicant might take to get the application ready for approval. Notwithstanding the submission of any requested additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval.
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and each may take several years to complete. Data obtained from clinical activities are not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. The FDA may not grant approval on a timely basis, or at all. AxoGen may encounter difficulties or unanticipated costs in its efforts to secure necessary governmental approvals, which could delay or preclude it from marketing its products. The FDA may limit the indications for use or place other conditions on any approvals that could restrict the commercial application of the products. After approval, some types of changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications, manufacturing changes and additional labeling claims, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Post-Approval Requirements
After regulatory approval of a product is obtained, AxoGen will be required to comply with a number of post-approval requirements. For example, as a condition of approval of a BLA, the FDA may require post marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the product’s safety or efficacy. In addition, holders of an approved BLA are required to keep extensive records, to report certain adverse reactions and production problems such as biologic deviation reports to the FDA, to provide updated safety and efficacy information and to comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotional labeling for their products. Also, quality control and manufacturing procedures must continue to conform to cGMP regulations as well as the manufacturing conditions of approval set forth in the BLA. The FDA periodically inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMP regulations, which imposes certain procedural, substantive and recordkeeping requirements. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain compliance with cGMP and other aspects of regulatory compliance.
Future FDA inspections may identify compliance issues at AxoGen’s facilities or at the facilities of its contract manufacturers that may disrupt production or distribution, or require substantial resources to correct and prevent recurrence of any deficiencies. In addition, discovery of problems with a product or the failure to comply with applicable requirements may result in restrictions on a product, manufacturer or holder of an approved BLA, including withdrawal or recall of the product from the market or other voluntary, FDA-initiated or judicial action that could delay or prohibit further marketing. Newly discovered or developed safety or effectiveness data may require changes to a product’s approved labeling, including the addition of new warnings and contraindications. Finally, new government requirements, including those resulting from new legislation, may be established that could delay or prevent regulatory approval of AxoGen products that are currently under development or regulatory activity.
The FDA has broad regulatory compliance and enforcement powers. If the FDA determines that AxoGen failed to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, it can take a variety of compliance or enforcement actions, such as issuing a FDA Form 483 notice of inspectional observations, warning letter, or untitled letter, imposing civil money penalties, suspending or delaying issuance of approvals, requiring product recall, imposing a total or partial shutdown of production, withdrawal of approvals or clearances already granted, and pursuing product seizures, consent decrees or other injunctive relief, and criminal prosecution through the U.S. Department of Justice (the “DOJ”). The FDA can also require AxoGen to repair, replace or refund the cost of devices that it manufactured or distributed. If any of these events were to occur, it could materially adversely affect AxoGen’s business.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are required to support a BLA or PMA and are sometimes required for 510(k) clearance. Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational product to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators. Clinical trials are conducted under strict requirements to ensure the protection of human subjects participating in the trial and under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used in monitoring and safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. Clinical trials for biological products require the submission and FDA acceptance of an IND and clinical trials for medical devices require the submission and
FDA approval of an Investigational Device Exemption application, or IDE, unless the device regulations provide for an exemption from the IDE requirement. Clinical trials for significant risk devices may not begin until the IDE is approved by the FDA and the Institutional Review Board (IRB) overseeing the particular clinical trial. If the product is considered a non-significant risk device under FDA regulations, the trial must only be approved by an IRB prior to its initiation. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND or IDE, for significant risk devices. In addition, for these studies, an IRB at each site at which the study is conducted must approve the protocol, subject consent form and any amendments for each site at which the study is conducted. All research subjects must be informed, among other things, about the risks and benefits of the investigational product and provide their informed consent in writing.
Clinical trials under an IND typically are conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap or be combined. In AxoGen’s case, AxoGen believes that the Phase 3 clinical trial study for the Avance® Nerve Graft represents the only new clinical data that will be required to evaluate safety and effectiveness. Phase 1 clinical trials usually involve the initial introduction of the investigational product into a small group of healthy volunteers (e.g., 10 to 20) to evaluate the product’s safety (dosage tolerance and pharmacokinetics if a biologic product) and, if possible, to gain an early indication of its effectiveness. Phase 2 clinical trials usually involve controlled trials in a larger but limited patient population (e.g., a few hundred) to:
|
·
| |
evaluate dosage tolerance and appropriate dosage; |
|
·
| |
identify possible adverse effects and safety risks; and |
|
·
| |
provide a preliminary evaluation of the efficacy of the product for specific indications. |
Phase 3 clinical trials usually further evaluate clinical efficacy and test further for safety in an expanded patient population (e.g., a hundred to several thousand). Phase 3 clinical trials usually involve comparison with placebo, standard treatments or other comparators. Usually at least one well-controlled large Phase 3 or pivotal clinical trial demonstrating safety and efficacy is required to support a BLA. These trials are intended to establish the overall risk-benefit profile of the product and provide an adequate basis for physician labeling. Phase 3 trials are almost always larger, more time consuming, complex and costly than Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical testing may not be completed successfully within any specified period, if at all. Furthermore, the FDA or AxoGen may suspend or terminate clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk, have experienced a serious and unexpected adverse event, or that continued use in an investigational setting may be unethical. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of research if the research is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB’s requirements or if the research has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
Investigational New Drug Application
For a biologic product, an IND must be submitted prior to the initiation of the clinical study. The IND application must contain information in three broad areas:
|
·
| |
Animal Pharmacology and Toxicology Studies - Preclinical data to permit an assessment as to whether the product is reasonably safe for initial testing in humans. Also included are any previous experiences with the product in humans (often foreign use). |
|
·
| |
Manufacturing Information - Information pertaining to the composition, manufacturer, stability, and controls used for manufacturing of the drug substance and the drug product. This information is assessed to ensure that the company can adequately produce and supply consistent batches of the drug. |
|
·
| |
Clinical Protocols and Investigator Information - Detailed protocols for proposed clinical studies to assess whether the initial-phase trials will expose subjects to unnecessary risks. Also, information on the qualifications of clinical investigators—professionals (generally physicians) who oversee the administration of the experimental compound—to assess whether they are qualified to fulfill their clinical trial duties. Finally, commitments to obtain informed consent from the research subjects, to obtain review of the study by an IRB, and to adhere to the investigational new drug regulations. |
Once the IND is submitted, the sponsor must wait 30 calendar days before initiating any clinical trials. During this time, the FDA has an opportunity to review the IND for safety to assure that research subjects will not be subjected to unreasonable risk.
AxoGen Clinical Trials
AxoGen has an active clinical research program to gather data on the Avance® Nerve Graft. AxoGen has completed two clinical studies and is performing two ongoing clinical studies. The ongoing studies are “A Multicenter Retrospective Study of Avance® Nerve Graft Utilization, Evaluations and Outcomes in Peripheral Nerve Injury Repair (“RANGER®”)” and “A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Patient and Evaluator Blinded Comparative Study of Nerve Cuffs and Avance® Nerve Graft Evaluating Recovery Outcomes for the Repair of Nerve Discontinuities (“RECON”)”. Completed studies are “A Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study of Hollow Nerve Conduit and Avance® Nerve Graft Evaluation Recovery Outcomes of the Nerve Repair in the Hand (“CHANGE”)” and a pilot study to evaluate the use of Avance® Nerve Graft in the reconstruction of nerves following prostatectomy.
AxoGen will continue to accept patients in the RANGER® clinical study, a utilization registry of Avance® Nerve Graft. Five publications and more than 50 scientific conference presentations have been generated to date from the registry. The RANGER® Study is an observational study in current enrollment. It is designed to allow enrollment of up to a total of 2,500 subjects over the next several years. The follow-up for the RANGER® Study is standard of care with a target of up to 36 months post peripheral nerve repair. At the time of the BLA submission, AxoGen will submit an interim report in the BLA for the enrolled subjects. In 2013, a Matched Autograft and Tube Conduit Case Control Cohort Arm of RANGER® (“MATCH”) comparative arm was added. Subjects treated with Avance® Nerve Graft were matched to the peripheral nerve autograft or tube conduit treated groups based on size of gap length. We anticipate having approximately 300 subjects treated with peripheral nerve autograft and/or tube conduit in the comparative arm.
AxoGen has worked with leading institutions, researchers and surgeons to support innovation in the field of surgical peripheral nerve repair. AxoGen believes that RANGER® is currently the largest multi-center observational clinical study conducted in peripheral nerve gap repair. AxoGen’s ongoing RECON study will also continue our clinical work, providing a new multi-center, prospective, randomized, clinical study on Avance® Nerve Graft. The January 2012 edition of Microsurgery, November 2012 edition of The Journal of Hand Surgery June 2015 edition of Journal of Reconstructive Microsurgery and the January 2017 edition of HAND, each contain an article summarizing RANGER® study results (Brooks, et al. Processed nerve allografts for peripheral nerve reconstruction: A multicenter study of utilization and outcomes in sensory, mixed, and motor nerve reconstructions. Microsurgery, 2012 Jan; 32(1): 1-14; and Cho, et al. Functional outcome following nerve repair in the upper extremity using processed nerve allograft. J Hand Surg Am 2012 Nov; 37(11):2340-9 and Rinker, et al. Outcomes of short-gap sensory nerve injuries reconstructed with processed nerve allografts from a multicenter registry study. J Reconstr Microsurg 2015 Jun; 31(5):384-90). Brooks et al. reported on 55 Avance® Nerve Graft nerve repairs and resulted in meaningful motor and sensory recovery in 87% of nerve discontinuities between 5 and 50 mm. Cho et al. showed that Avance® Nerve Graft provided 89% meaningful recovery for digital nerve injuries, and 80% meaningful recovery for motor function in mixed and motor nerve injuries. An expanded data milestone was presented at the 5th Vienna Symposium on Surgery of Peripheral Nerves in June 2014 and such expanded RANGER® data provides that of the injuries repaired with the Avance® Nerve Graft 90%, 80% and 87% achieved meaningful recovery for gap lengths of 5-14 mm, 15-29 mm and 30-65 mm, respectively. Rinker et al. reported on a subgroup from the RANGER® registry on sensory recovery of short-gap digital nerve repairs between 5-15 mm using Avance® Nerve Graft. The study cohort included 24 subjects with 37 digital nerve repairs. Outcomes analysis demonstrated meaningful levels of sensory recovery. No implant related adverse experiences were reported in any of such reports. Isaacs and Safa reported on a subgroup of subjects with large diameter nerve injuries repaired with Avance® Nerve Graft. The study included 15 nerve repairs with 4-5 mm diameter Avance® Nerve Grafts. Outcomes analysis found that meaningful levels of sensory and motor function were achieved and no safety concerns were reported.
The following describes available clinical outcomes data from published papers on the leading synthetic and collagen conduit. Published papers on the leading synthetic collagen conduit by Weber, et al., 2000 and Wangensteen and Kalliainen, 2009, showed meaningful improvement: 74% in sensory nerves and 43% in sensory, mixed and motor nerves, respectively, of cases bridging a gap in the particular type of nerve. A paper published by Haug, et al., 2013 on
the leading synthetic and collagen conduit showed meaningful improvement in 40% sensory nerves using the static 2-point discrimination test. Autograft studies where autograft and direct repair or direct suture were tested by Weber, et al., 2000, Kim and Kline 2001-2006, Frykman and Gramyk, 1991, Frykman and Gramyk, 1991 and Kallio, 1993, as interpreted by Brooks et al. 2012, reported meaningful recovery: 86% in sensory nerves, 67-86% in sensory and mixed nerves, 80% in sensory nerves, 75-78% mixed nerves and 70% sensory nerves, respectively, of cases bridging a gap in the particular type of nerve. Published papers by Kim and Kline 2001-2006 and Frykman and Gramyk, 1991 reported successful recovery in 75% and 78% of mixed and motor nerves, respectively. A study by Kallio et al., 1993 showed recovery in 67% of mixed and motor nerves where recovery was defined as results indicating a classification of useful or better motor and sensory recovery.
The RECON study will include up to 20 centers and is a prospective, randomized, controlled, patient and evaluator blinded, comparative study of Avance® Nerve Graft and Collagen Nerve Cuffs in the repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities. The study is a non-inferiority study designed to assess the outcome of peripheral nerve repair in approximately 170 subjects. Subjects will be followed over the course of 12 months to assess safety and efficacy outcomes with assessments being performed at various defined intervals up to 12 months. The study is currently in early enrollment and no outcome data is available at this time.
CHANGE was a prospective randomized controlled pilot study of nerve cuffs and Avance® Nerve Graft for the reconstruction of peripheral nerve discontinuities in male and female subjects that sustained injury to at least one nerve in the hand, distal to the superficial palmar arch that after resection resulted in a nerve gap of >5 mm and ≤20 mm. The study results were published by Means et al in the June 2016 edition of HAND. The authors randomized 23 participants with 31 digital nerve injuries. Sixteen participants with 20 repairs had at least six months of follow-up while 12-month follow-up was available for 15 repairs. There were no significant differences in participant and baseline characteristics between treatment groups. The average static two point discrimination (s2PD) for the Avance® Nerve Graft was 5 ± 1 mm (n = 6) compared with 8 ± 5 mm (n = 9) for hollow conduits. All injuries randomized to processed nerve allograft returned some degree of s2PD as compared with 75% of the repairs in the conduit group. The authors concluded that in this pilot study, patients whose digital nerve reconstructions were performed with processed nerve allografts had significantly improved and more consistent functional sensory outcomes compared with hollow conduits.
A pilot study on the repair of the cavernous nerves in prostate cancer patients at Vanderbilt with 24 month follow-up has been completed. A total of 12 subjects were enrolled in this single center study. The primary objective of this study was to assess the technical feasibility of using Avance® Nerve Graft for neurovascular bundle (NVB) reconstruction during Robotic Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy (RALP). The secondary objective of the study was to assess the long term safety and efficacy of NVB reconstruction by assessing quality of life and erectile function through validated questionnaires 24 months post-repair.
Clinical trials are subject to extensive recordkeeping and reporting requirements. AxoGen’s clinical trials must be conducted under the oversight of an IRB for the relevant clinical trial sites and must comply with FDA regulations, including but not limited to those relating to good clinical practices. AxoGen is also required to obtain the patients’ written informed consent in form and substance that complies with both FDA requirements and state and federal privacy and human subject protection regulations. AxoGen, the FDA or the IRB may suspend a clinical trial at any time for various reasons, including a belief that the risks to study subjects outweigh the anticipated benefits. Even if a trial is completed, the results of clinical testing may not adequately demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the biological product or device, or may otherwise not be sufficient to obtain FDA approval to market the product in the U.S. Similarly, in Europe, the clinical study for a medicine product must be authorized by the Competent Authority in each Member State in which the clinical trial is to be conducted, and must receive a favorable opinion from an ethics committee.
Pervasive and Continuing Regulation
There are numerous regulatory requirements that apply after a product is cleared or approved. For medical devices, these include, but are not limited to: the FDA’s regulations for device labeling (21 CFR Part 801), medical device reporting (21 CFR Part 803), reporting of corrections and removals (21 CFR Part 806), establishment registration and device listing requirements (21 C.F.R. Part 807); and compliance with the Quality System Regulation (QSR) per 21 CFR
Part 820. Distribution of medical devices is also subject to license/registration requirements in some states. For tissue and biologic products, the regulatory requirements include: the FDA’s registration and listing requirements, donor eligibility requirements and compliance with Good Tissue Practices (“GTP”) in 21 CFR Part1271 for human tissue products, compliance with the FDA’s cGMP in 21 CFR Parts 210, 211, and 600 for biological products, and postmarket BLA requirements (21 CFR Part 601). Among other things, these regulations require manufacturers, including third party manufacturers to:
|
·
| |
follow stringent design, testing, control, documentation and other quality assurance procedures during all aspects of the manufacturing process; |
|
·
| |
comply with labeling regulations and FDA prohibitions against the false or misleading promotion or the promotion of products for uncleared, unapproved or off-label uses or indications; |
|
·
| |
comply with requirements to obtain clearance or approval for certain changes affecting the product, including changes to the product’s manufacturing, labeling, or intended use; |
|
·
| |
report to the FDA certain adverse events, adverse reactions and deviations: (a) for medical devices, a report to FDA is required if the device may have caused or contributed to a death or serious injury or malfunctioned in a way that would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if the malfunction were to recur; (b) for biologics, a deviation from current GMP or an unexpected or unforeseeable event that may affect the safety, purity, or potency of the product must be reported; and (c) for human tissue products, FDA requires reporting of certain adverse reactions involving a communicable disease related to an HCT/P that the company made available for distribution; |
|
·
| |
comply with post-approval restrictions or conditions, including post-approval study commitments and post-market safety and annual reporting requirements; |
|
·
| |
follow post-market surveillance regulations that may apply when necessary to protect the public health or to provide additional safety and effectiveness data for the device; and |
|
·
| |
follow requirements to issue notices of correction or removal, or conduct market withdrawals or recalls where quality or other issues arise. |
AxoGen has not received any reports of adverse events concerning the Avance® Nerve Graft or Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane products. Six adverse events have been reported for the AxoGuard® products (one each in 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016 and two in 2017). AxoGen has not had to submit any Medical Device Reports (“MDRs”), biological deviation reports, or tissue adverse reaction reports to the FDA. Cook Biotech submitted a MDR for the AxoGuard® adverse events in 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017. Although AxoGen’s AxoGuard® products have had just six adverse events reported to date, there may have been other incidents, including patient deaths, which may have occurred during procedures utilizing AxoGen’s products without AxoGen being aware of any such incidents. In addition, there can be no assurance that in the future AxoGen’s products will not cause or contribute to an adverse event that would require AxoGen to submit MDRs, biological deviation reports, or tissue adverse reaction reports to the FDA.
The advertising and promotion of medical products are also regulated by the Federal Trade Commission and by state regulatory and enforcement authorities. Recently, some promotional activities for FDA-regulated products have been the subject of enforcement action brought under healthcare reimbursement laws and consumer protection statutes. In addition, under the Federal Lanham Act and similar state laws, competitors and others can initiate litigation relating to advertising claims.
AxoGen is registered with the FDA as a tissue establishment for the Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. The FDA has broad post-market and regulatory enforcement powers. AxoGen is subject to unannounced inspections by the FDA to determine compliance with the GTP, GMP and other regulations, and these inspections may also include the manufacturing facilities of suppliers.
Failure by AxoGen or by AxoGen’s suppliers to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can result in enforcement action by the FDA or other federal or state authorities, which may include any of the following sanctions, among others:
|
·
| |
warning letters, fines, injunctions, consent decrees and civil penalties; |
|
·
| |
customer notifications, repair, replacement, refunds, recall or seizure of our products; |
|
·
| |
operating restrictions, partial suspension or total shutdown of production; |
|
·
| |
suspension or termination of our clinical trials; |
|
·
| |
refusing our PMA or BLA for new products, new intended uses or modifications to existing products; and |
|
·
| |
withdrawing or spending premarket approvals that have already been granted; and criminal prosecution. |
Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws
Educational Grants
A medical product manufacturer may provide financial support, including support by way of grants, to third-parties for the purpose of conducting medical educational activities. If these funded activities are considered by the FDA to be independent of the manufacturer, then the activities fall outside the FDA restrictions on promotion to which the manufacturer is subject.
The FDA considers several factors in determining whether an educational event or activity is independent from the substantive influence of the product manufacturer and therefore non-promotional, including, but not limited to, the following:
|
·
| |
whether the intent of the funded activity is to present clearly defined educational content, free from commercial influence or bias; |
|
·
| |
whether the third-party grant recipient and not the manufacturer has maintained control over selecting the faculty, speakers, audience, program content and materials; |
|
·
| |
whether the program focuses on a single product of the manufacturer without a discussion of other relevant existing competitive products or treatment options; |
|
·
| |
whether there was meaningful disclosure to the audience, at the time of the program, regarding the manufacturer’s funding of the program, any significant relationships between the provider, presenters, or speakers and the supporting manufacturer; whether any unapproved uses will be discussed; |
|
·
| |
whether there are legal, business, or other relationships between the supporting manufacturer and provider or its employees that could permit the supporting manufacturer to exert influence over the content of the program; |
|
·
| |
whether the individuals employed by the provider and involved in designing or conducting the educational activities are also involved in advising or assisting the company with respect to sales or marketing; |
|
·
| |
whether the information about the company’s products is further disseminated after the initial program, by or at the direction of the company, other than in response to an unsolicited request or through an independent provider; and |
|
·
| |
whether the provider is compliant with standards for independence, balance, objectivity, and scientific rigor when putting on ostensibly independent educational programs. |
AxoGen seeks to ensure that the activities it supports pursuant to educational grants program are in accordance with these criteria for independent educational activities. However, AxoGen cannot provide assurance that the FDA or other government authorities would view the programs supported as being independent.
Fraud, Abuse and False Claims
AxoGen is directly and indirectly subject to various federal and state laws governing relationships with healthcare providers and pertaining to healthcare fraud and abuse, including anti-kickback laws. In particular, the federal healthcare program Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in exchange for or to induce either the referral of an individual, or the furnishing, arranging for or recommending a good or service for which payment may be made in whole or part under federal healthcare programs, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Penalties for violations include criminal penalties and civil sanctions such as fines, imprisonment and possible exclusion from Medicare, Medicaid and other
federal healthcare programs. The Anti-Kickback Statute is broad and prohibits many arrangements and practices that are lawful in businesses outside of the healthcare industry. In implementing the statute, the Office of Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (“OIG”) has issued a series of regulations, known as the “safe harbors.” These safe harbors set forth provisions that, if all their applicable requirements are met, will assure healthcare providers and other parties that they will not be prosecuted under the Anti-Kickback Statute for activities that fit within a safe harbor. The failure of a transaction or arrangement to fit precisely within one or more safe harbors does not necessarily mean that it is illegal or that prosecution will be pursued. However, conduct and business arrangements that do not fully satisfy each applicable element of a safe harbor may result in increased scrutiny by government enforcement authorities, such as the OIG, and are at risk activities unless a favorable advisory opinion is obtained from the OIG.
The Federal False Claims Act (“FCA”) imposes civil liability on any person or entity that submits, or causes the submission of, a false or fraudulent claim to the U.S. government. Damages under the FCA can be significant and consist of the imposition of fines and penalties. The FCA also allows a private individual or entity with knowledge of past or present fraud against the federal government to sue on behalf of the government to recover the civil penalties and treble damages. The DOJ has previously alleged that the marketing and promotional practices of pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers included the off-label promotion of products or the payment of prohibited kickbacks to doctors violated the FCA resulting in the submission of improper claims to federal and state healthcare entitlement programs such as Medicaid. In certain cases, manufacturers have entered into criminal and civil settlements with the federal government under which they entered into plea agreements, paid substantial monetary amounts and entered into corporate integrity agreements that require, among other things, substantial reporting and remedial actions going forward.
AdvaMed is one of the primary voluntary U.S. trade associations for medical device manufacturers. This association has established guidelines and protocols for medical device manufacturers in their relationships with healthcare professionals on matters including research and development, product training and education, grants and charitable contributions, support of third party educational conferences, and consulting arrangements. Adoption of the AdvaMed Code by a medical device manufacturer is voluntary, and while the OIG and other federal and state healthcare regulatory agencies encourage its adoption and may look to the AdvaMed Code, they do not view adoption of the AdvaMed Code as proof of compliance with applicable laws. AxoGen has incorporated the principles of the AdvaMed Code in its standard operating procedures, sales force training programs, and relationships with doctors. Key to the underlying principles of the AdvaMed Code is the need to focus the relationships between manufacturers and healthcare professionals on matters of training, education and scientific research, and limit payments between manufacturers and healthcare professionals to fair market value for legitimate services provided and payment of modest meal, travel and other expenses for a healthcare professional under limited circumstances. AxoGen has incorporated these principles into its relationships with healthcare professionals under its consulting agreements, payment of travel and lodging expenses, research and educational grant procedures and sponsorship of third party conferences. In addition, AxoGen has conducted training sessions on these principles. Finally, the Sunshine act, as defined below, imposes additional new reporting and disclosure requirements on AxoGen for any “transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as reporting of certain physician ownership interests. AxoGen cannot provide any assurance that regulatory or enforcement authorities will view its relationships with physicians or policies as being in compliance with applicable regulations and laws.
Regulation Outside of the United States
Distribution and sales of medical products outside of the U.S. are subject to foreign governmental regulations that vary substantially from country to country. The time required to obtain certification or approval by a foreign country may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA clearance or approval and the requirements may be different.
There are restrictions under U.S. law on the export from the U.S. of medical devices and biological product that cannot be legally distributed in the U.S. If a Class I or Class II device does not have 510(k) clearance and the manufacturer reasonably believes that the device could obtain 510(k) clearance in the U.S., then the device can be exported to a foreign country for commercial marketing without the submission of any type of export request or prior FDA approval if (i) the device is not sold or offered for sale in the U.S., (ii) is labeled for export only and (iii) satisfies certain criteria relating primarily to specifications of the foreign purchaser and compliance with the laws of the country
to which it is being exported, known as Importing Country Criteria. An unapproved Class III device can be exported if it (i) complies with the criteria discussed above for devices that could obtain 510(k) clearance, (ii) meets certain other quality and labeling requirements, and (iii) has a valid marketing authorization from one of a list of countries listed in the FD&C Act. If an unapproved Class III device does not have a valid marketing authorization from one of the listed countries, an export permit from the FDA is required in order to export it. An unapproved biological product can be exported without submitting an export request to FDA if the product has received a marketing authorization in one of a list of countries listed in the FD&C Act and it meets applicable requirements of the FD&C Act and the laws of the country to which it is exported. An investigational biological product may also be exported under an IND if a listed investigator is in a foreign country and certain requirements specified in FDA’s regulations are met. AxoGen currently believes it complies with applicable regulations when exporting its products and AxoGen intends to continue such compliance in the event there are any regulatory changes regarding its products in the United States.
The primary regulatory body in Europe is the E.U. which has adopted numerous directives and promulgated voluntary standards regulating the design, manufacture and labeling of, and clinical trials and adverse event reporting for, medical devices. Devices that comply with the requirements of a relevant directive will be entitled to bear CE marking, indicating that the device conforms to the essential requirements of the applicable directives and, accordingly, can be commercially distributed throughout the member states of the E.U. and other countries that comply with these directives. The method for assessing conformity varies depending on the type and class of the device, but normally involves an assessment by the manufacturer and a third-party assessment by a notified body, an independent and neutral institution appointed by a country to conduct the conformity assessment. This third-party assessment may consist of an audit of the manufacturer’s quality system and specific testing of the manufacturer’s device. Such an assessment is required for a manufacturer to commercially distribute the product throughout these countries. In the second quarter of 2014, AxoGen’s Quality System became registered to ISO 13485 for Receipt, Handling, Storage and Distribution of Medical Devices related to nerve repair.
Cook Biotech is responsible for all regulatory filings for the AxoGuard® Connector and Protector products including international registrations. AxoGen works with Cook Biotech by providing the countries for Cook to register or get approval for these AxoGuard® products. Cook Biotech prepares the product filing documentation and submits this documentation to the Ministry of Health (“MOH”) for the country. Each country or region has its own regulations and the documentation required for submission varies. It typically takes less than nine months from the initiation of the project to obtain clearance in a given country or region. To date, the AxoGuard® Connector and Protector product lines were registered in May 2013 in Canada for distribution and in April 2013 the product lines were awarded the CE Mark allowing distribution into the E.U. and other countries that accept the CE Mark.
Tissue products are not currently regulated under the CE Mark
AxoGen is responsible for all regulatory filings for Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane including international registrations. To obtain approvals AxoGen will prepare the product filing documentation and submit this documentation to the Ministry of Health (“MOH”) for a country.
Although some standards of harmonization exist, each country in which AxoGen conducts business has its own specific regulatory requirements. AxoGen procures and processes its tissue for the Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane in the U.S., and markets the Avance® Nerve Graft in Canada, United Kingdom, and certain other countries under compliance with the individual country regulations. These requirements are dynamic in nature and, as such, are continually changing. New regulations may be promulgated at any time and with limited notice. AxoGen will review the regulations at the time of submission of the product dossier for regulatory review. This review involves reviewing the appropriate MOH regulations, discussion with in-country distributors and use of consultants. It typically takes less than nine months from the initiation of the product to develop a product dossier (specific for that country), submission of the documentation and MOH review of the product filing. While AxoGen believes that it is in compliance with all existing pertinent international and domestic laws and regulations, there can be no assurance that changes in governmental administrations and regulations will not negatively impact AxoGen’s operations. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is only available in the U.S. and has not, as of this time period, received any regulatory registration allowing for distribution outside the U.S.
The FDA and international regulatory bodies conduct periodic compliance inspections of AxoGen’s U.S. processing facilities. AxoGen’s operations are registered with the U.S. FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), as a tissue establishment. AxoGen is also accredited by the AATB and is licensed in the states of Florida, New York, California, Maryland, Delaware, Oregon and Illinois. AxoGen believes that worldwide regulation of tissue products is likely to intensify as the international regulatory community focuses on the growing demand for these implant products and the attendant safety and efficacy issues of recipients. Changes in governing laws and regulations could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s financial condition and results of operations. AxoGen management further believes that it can help to mitigate this exposure by continuing to work closely with government and industry regulators.
Environmental
AxoGen’s products, as well as the chemicals used in processing, are handled and disposed of in accordance with country-specific, federal, state and local environmental regulations. Since 2007, AxoGen has used outside third parties to perform all biohazard waste disposal.
AxoGen contracts with independent, third parties to perform sterilization of its allografts. In view of the engagement of a third party to perform irradiation services, the requirements for compliance with radiation hazardous waste do not apply, and therefore AxoGen does not anticipate that this engagement will have any material adverse effect upon its capital expenditures, results of operations or financial condition. However, AxoGen is responsible for assuring that the service is being performed in accordance with applicable regulations. Although AxoGen believes it is in compliance with all applicable environmental regulations, the failure to fully comply with any such regulations could result in the imposition of penalties, fines and/or sanctions which could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business.
Corporate History
On September 30, 2011, AxoGen Corporation (“AC”), a Delaware corporation, completed its business combination with LecTec Corporation (“LecTec”), a Minnesota corporation, in accordance with the terms of an Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 31, 2011, by and among LecTec, Nerve Merger Sub Corp., a subsidiary of LecTec (“Merger Sub”), and AC, which the parties amended on August 9, 2011 and September 30, 2011 (as amended, the “Merger Agreement”). Pursuant to the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub merged with and into AC, with AC continuing after the merger as the surviving corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of LecTec (the “Merger”). Immediately following the Merger, LecTec changed its name to AxoGen, Inc. In October 2011, AxoGen Inc. moved its corporate headquarter facilities (principal executive office) from Texarkana, Texas to Alachua, Florida.
LecTec was organized in 1977 as a Minnesota corporation and went public in December 1986. Prior to the Merger it was an intellectual property licensing and holding company. LecTec held multiple domestic and international patents based on its original hydrogel patch technology and filed patent applications on a hand sanitizer patch. LecTec also had a licensing agreement with Novartis Consumer Health, Inc. LecTec took legal action to protect its IP and settled all of its litigation prior to the Merger and AxoGen subsequent to the Merger continued to hold LecTec IP until it expired.
Our website address is http://www.axogeninc.com. We have included our website address as an inactive textual reference only. We make available, free of charge through our website, our annual reports on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material, or furnish it to the SEC. We also similarly make available, free of charge on our website, the reports filed with the SEC by our executive officers, directors and 10% stockholders pursuant to Section 16 under the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after copies of those filings are provided to us by those persons. We are not including the information contained at http://www.axogeninc.com, or at any other website.
Employees
At December 31, 2017, AxoGen had 199 total employees, including 15 part-time employees and 184 full-time employees. Of the full-time employees, 20 employees work in administration, information technology and finance, 25 employees work in manufacturing and quality control, 27 employees work in research and development and regulatory and 112 employees work in sales and marketing. As of the date of this annual report on Form 10-K AxoGen has not had a work stoppage and no employees are represented by a labor union. AxoGen believes its relationship with its employees is satisfactory.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table lists the names and positions of the individuals who are, as of February 28, 2018, executive officers of AxoGen:
|
|
|
|
|
Name
|
|
Title
|
|
Karen Zaderej
|
|
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director
|
|
Peter Mariani
|
|
Chief Financial Officer
|
|
Gregory G. Freitag, JD CPA
|
|
General Counsel, Senior Vice President of Business Development and Director
|
|
Jon Gingrich
|
|
Chief Commercial Officer
|
|
Mark Friedman, Ph.D.
|
|
Vice President of Regulatory and Quality
|
|
David Hansen
|
|
Vice President of Finance and Treasurer
|
|
Shawn McCarrey
|
|
Senior Vice President of Sales
|
|
Kevin Leach
|
|
Vice President of Marketing
|
|
Erick DeVinney
|
|
Vice President of Clinical and Translational Sciences
|
|
Mike Donovan
|
|
Vice President of Operations
|
Biographical information for each of our executive officers is included below.
Karen Zaderej, President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Age 56)
Ms. Zaderej has served as AxoGen’s President, Chief Executive Officer and a member of our board of directors (the “Board of Directors”) since September 2011. She has served as the Chief Executive Officer of AxoGen, and a member of AxoGen’s board of directors since May 2010. Ms. Zaderej joined AxoGen in May 2006 and served as Vice President of Marketing and Sales from May 2006 to October 2007 and as Chief Operating Officer from October 2007 to May 2010. From October 2004 to May 2006, Ms. Zaderej worked for Zaderej Medical Consulting, a consulting firm she founded, which assisted medical device companies in building and executing successful commercialization plans. From 1987 to 2004, Ms. Zaderej worked at Ethicon, Inc., a Johnson & Johnson company, where she held senior positions in marketing, business development, and research & development, as well as ran a manufacturing business. Ms. Zaderej is a Director of SEBio, a non-profit supporting the life science industry in the southeastern United States. Ms. Zaderej has a MBA from the Kellogg Graduate School of Business and a BS in Chemical Engineering from Purdue University.
Peter Mariani, Chief Financial Officer (Age 54)
Mr. Mariani, has been AxoGen’s Chief Financial Officer since March of 2016. Prior to joining AxoGen, he served as Chief Financial Officer of Lensar, Inc, a privately held laser refractive cataract surgery company, from July 2014 through January 2016, which was sold in December 2015. From June 2011 to June 2014 Mr. Mariani served as Chief Financial Officer of Hansen Medical, a publicly traded medical device company developing robotic solutions for intravascular procedures. From 2007 through 2010 Mr. Mariani served as Chief Financial Officer for two privately held companies: Harlan Laboratories (2007 – 2009); and BMW Constructors (2009 – 2010). From 1994 through 2006 Mr. Mariani served in various senior financial roles with Guidant Corporation, a publicly traded leader in the development and sale of medical devices for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Mr. Mariani began his career with Guidant as Director of Corporate Financial Reporting where he supported the initial public offering of Guidant and ultimately served as Vice President, Controller and Chief Accounting Officer. Mr. Mariani’s experience at Guidant included two years as Director of Financial Reporting, Guidant Vascular Intervention in Santa Clara, California, and four years in Tokyo, Japan, mostly as Vice President Finance and Administration where he helped to facilitate the conversion and scale of the Japan business from a distributor network to a direct sales and marketing organization. Following the 2006 sale of Guidant to Boston Scientific Corporation, Mr. Mariani co-led the initial integration of the two companies. From 1987 to 1994, Mr. Mariani worked with Ernst and Young, LLP, where he served a diverse client base as a Certified Public Accountant. Mr. Mariani received a Bachelor of Science Degree in Accounting from Indiana University.
Gregory G. Freitag, JD, CPA, General Counsel, Senior Vice President Business Development and Director (Age 56)
Mr. Freitag, J.D., CPA, has been AxoGen’s General Counsel and a member of our Board of Directors since September 2011, has been AxoGen’s Senior Vice President Business Development since May 2014, and was AxoGen’s Chief Financial Officer from September 2011 to May 2014 and August 2015 to March 2016. He was Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and a board member of LecTec Corporation, an IP licensing and holding company that merged with AxoGen in September 2011, from June 2010 through September 2011. From May 2009 to the present, Mr. Freitag has been a principal of FreiMc, LLC, a healthcare and life science consulting and advisory firm he founded that provides strategic guidance and business development advisory services. Prior to founding FreiMc, LLC, Mr. Freitag was a Director of Business Development at Pfizer Health Solutions, a former subsidiary of Pfizer, Inc., from January 2006 to May 2009. From July 2005 to January 2006, Mr. Freitag worked for Guidant Corporation in its business development group. Prior to Guidant Corporation, Mr. Freitag was the Chief Executive Officer of HTS Biosystems, a biotechnology tools start-up company, from March 2000 until its sale in early 2005. Mr. Freitag was the Chief Operating Officer, Chief Financial Officer and General Counsel of Quantech, Ltd., a public point of care diagnostic company, from December 1995 to March 2000. Prior to that time, Mr. Freitag practiced corporate law in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Mr. Freitag is also a director of the Foundation Board of HealthEast Care System, a health care system in Minnesota, and PDS Biotechnology Corporation, a private, clinical stage biopharmaceutical company developing immunotherapies for cancer and other disease areas such as infectious disease. Mr. Freitag holds a JD from the University of Chicago and a BA Economics & Business and Law & Society from Macalester College, Minnesota.
Jon Gingrich, Chief Commercial Officer (Age 49)
Mr. Gingrich, has been AxoGen’s Chief Commercial Officer since July 2017. From April 1, 2013 until joining AxoGen he served as Global Vice President and General Manager, Skeletal Health Solutions and Group Global Vice President, Marketing, Breast and Skeletal Health Solutions for Hologic Inc., a global health care and life science developer, manufacturer, and supplier of diagnostic, medical imaging, and surgical products. Prior to joining Hologic, he spent 15 years (July 1, 1997- December 31, 2012) with Boston Scientific, holding several commercial and international positions of increasing responsibility. From 2011-2012 Mr. Gingrich served as Vice President, International Commercialization, Cardiac Rhythm Management and as General Manager, Cardiac Rhythm Management of Japan from 2008-2011. Other Boston Scientific roles included Director, International Sales Operations and Training; Director, Marketing and Sales, Japan; Director, Sales Operations, Endoscopy; Global Marketing Product Manager, Endoscopy;
and Executive Territory Sales Manager, Endoscopy. He was also in sales and marketing roles with Unilever N.V., a consumer goods companies. Gingrich earned a Bachelor of Science Degree in Business Administration (Marketing and Management) from the University of Richmond.
Mark Friedman, Ph.D., Vice President of Regulatory and Quality (Age 60)
Dr. Friedman has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Regulatory and Quality since September 2011. He has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Regulatory and Quality since June 2011 and served as AxoGen’s Director of Quality Assurance and Regulatory Affairs from September 2006 to June 2011. Prior to joining AxoGen, Dr. Friedman held several regulatory and quality leadership positions at Enable Medical Corporation, a medical device company, including Director of Quality Assurance from 1997 to 1998 and Vice President of Quality and Regulatory from 1998 to 2001 and from 2004 to 2005. Dr. Friedman also worked for AtriCure, Inc., a company that develops, manufactures and sells surgical ablation systems to treat atrial fibrillation, as Vice President of Quality and Regulatory from 2001 to 2004 and as Vice President of Operations in 2004. AtriCure acquired Enable Medical in 2005. Dr. Friedman has over 25 years of experience in developing and directing regulatory strategy and quality systems for medical products, including 15 years with start-up medical product firms. Dr. Friedman has a Ph.D. in Chemistry specializing in protein biochemistry from the University of Cincinnati. Dr. Friedman sits on various agency committees for the Alliance of Regenerative Medicine, Medical Device Manufacturer’s Association and American Association of Tissue Banks, working on improving regulatory laws and standards for regenerative products and medical devices.
David Hansen, Vice President of Finance and Treasurer (Age 57)
Mr. Hansen has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Finance and Treasurer since June 2017. Mr. Hansen previously served as Chief Accounting Officer of AxoGen from December 2015 to May 2017, and as Corporate Controller of AxoGen from June 2006 to November 2015. Mr. Hansen was Vice President of Finance—Corporate Controller and Treasurer of Perma-Fix Environmental Services, Inc., a publicly-traded environmental services company, and held other corporate and regional accounting positions at Perma-Fix Environmental Services from 1995 to 2005. Mr. Hansen was also the Vice President - Finance at Kraft Foodservice, Inc., Ocala, Florida from 1994 to 1995 and held other accounting and procurement positions at Kraft Foodservice, Inc. from 1985 to 1994. Mr. Hansen has over 20 years of experience in senior financial positions at both publicly traded and private companies. Mr. Hansen holds a BBA degree in Accounting from the University of Oklahoma.
Shawn McCarrey, Senior Vice President of Sales (Age 61)
Mr. McCarrey has served as AxoGen’s Senior Vice President of Sales since February 2013. Mr. McCarrey was Executive Vice President of North American Cardiovascular Sales at Bayer Interventional/MEDRAD Interventional from January 2009 to May 2012. Bayer HealthCare, a subgroup of Bayer AG, is one of the world’s leading, innovative companies in the healthcare and medical products industry. Bayer Interventional, now doing business as part of Bayer Medical Care’s Radiology and Interventional business, is the interventional franchise formerly operated under Bayer’s MEDRAD brand. From 1998 to 2009, Mr. McCarrey held multiple escalating positions with Possis Medical, Inc., a company that developed, manufactured and marketed medical devices for the cardiovascular and vascular treatment markets, and served as Director or Sales, VP of US Sales, VP of Worldwide Sales and EVP of Worldwide Sales & Marketing. For more than 15 years prior to joining Possis, Mr. McCarrey served in a series of progressively responsible roles with two divisions of C.R. Bard, United States Catheter and Instrument Corporation (USCI) which specialized in the treatment of coronary disease in the cardiac catheterization laboratory and Davol, an operating room division that promoted Thoraclex and Simpulse to cardiovascular and orthopedic surgeons. Mr. McCarrey holds a BS degree in Marketing from Central Michigan University.
Kevin Leach, Vice President of Marketing (Age 48)
Mr. Leach has been AxoGen’s Vice President of Marketing since March 2016. Prior to joining AxoGen, Mr. Leach worked in a consulting capacity between September 2015 and March 2016 for start-up companies supporting strategic planning and due diligence activities for targeted acquisitions. Mr. Leach previously served as Vice President of Marketing for Stryker within their orthopedic division, where he led the overall knee strategy from September 2013 through August 2015. From February 2013 to September 2013 Mr. Leach served as marketing consultant for SteadMed
Medical, a medical device company focusing on acute and chronic wounds. From January 2008 to February 2013 Mr. Leach served in marketing roles with increasing responsibility including as Vice President, Marketing with ConvaTec, a medical products and technologies company with leading market positions in Wound Therapeutics, Ostomy Care, Continence and Infusion Devices. ConvaTec was acquired by private equity firms Nordic Capital and Avista Capital Partners in 2008. Prior to moving to the United States, from October 2000 to January 2008, Mr. Leach was a global marketing leader for ConvaTec, a Bristol-Myers Squibb company where he led the launch of new products globally. From February 1999 to October 2000 Mr. Leach served as Business Unit Manager at Zimmer UK, within a newly established division for the orthopedic business unit focusing on market development and commercialization of an injectable hyaluronic acid for the relief of joint pain. From January 1992 to February 1999 Mr. Leach held various sales and marketing roles within the UK division of ConvaTec. Mr. Leach qualified as a Podiatrist from Queen Margaret University in Edinburgh.
Erick DeVinney, Vice President of Clinical and Translational Sciences (Age 43)
Mr. DeVinney has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Clinical and Translational Sciences since January 2014. Prior to January 2014, Mr. DeVinney was the Director of Clinical and Translational Sciences for AxoGen from April 2007 until January 2014. Erick has over 14 years of experience in the successful planning and management of clinical development. Prior to joining AxoGen Mr. DeVinney served as Manager of Clinical Operations for Angiotech Pharmaceuticals from 2005 to 2007 and Clinical Program Lead for Pharmaceutical Research Associates International from 2001 to 2005. Mr. DeVinney has been involved in the successful submission of numerous 510(k), IDE and NDA applications. He has a BS in Chemistry from Virginia Commonwealth University.
Mike Donovan, Vice President of Operations (Age 54)
Mr. Donovan has served as AxoGen’s Vice President of Operations since September 2015. Prior to September 2015, Mr. Donovan was AxoGen’s Director of Operations from January 2011 until September 2015. From 1988 to 2010, Mr. Donovan held positions at Zimmer Holdings in manufacturing, continuous improvement, quality assurance and sterilization including Director of Manufacturing from 2002 to 2010. Mr. Donovan has a BS in Chemical Engineering and an MBA from the University of Akron.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
AxoGen’s business involves a number of risks, some of which are beyond its control. The risk and uncertainties described below are not the only ones the Company faces. Set forth below is a discussion of the risks and uncertainties that management believes to be material to AxoGen.
Risks Related To The Company
AxoGen has not experienced positive cash flow from its operations, and the ability to achieve positive cash flow from operations will depend on increasing revenue from distribution of its products, which may not be achievable.
AxoGen has historically operated with negative cash flow from its operations. As of December 31, 2017, AxoGen had an accumulated deficit of approximately $128 million. If AxoGen revenue does not increase as anticipated, then it will continue to experience negative cash flows and adverse operating conditions. AxoGen’s continuing capital needs and other factors could cause the Company to raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or from other sources. The sale of additional equity may result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that AxoGen will be able to secure funding on terms acceptable to it, or at all.
AxoGen’s revenue growth depends on its ability to expand its sales force, increase distribution and sales to existing customers and develop new customers, and there can be no assurance that these efforts will result in significant increase in sales.
AxoGen is in the process of investing in its distribution and sales channels composed of a combination of its direct sales force and independent distributors to allow it to increase distribution and sales to existing customers and reach new customers. There can be no assurance that these efforts will be successful in expanding AxoGen’s revenue. AxoGen
currently distributes tissue and sells products directly through its employees and indirectly through distributor relationships. AxoGen is engaged in an initiative to build and further expand sales and marketing capabilities. The incurrence of these expenses impacts AxoGen’s operating results, and there can be no assurance of their effectiveness. If AxoGen is unable to develop its sales force, increase sales to existing customers and attract new customers, it may not be able to grow revenue or maintain its current level of revenue generation.
AxoGen’s revenue depends primarily on four products.
Substantially all of AxoGen’s revenue is currently derived from only four products, the Avance® Nerve Graft, Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector and AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, for the treatment of peripheral nerve damage. Of these four products, the Avance® Nerve Graft represents approximately half of the Company’s total revenues. Any disruption in AxoGen’s ability to generate revenue from the distribution of tissue and sale of products will have a material adverse impact on AxoGen’s business, results of operations, financial condition and growth prospects.
The AxoGuard® products are only available through an exclusive distribution agreement with Cook Biotech. The agreement was amended February 26, 2018 to run through June 30, 2027. However, there are conditions for continuation of the agreement, including payment terms and minimum purchase requirements, that if breached could result in an earlier termination of the agreement; except that through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforced such minimum purchase provision. Additionally, in the event that AxoGen and Cook Biotech were to fail to reach an agreement as to minimum purchase quantities, Cook Biotech could terminate the agreement if it was deemed that AxoGen had failed to generate commercially reasonable sales of AxoGuard® as measured by sales similar to a competitive product at the same stage in its commercial launch as verified by a mutually acceptable third party. Although there are products that AxoGen believes it could develop or obtain that would replace the AxoGuard® products obtained through the agreement with Cook Biotech, the loss of the ability to sell the AxoGuard® products could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business until other replacement products are available.
AxoGen’s success will be dependent on continued acceptance of its products by the medical community.
Continued market acceptance of AxoGen’s products will depend on its ability to demonstrate that its products are an attractive alternative to existing nerve reconstruction treatment options and provide appropriate solutions for nerve repair. Its ability to do so will depend on surgeons’ evaluations of clinical safety, efficacy, ease of use, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of AxoGen’s nerve repair products. For example, although AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft follows stringent safety standards, including sterilization by gamma irradiation, AxoGen believes that a small portion of the medical community has lingering concerns over the risk of disease transmission through the use of allografts in general. Furthermore, AxoGen believes that even if its products receive general acceptance within the medical community, acceptance and clinical recommendations by influential surgeons will be important to the commercial success of AxoGen’s products.
Negative publicity concerning methods of donating human tissue and screening of donated tissue, in the industry in which AxoGen operates, may reduce demand for its products and negatively impact the supply of available donor tissue.
AxoGen is highly dependent on its ability to recover human tissue from tissue donors for its Avance® Nerve Graft product and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. The availability of acceptable donors is relatively limited, and this availability is impacted by regulatory changes, general public opinion of the donation process and AxoGen’s reputation for its handling of the donation process. Media reports or other negative publicity concerning both improper methods of tissue recovery from donors and disease transmission from donated tissue, including bones and tendons, may limit widespread acceptance of AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. Unfavorable reports of improper or illegal tissue recovery practices, both in the U.S. and internationally, as well as incidents of improperly processed tissue leading to transmission of disease, may broadly affect the rate of future tissue donation and market acceptance of allograft technologies and donated tissue use. Potential patients may not be able to distinguish AxoGen products, technologies, and tissue recovery and processing procedures from others engaged in tissue recovery. In
addition, unfavorable reports could make families of potential donors or donors themselves from whom AxoGen is required to obtain consent before processing tissue reluctant to agree to donate tissue to for-profit tissue processors. Any disruption in the supply could have negative consequences for AxoGen’s revenue, operating results and continued operations.
AxoGen is highly dependent on the continued availability of its facilities and could be harmed if the facilities are unavailable for any prolonged period of time.
Any failure in the physical infrastructure of AxoGen’s facilities, including the facility it licenses from CTS, could lead to significant costs and disruptions that could reduce its revenues and harm its business reputation and financial results. Any natural or man-made event that impacts AxoGen’s ability to utilize its facilities could have a significant impact on its operating results, reputation and ability to continue operations. This includes termination of the CTS facility service agreement which can occur upon 18 months’ prior notice from either party. Although AxoGen believes it can find and make operational a new facility in less than six months, the regulatory process for approval of facilities is time-consuming and unpredictable. AxoGen’s ability to rebuild or find acceptable service facilities takes a considerable amount of time and expense and could cause a significant disruption in service to its customers. Although AxoGen has business interruption insurance which would, in instances other than service agreement termination, cover certain costs, it may not cover all costs nor help to regain AxoGen’s standing in the market.
AxoGen must maintain high quality processing of its products.
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft is processed through its Avance® Process which requires careful calibration and precise, high-quality processing and manufacturing. Its Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is also human tissue that requires skill in its processing. Achieving precision and quality control requires skill and diligence by its personnel. If it fails to achieve and maintain these high levels of quality control and processing standards, including avoidance of processing errors, defects or product failures, AxoGen could experience recalls or withdrawals of its product, delays in delivery, cost overruns or other problems that would adversely affect its business. AxoGen cannot completely eliminate the risk of errors, defects or failures. In addition, AxoGen may experience difficulties in scaling-up processing of its Avance® and Avive® products, including problems related to yields, quality control and assurance, tissue availability, adequacy of control policies and procedures, and lack of skilled personnel. If AxoGen is unable to process and produce its human tissue products on a timely basis, at acceptable quality and costs, and in sufficient quantities, or if it experiences unanticipated technological problems or delays in production, its business would be adversely affected.
Delays, interruptions or the cessation of production by AxoGen’s third party suppliers of important materials or delays in qualifying new materials, may prevent or delay AxoGen’s ability to manufacture or process the final products.
Most of the raw materials used in the process for Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane are available from more than one supplier. However, one of the chemicals AxoGen uses in the processing of Avance® Nerve Graft is no longer manufactured by the original single source provider. AxoGen has inventory of such chemical which it believes provides more than one year of production. AxoGen is currently evaluating multiple avenues including new suppliers of the chemical and acceptable substitutes for the chemical. In addition, some of the test results, packaging and reagents/chemicals AxoGen uses in its manufacturing process are also obtained from single suppliers. AxoGen does not have written contracts with any of its single source suppliers, and at any time they could stop supplying AxoGen’s orders. FDA approval of a new supplier may be required if these materials become unavailable from AxoGen’s current suppliers. Although there may be other suppliers that have equivalent materials that would be available to AxoGen, FDA approval of any alternate suppliers, if required, could take several months or years to obtain, if able to be obtained at all. Any delay, interruption or cessation of production by AxoGen’s third party suppliers of important materials, or any delay in qualifying new materials, if necessary, would prevent or delay AxoGen’s ability to manufacture products. In addition, an uncorrected impurity, a supplier’s variation in a raw material or testing, either unknown to AxoGen or incompatible with its manufacturing process, or any other problem with AxoGen’s materials, testing or components, would prevent or delay its ability to process tissue. These delays may limit AxoGen’s ability to meet demand for its products and delay its clinical trial, which would have a material adverse impact on its business, results of operations and financial condition.
The failure of third parties to perform many necessary services for the commercialization of Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, including services related to recovery, distribution and transportation, would impair AxoGen’s ability to meet commercial demand.
AxoGen relies upon third parties for certain recovery, distribution and transportation services. In accordance with product specifications, third parties ship Avance® Nerve Graft in specially validated shipping containers at frozen temperatures. If any of the third parties that AxoGen relies upon in its recovery, distribution or transportation process fail to comply with applicable laws and regulations, fail to meet expected deadlines, or otherwise do not carry out their contractual duties to AxoGen, or encounter physical damage or natural disaster at their facilities, AxoGen’s ability to deliver product to meet commercial demand may be significantly impaired.
AxoGen is dependent on its relationships with distributors to generate revenue.
AxoGen derives material revenues through its relationships with distributors. If such distributor relationships were terminated for any reason, it could materially and adversely affect AxoGen’s ability to generate revenues and profits. AxoGen intends to obtain the assistance of additional distributors to continue its revenue growth. It may not be able to find additional distributors who will agree to market and distribute its products on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If AxoGen is unable to establish new distribution relationships or renew current distribution agreements on commercially acceptable terms, its operating results could suffer.
Loss of key members of management, who it needs to succeed, could adversely affect its business.
AxoGen’s future success depends on the continued efforts of the members of its senior management team. Competition for experienced management personnel in the healthcare industry is intense. If one or more of AxoGen’s senior executives or other key personnel are unable or unwilling to continue in their present positions, or if AxoGen is unable to attract and retain high quality senior executives or key personnel in the future, its business may be adversely affected.
AxoGen’s operating results will be harmed if it is unable to effectively manage and sustain its future growth or scale its operations.
There can be no assurance that AxoGen will be able to manage its future growth efficiently or profitably. Its business is unproven on a large scale and actual revenue and operating margins, or revenue and margin growth, may be less than expected. If AxoGen is unable to scale its production capabilities efficiently or maintain pricing without significant discounting, it may fail to achieve expected operating margins, which would have a material and adverse effect on its operating results. Growth may also stress AxoGen’s ability to adequately manage its operations, quality of products, safety and regulatory compliance. If growth significantly decreases it will negatively impact AxoGen’s cash reserves, and it may be required to obtain additional financing, which may increase indebtedness or result in dilution to shareholders. Further, there can be no assurance that AxoGen would be able to obtain additional financing on acceptable terms if all at.
There may be significant fluctuations in AxoGen’s operating results.
Significant quarterly fluctuations in AxoGen’s results of operations may be caused by, among other factors, its volume of revenues, seasonal changes in nerve repair activity, timing of sales force expansion and general economic conditions. There can be no assurance that the level of revenues and profits, if any, achieved by AxoGen in any particular fiscal period, will not be significantly lower than in other comparable fiscal periods. AxoGen’s expense levels are based, in part, on its expectations as to future revenues. As a result, if future revenues are below expectations, net income or loss may be disproportionately affected by a reduction in revenues, as any corresponding reduction in expenses may not be proportionate to the reduction in revenues.
AxoGen’s revenues depend upon prompt and adequate reimbursement from public and private insurers and national health systems.
Political, economic and regulatory influences are subjecting the healthcare industry in the U.S. to fundamental change. The ability of hospitals to pay fees for AxoGen’s products depends in part on the extent to which reimbursement for the costs of such materials and related treatments will continue to be available from governmental health administration authorities, private health coverage insurers and other organizations. Major third-party payers of hospital services and hospital outpatient services, including Medicare, Medicaid and private healthcare insurers, annually revise their payment methodologies which can result in stricter standards for reimbursement of hospital and/or surgeon charges for certain medical procedures or the elimination of reimbursement. Further, Medicare, Medicaid and private healthcare insurer cutbacks could create downward price pressure on AxoGen’s products.
AxoGen may be subject to future product liability litigation which could be expensive and its insurance coverage may not be adequate.
Although AxoGen is not currently subject to any product liability proceedings and it has no reserves for product liability disbursements, it may incur material liabilities relating to product liability claims in the future, including product liability claims arising out of the usage of AxoGen products. Although AxoGen currently carries product liability insurance in an amount consistent with industry averages, its insurance coverage and any reserves it may maintain in the future for product related liabilities may not be adequate and AxoGen’s business could suffer material adverse consequences.
Technological change could reduce demand for AxoGen’s products.
The medical technology industry is intensely competitive. AxoGen competes with both U.S. and international companies that engage in the development and production of medical technologies and processes including:
|
·
| |
biotechnology, orthopedic, pharmaceutical, biomaterial, chemical and other companies; |
|
·
| |
academic and scientific institutions; and |
|
·
| |
public and private research organizations. |
AxoGen products compete with autograft, hollow-tube conduits, commercially available wraps and amnion products, as well as with alternative medical procedures. For the foreseeable future, AxoGen believes a significant number of surgeons will continue to choose to perform autograft procedures when feasible, despite the necessity of performing a second operation and its drawbacks. In addition, many members of the medical community will continue to prefer the use of hollow-tube conduits due in part to their familiarity with these products and the procedures required for their use. Amnion products are widely available and AxoGen may not be able to distinguish the Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane from such other products so as to produce significant revenue from its distribution. Also, steady improvements have been made in synthetic human tissue substitutes, which could compete with AxoGen’s products in the future. Unlike allografts, synthetic tissue technologies are not dependent on the availability of human or animal tissue. Although AxoGen’s growth strategy contemplates the introduction of new technologies, the development of these technologies is a complex and uncertain process, requiring a high level of innovation, as well as the ability to accurately predict future technology and market trends. AxoGen may not be able to respond effectively to technological changes and emerging industry standards, or to successfully identify, develop or support new technologies or enhancements to existing products in a timely and cost-effective manner, if at all. Finally, there can be no assurance that in the future AxoGen’s competitors will not develop products that have superior performance or are less expensive relative to AxoGen’s products rendering AxoGen’s products obsolete or noncompetitive. Due to its limited resources, its smaller size and its relatively early stage, AxoGen may face competitive challenges and barriers that are difficult to overcome and could negatively impact its growth.
AxoGen may be unsuccessful in commercializing its products outside the U.S.
To date, AxoGen has focused its commercialization efforts in the U.S., except for minor revenues in certain countries outside the U.S. AxoGen intends to expand distribution and sales in these and other countries outside the U.S.
and will need to comply with applicable foreign regulatory requirements, including obtaining the requisite approvals to do so. Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is only available in the U.S. and has not, as of this time period, received any regulatory registration allowing for distribution outside the U.S. Additionally, AxoGen will need to either enter into distribution agreements with third parties or develop a direct sales force in these foreign markets. If it does not obtain adequate levels of reimbursement from third party payers outside of the U.S., it may be unable to develop and grow its revenue internationally. Outside of the U.S., reimbursement systems vary significantly by country. Many foreign markets have government-managed healthcare systems that govern reimbursement for medical devices, implants and procedures. Additionally, some foreign reimbursement systems provide for limited payments in a given period and therefore result in extended payment periods. If AxoGen is unable to successfully commercialize its products internationally, its long-term growth prospects may be limited.
If AxoGen does not manage tissue and tissue donation in an effective and efficient manner, it could adversely affect its business.
Many factors affect the supply, quantity and timing of donor medical releases, such as effectiveness of donor screening, the effective recovery of tissue, the timely receipt, recording, review and approval of required medical and testing documentation, and employee loss and turnover in AxoGen’s and its contractor’s recovery department. AxoGen can provide no assurance that tissue recovery or donor medical releases will occur at levels that will maximize processing efficiency and minimize AxoGen’s costs.
If AxoGen does not manage product inventory in an effective and efficient manner, it could adversely affect profitability.
Many factors affect the efficient use and planning of product inventory, such as effectiveness of predicting demand, effectiveness of preparing manufacturing to meet demand, efficiently meeting product mix and product demand requirements and product expiration. AxoGen may be unable to manage its inventory efficiently, keep inventory within expected budget goals, keep its work-in-process inventory on hand or manage it efficiently, control expired product or keep sufficient product on hand to meet demand. Finally, AxoGen can provide no assurance that it can keep inventory costs within its target levels. Failure to do so may harm long term growth prospects.
AxoGen’s payment obligations under the MidCap Financial Trust Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement may adversely affect our financial position and our ability to obtain additional funds, and may increase our vulnerability to economic or business downturns.
As described in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Liquidity and Capital Resources,” on October 25, 2016 (the “Closing Date”), AxoGen and AC, each as borrowers, entered into the term loan agreement (the “MC Term Loan Agreement”) with the lenders party thereto and MidCap Financial Trust (“MidCap”), as administrative agent and lender. Under the MC Term Loan Agreement, MidCap provided AxoGen a term loan in the aggregate principal amount of $21 million (the "Term Loan"). On the Closing Date AxoGen and AC, each as borrows, also entered into a Credit and Security Agreement (Revolving Loan) (the ''Revolving Loan Agreement") with the lenders party thereto and MidCap, as administrative agent and a lender. Under the Revolving Loan Agreement, MidCap has agreed to lend AxoGen up to $10 million under a revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Loan") which amount may be drawn down by AxoGen based upon an available borrowing base. The Revolving Loan may be increased to up to $15 million at AxoGen’s request and with the approval of MidCap. As of December 31, 2017, AxoGen’s borrowing base under the Revolving Loan provided availability of approximately $7.7 million and had an outstanding balance of $4 million. The MC Term Loan Agreement, Revolving Loan Agreement and the indebtedness pursuant thereto are secured by substantially all of AxoGen’s tangible and intangible assets.
Outstanding debt could have important negative consequences to the holders of AxoGen’s securities, including the following:
|
·
| |
a portion of our cash flow from operations will be needed to pay debt service and will not be available to fund future operations; |
|
·
| |
AxoGen is required to maintain certain covenants, the breach of which would result in default under the MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement; |
|
·
| |
AxoGen has increased vulnerability to adverse general economic and industry conditions; and |
|
·
| |
AxoGen may be vulnerable to higher interest rates because interest expense on the Term Loan in limited circumstances could increase. |
Payment requirements under the MC Term Loan Agreement and the Revolving Loan Agreement increase AxoGen’s cash burden. AxoGen’s future operating performance is subject to market conditions and business factors that are beyond its control. If AxoGen’s cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to allow AxoGen to make required payments, AxoGen may have to reduce or delay capital expenditures, sell assets, seek additional capital or restructure or refinance its debt. If AxoGen raises funds by selling additional equity, such sale would result in dilution to its shareholders. There is no assurance that if AxoGen is required to secure funding it can do so on terms acceptable to it, or at all. Failure to pay interest or the principal amount when due would result in a default under the MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement and result in foreclosure on AxoGen’s assets which would have a material adverse effect.
The MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement each contain certain covenants and failure to comply with the terms of such indebtedness could result in a default that could have material adverse consequences for us.
The MC Term Loan Agreement and the Revolving Loan Agreement each contain covenants that place restrictions on AxoGen’s operations, including, without limitation, covenants related to debt restrictions, investment restrictions, dividend restrictions, restrictions on transactions with affiliates and certain revenue covenants. AxoGen’s ability to comply with these covenants may be affected by general economic and industry conditions, as well as market fluctuations and other events beyond AxoGen’s control. AxoGen does not know if it will be able to satisfy all such covenants in the future. AxoGen’s breach of the covenants could result in a default under such agreements. In the event of a default under such agreements, the lender could require AxoGen to repay some of its outstanding debt prior to maturity, and/or to declare all amounts borrowed by it, together with accrued interest, to be due and payable. In the event that this occurs, AxoGen may be unable to repay all such accelerated indebtedness. Any indebtedness that it incurs under the MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement is secured by substantially all of its tangible and intangible assets. If AxoGen defaults under the indebtedness secured by its assets, those assets would be available to the secured creditors to satisfy AxoGen’s obligations to the secured creditors. As of December 31, 2017, AxoGen was in compliance with the loan covenants.
AxoGen incurs costs as a result of operating as a public company, and its management is required to devote substantial time to compliance initiatives.
As a public company, AxoGen incurs legal, accounting and other expenses to comply with relevant securities laws and regulations, including, without limitation, the requirement of establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and corporate governance practices. AxoGen’s management devotes substantial time and financial resources to these compliance initiatives. Failure to comply with public company requirements could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business.
Our business and stock price may be adversely affected if our internal controls are not effective.
Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 requires that public companies conduct a comprehensive evaluation of their internal control over financial reporting. To comply with this statute, each year we are required to document and test our internal control over financial reporting and our management is required to assess and issue a report concerning it.
In our annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, we reported material weaknesses in our internal control as of December 31, 2016 relating to the design and operation of key controls around the calculations of significant judgment and estimates and quarterly cycle count procedures related to consigned inventories. These control deficiencies did not result in any changes of prior period financial statements or previously released financial results. We believe we took appropriate actions to remediate the control deficiencies we identified in these instances.
Although we have taken actions to correct the control deficiencies we identified and to strengthen our internal control over financial reporting, we cannot assure you that we will not discover other material weaknesses in the future or that no material weakness will result from any difficulties, errors, delays or disruptions while we implement and transition to new internal systems. The existence of one or more material weaknesses could result in errors in our financial statements, and substantial costs and resources may be required to rectify these or other internal control deficiencies. If we cannot produce reliable financial reports, investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, the market price of our common stock could decline significantly, we may be unable to obtain additional financing to operate and expand our business and our business and financial condition could be harmed.
Our business and financial performance could be adversely affected, directly or indirectly, by disasters, by terrorist activities or by international hostilities.
Neither the occurrence nor the potential impact of disasters (such as hurricanes and other natural disasters), terrorist activities and international hostilities can be predicted. However, these occurrences could impact us directly as a result of damage to our facilities or by preventing us from conducting our business in the ordinary course, or indirectly as a result of their impact on our customers, suppliers or other counterparties. We could also suffer adverse consequences to the extent that disasters, terrorist activities or international hostilities affect the financial markets or the economy in general or in any particular region.
Our ability to mitigate the adverse consequences of such occurrences is in part dependent on the quality of our resiliency planning, and our ability, if any, to anticipate the nature of any such event that occurs. The adverse impact of disasters or terrorist activities or international hostilities also could be increased to the extent that there is a lack of preparedness on the part of national or regional emergency responders or on the part of other organizations and businesses that we deal with, particularly those that we depend upon but have no control over.
Risks Related to the Regulatory Environment in which AxoGen Operates
AxoGen’s business is subject to continuing regulatory compliance by the FDA and other authorities which is costly and could result in negative effects on its business.
AxoGen is subject to extensive regulation by foreign and domestic government entities and healthcare professionals, such as physicians, hospitals and those to whom and through whom we may market our products. We are subject to scrutiny under various federal, state and territorial laws in the United States and other jurisdictions in which we conduct business. These include, for example, anti-kickback laws, physician self-referral laws, false claims laws, criminal health care fraud laws, and anti-bribery laws such as the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act. Violations of these laws are punishable by criminal and/or civil sanctions, including, in some instances, fines, imprisonment and, within the United States, exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs, including Medicare, Medicaid and Veterans Administration health programs. These laws are administered by, among others, the U.S. Department of Justice (“DOJ”), the Office of Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services, state attorneys general, and their respective counterparts in the applicable foreign jurisdictions in which we conduct business. Many of these agencies have increased their enforcement activities with respect to medical device manufacturers in recent years. There can also be changes to the regulations by foreign and domestic government entities that require AxoGen to update or upgrade business processes or to perform additional validation activities for product or processes. Compliance with such changes can be costly to implement or result in non-compliance and restricting the ability to distribute tissue or sell products that would have a material adverse effect.
Our products are also subject to regulation by the FDA in the U.S. The FDA regulates the development, clinical testing, marketing, distribution, manufacturing, labeling, and promotion of biological products, such as that of AxoGen’s
Avance® Nerve Graft product. The Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is processed and distributed in accordance with FDA requirements for Human Cellular and Tissue-based Products (HCT/P) under 21 CFR Part 1271 regulations, U.S. State regulations. The FDA also regulates medical devices, for example the AxoGuard® products. The FDA requires the approval of a biological product, like the Avance® Nerve Graft product, through a BLA prior to marketing. Although the Avance® Nerve Graft product has not yet been approved by FDA through a BLA, FDA is permitting the product to be distributed, subject to FDA enforcement discretion, provided that AxoGen: (1) transitions to compliance with section 501(a)(2)(B) of the FD&C Act, the cGMP regulations in 21 CFR Parts 210 and 211 and the applicable regulations and standards in 21 CFR Parts 600-610 prior to initiation of a phase 3 clinical trial designed to demonstrate the safety, purity, and potency of the Avance® Nerve Graft; (2) conducts a phase 3 clinical trial to demonstrate safety, purity and potency of the Avance® Nerve Graft under an SPA; (3) continues to comply with the requirements of 21 CFR Part 1271; and (4) exercises due diligence in executing the transition plan. See “Business — Government Regulations — U.S. Government Regulation Review.”
The FDA also regulates medical devices and requires certain medical devices, such as the AxoGuard® products, be cleared through the 510(k) premarket notification process prior to marketing. The FDA’s premarket review process for new and modified existing devices that precedes product marketing can be time consuming and expensive. Some of the future products and enhancements to such products that AxoGen expects to develop and market may require marketing clearance or approval from the FDA.
There can be no assurance, however, that clearance or approval will be granted with respect to any of AxoGen’s device products or enhancements of marketed products or that AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft will achieve an effective IND or ultimately an approved BLA. FDA review of AxoGen’s devices or biological products may encounter significant delays during FDA’s premarket review process that would adversely affect AxoGen’s ability to market its products or enhancements. In addition, there can be no assurance that AxoGen products, including the Avance® Nerve Graft, or enhancements will not be subject to a lengthy and expensive approval process with the FDA.
It is possible that if regulatory clearances or approvals to market a product are obtained from the FDA, the clearances or approvals may contain limitations on the indicated uses of such product and other uses may be prohibited. Product approvals by the FDA can also be withdrawn due to failure to comply with regulatory standards or the occurrence of unforeseen problems following initial approval. Furthermore, the FDA could limit or prevent the distribution of AxoGen products and the FDA has the power to require the recall of such products. FDA regulations depend heavily on administrative interpretation, and there can be no assurance that future interpretations made by the FDA or other regulatory bodies will not adversely affect AxoGen’s operations. AxoGen, and its facilities, may be inspected by the FDA from time to time to determine whether it is in compliance with various regulations relating to specifications, development, documentation, validation, testing, quality control and product labeling. A determination that AxoGen is in violation of such regulations could lead to imposition of civil penalties, including fines, product recalls or product seizures and, in certain cases, criminal sanctions.
The use, misuse or off-label use of AxoGen’s products may harm its reputation or the image of its products in the marketplace, or result in injuries that lead to product liability suits, which could be costly to AxoGen’s business or result in FDA sanctions if the company is deemed to have engaged in off-label promotion. AxoGen is seeking a biologics license through the BLA process for specific uses of Avance® Nerve Graft under specific circumstances. Its promotional materials and training methods must comply with FDA requirements and other applicable laws and regulations, including the prohibition against off-label promotion. AxoGen’s promotion of the AxoGuard® products, which are regulated as medical devices, also must comply with FDA’s requirements and must only use labeling that is consistent with the specific indication(s) for use included in the FDA substantial equivalence order that results in marketing the devices. The Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is processed and distributed in accordance with FDA requirements for (HCT/P) under 21 CFR Part 1271 regulations and is to be dispensed only by or on the order of a licensed physician and is contraindicated for use in any patient in whom soft tissue implants are contraindicated. The FDA does not restrict or regulate a physician’s use of a medical product within the practice of medicine, and AxoGen cannot prevent a physician from using its products for an off-label use. However, the FD&C Act and the FDA’s regulations restrict the kind of promotional communications that may be made about AxoGen’s products and if the FDA determines that AxoGen’s promotional or training materials constitute the unlawful promotion of an off-label use, it could request that AxoGen modify its training or promotional materials and/or subject the Company to regulatory or enforcement actions, including
the issuance of an untitled letter, a warning letter, civil money penalties, seizure, injunction or criminal fines and penalties. Other federal, state or foreign governmental authorities might also take action if they consider AxoGen promotion or training materials to constitute promotion of an uncleared or unapproved use, which could result in significant fines or penalties under other statutory authorities, such as laws prohibiting false claims for reimbursement, or exclusion from participation in federal health programs. In that event, AxoGen’s reputation could be damaged and the use of its products in the marketplace could be impaired.
In addition, there may be increased risk of injury if physicians or others attempt to use AxoGen products off-label. Furthermore, the use of AxoGen’s product for indications other than those for which its products have been approved, cleared or licensed by the FDA may not effectively treat the conditions not referenced in product indications, which could harm AxoGen’s reputation in the marketplace among physicians and patients. Physicians may also misuse AxoGen’s product or use improper techniques if they are not adequately trained in the particular use, potentially leading to injury and an increased risk of product liability. Product liability claims are expensive to defend and could divert management’s attention from its primary business and result in substantial damage awards against AxoGen. Any of these events could harm AxoGen’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product is currently allowed to be distributed pursuant to a transition plan with the FDA and a change in position by the FDA regarding its use of enforcement discretion to permit the sale of Avance® Nerve Graft would have a material adverse effect on AxoGen.
The FDA considers AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product to be a biological product, subject to BLA approval requirements. Although the Avance® Nerve Graft product has not yet been approved by FDA through a BLA, AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft product is currently distributed under the controls applicable to a HCT/P pursuant to section 361 of the Public Health Service Act and 21 CFR Part 1271 of FDA’s regulations, subject to FDA’s enforcement discretion and AxoGen’s compliance with a transition plan established by the FDA. See “Business — Government Regulations — U.S. Government Regulation Review.” AxoGen has continued to communicate with the FDA’s CBER since the acceptance of the transition plan on clinical trial design, preclinical studies, Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls (“CMC”) for the Avance® Nerve Graft, and other issues related to the effective IND Subject to the FDA’s enforcement discretion, AxoGen can commercially distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft until the FDA makes a final determination on an Avance® Nerve Graft BLA submission, assuming AxoGen remains in compliance with the transition plan and exercises due diligence in executing the transition plan. In the event that the FDA becomes dissatisfied with AxoGen’s progress or actions with respect to the transition plan or the FDA changes its position for any reason regarding its use of enforcement discretion to permit AxoGen to distribute Avance® Nerve Graft product in accordance with the transition plan, AxoGen would no longer be able to distribute Avance® Nerve Graft, which would have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s operations and financial viability. In addition, if AxoGen does not meet the conditions of the transition plan, or fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, the FDA could impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures, injunctions or product recalls and, in certain cases, criminal sanctions. These consequences also would have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s operations and financial viability.
AxoGen’s business is subject to continuing compliance to standards by various accreditation and registration bodies which is costly and loss of accreditation or registration could result in negative effects on its business.
AxoGen is subject to accreditation such as that by the AATB and as a Verified-Accredited Wholesale Distributor. AxoGen has registration requirements such as that with the National Association of Boards of Pharmacy and ISO 13485 registration bodies. These accreditations and regulations can affect distribution and sale of AxoGen products on a state-by-state basis, within the United States and also affects distribution and sale of AxoGen products outside of the United States. The loss of accreditation or registration could keep AxoGen from selling and distributing its product which may have negative effects on its business.
AxoGen’s AxoGuard® and Avive® products are subject to FDA and other regulatory requirements.
AxoGen’s AxoGuard® product line is regulated as a medical device under the FD&C Act and subject to premarket notification and clearance requirements under section 510(k) of the FD&C Act, 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation) and other FDA regulations. AxoGen distributes for Cook Biotech the AxoGuard® product line and Cook
Biotech is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the AxoGuard® Connector and Protector product lines. Cook Biotech has obtained a 510(k) premarket clearance from the FDA for porcine (pig) small intestine submucosa for the repair of peripheral nerve discontinuities where gap closure can be achieved by flexion of the extremity. Cook Biotech has also obtained a 510(k) premarket clearance for the AxoGuard® Nerve Protector for the repair of peripheral nerve damage in which there is no gap or where a gap closure is achieved by flexion of the extremity. AxoGen is responsible for the regulatory compliance of the AxoGuard® Nerve Cap. AxoGen has obtained a 510(k) premarket clearance for AxoGuard® Nerve Cap to protect a peripheral nerve end and separate the nerve from the surrounding environment to reduce the development of symptomatic or painful neuroma. If AxoGen or Cook Biotech fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, the FDA could deny or withdraw 510(k) clearance for the AxoGuard® products, or impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures or product recalls and, in certain cases, criminal sanctions.
Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane is processed and distributed in accordance with U.S. FDA requirements for Human Cellular and Tissue-based Products (HCT/P) under 21 CFR Part 1271 regulations, U.S. State regulations and the guidelines of the American Association of Tissue Banks (AATB). If AxoGen fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, the FDA could require AxoGen to stop providing Avive®, or impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures or product recalls and, in certain cases, criminal sanctions.
AxoGen’s AxoTouch® and AcroVal® products are subject to FDA and other regulatory requirements.
AxoGen’s AxoTouch® and AcroVal® products are regulated as medical devices under the FD&C Act and subject to premarket notification and clearance requirements under section 510(k) of the FD&C Act, 21 CFR Part 820 (Quality System Regulation) and other FDA regulations. If AxoGen fails to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, the FDA could deny or withdraw 510(k) clearance for these products, or impose civil penalties, including fines, product seizures or product recalls and, in certain cases, criminal sanctions.
Defective AxoGen product could lead to recall or other negative business conditions.
If AxoGen’s products are defective or otherwise pose safety risks, the FDA could require their recall or AxoGen may initiate a voluntary recall of its products. The FDA may require recall of a marketed medical device product, such as the AxoGuard® products, in the event that it determines the medical device presents a reasonable probability of serious adverse health consequences or death. However, most device recalls do not rise to this level of health significance and result from voluntary action. The FDA has authority to recall biological products when a batch, lot or other quantity of the product presents an imminent or substantial hazard to the public health. However, in such circumstances, the FDA usually initially requests, voluntary recalls of biological products, such as the Avance® Nerve Graft. If a company does not comply with an FDA request for a recall, the FDA can order one under the above-referenced circumstances or take other enforcement actions, such as product seizure. In addition, manufacturers may, on their own initiative, recall a product to remove or correct a deficiency or to remedy a violation of the FD&C Act that may pose a risk to health. A government-mandated, government-requested or voluntary recall could occur as a result of an unacceptable risk to health, reports of safety issues, failures, manufacturing errors, design or labeling defects or other deficiencies and issues. Recalls and other field corrections for any of AxoGen’s products would divert managerial and financial resources and have an adverse effect on its business, results of operations and financial condition. A recall could harm AxoGen’s reputation with customers and negatively affect its sales. AxoGen may initiate recalls involving some of its products in the future that it determines do not require notification of the FDA. If the FDA were to disagree with AxoGen’s determinations, it could request that it report those actions as recalls, and take regulatory or enforcement action against AxoGen or the product.
If AxoGen’s products cause or contribute to a death, a serious injury or any adverse reaction involving a communicable disease related to its products, or malfunction in certain ways, it will be subject to reporting regulations, which can result in voluntary corrective actions or agency enforcement actions. See “Business — Regulation — Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws — Pervasive and False Claims.” If AxoGen fails to report these events to the FDA within the required timeframes, or at all, the FDA could take regulatory or enforcement action against AxoGen. Any adverse event involving AxoGen’s products could result in future voluntary corrective actions, such as recalls or customer notifications, or agency action, such as inspection, mandatory recall or other enforcement action. Any corrective action, whether voluntary or involuntary, as
well as AxoGen defending itself in a lawsuit, would require the dedication of time and capital, distract management from operating its business, and may harm AxoGen’s reputation, business, results of operations and financial condition.
AxoGen’s operations must comply with FDA and other governmental requirements.
AxoGen’s operations require it to comply with the FDA’s and other governmental authorities’ laws and regulations regarding the manufacture and production of medical products, which is costly and could subject AxoGen to enforcement action. See “Business — Government Regulations — Education Grants, U.S. Anti-kickback, False Claims and Other Healthcare Fraud and Abuse Laws — Fraud, Abuse and False Claims”. Any of these actions could impair AxoGen’s ability to produce its products in a cost-effective and timely manner in order to meet customer demands. AxoGen may also be required to bear other costs or take other actions that may have an adverse impact on its future revenue and its ability to generate profits. Furthermore, AxoGen’s key material suppliers, licensors and or other contractors may not continue to be in compliance with all applicable regulatory requirements, which could result in AxoGen’s failure to produce its products on a timely basis and in the required quantities, if at all.
Distribution of AxoGen human tissue products outside the U.S. are subject to foreign regulatory requirements that vary from country to country. In the European Union (“E.U.”), human tissue regulations, if applicable, differ from one E.U. member state to the next. Because of the absence of a harmonized regulatory framework and the proposed regulation for advanced therapy medicinal products in the E.U., as well as for other countries, the approval process for human derived cell or tissue based medical products may be extensive, lengthy, expensive and unpredictable. AxoGen products will be subject to E.U. member states’ regulations that govern the donation, procurement, testing, coding, traceability, processing, preservation, storage, and distribution of human tissues and cells and cellular or tissue-based products. In addition, some E.U. member states have their own tissue banking regulations. The inability to meet foreign regulatory requirements could materially affect AxoGen’s future growth and compliance with such requirements could place a significant financial burden on AxoGen.
In addition, the United Kingdom voted to exit the European Union (“Brexit”) and the timing and scope remain unclear. AxoGen’s current notified body for its CE Mark for AxoGuard® products is in the United Kingdom. To date there is no business disruption, but AxoGen cannot be sure what changes could occur. If the notified body must change to a E.U. member there could be an interruption in sales in the E.U. Cost of regulatory compliance with both the United Kingdom and E.U. could be significant and time consuming.
Finally, regulations in both the United States and other countries are subject to constent change. There can be no assurance that AxoGen can meet the requirements of future regulations or that compliance with current regulations assures future capability to distribute and sell its products.
Clinical trials can be long, expensive and ultimately uncertain which could jeopardize AxoGen’s ability to obtain regulatory approval and continue to market its Avance® Nerve Graft product.
AxoGen is required to perform a clinical trial for its Avance® Nerve Graft under FDA’s statutory requirements to obtain approval of a BLA for the product. This trial is expensive, is expected to take several years to execute, and is subject to factors within and outside of AxoGen’s control. The outcome of this trial is uncertain.
AxoGen submitted an IND for the Avance® Nerve Graft in April 2013 and received FDA approval in March 2015. The phase 3 clinical trial was initiated in the second quarter of 2015. Additionally, AxoGen was audited by the FDA at its processing facility in March 2013, March 2015 and October 2016 and its Distribution Facility in October 2015. The quality system was found to be in compliance with 21 CFR Part 1271. AxoGen is working to ensure compliance with the applicable regulations by having ongoing discussions on the transition of the quality system to 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 regulations with the FDA. Final determination of regulatory compliance with 21 CFR Parts 210/211 and 600-610 will be made during FDA’s pre-license inspection as part of the BLA review. If the FDA is unable to agree with AxoGen, or AxoGen is unable to meet the standards required of it by the FDA, regarding preclinical studies, clinical studies and CMC, the approval of AxoGen’s BLA would not occur or be delayed.
AxoGen continues to work diligently with the FDA and, in this context, continues to distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft products. The FDA will end the period of enforcement discretion upon a final determination of AxoGen’s BLA submission or if the FDA finds that AxoGen does not meet the conditions for the transition plan or is not exercising due diligence in executing the transition (e.g., not progressing toward the IND submission, study completion, or BLA submission in a timely or adequate fashion). If final action on the BLA is negative or AxoGen is found to not meet the conditions for the transition plan or its execution, AxoGen will not be able to continue to distribute the Avance® Nerve Graft, and AxoGen’s business and financial condition will be materially adversely affected.
The results of non-clinical studies do not necessarily predict future clinical trial results and predecessor clinical trial results may not be repeated in subsequent clinical trials. Additionally, the FDA may disagree with AxoGen’s interpretation of the data from its non-clinical studies and clinical trials and may require the company to pursue additional non-clinical studies or clinical trials, or not approve AxoGen’s BLA. If AxoGen is unable to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of its product through its clinical trials, it will be unable to obtain regulatory approval to market the Avance® Nerve Graft and will not be able to continue to provide it.
AxoGen will rely on third parties to conduct its clinical trial and they may not perform as contractually required or expected.
AxoGen will rely on third parties, such as contract research organizations (“CROs”), medical institutions, clinical investigators and contract laboratories to conduct its clinical trial and certain nonclinical studies. AxoGen and its CROs are required to comply with all applicable regulations governing clinical research, including good clinical practice, or GCP. The FDA enforces these regulations through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators, CROs and trial sites. If AxoGen or its CROs fail to comply with applicable FDA regulations, the data generated in its clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA may require AxoGen to perform additional clinical trials before approving its applications. AxoGen cannot be certain that, upon inspection, the FDA and similar foreign regulatory authorities will determine that AxoGen’s clinical trial complies or complied with clinical trial regulations, including GCP. In addition, AxoGen’s clinical trial must be conducted with product produced under applicable cGMP regulations. Failure to comply with the clinical trial regulations may require AxoGen to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or regulatory obligations or meet expected deadlines, if these third parties need to be replaced, or if the quality or accuracy of the data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to AxoGen’s clinical protocols or regulatory requirements or for other reasons, AxoGen’s non-clinical development activities or clinical trials may be extended, delayed, suspended or terminated, and it would not be able to obtain regulatory approval for its products on a timely basis, if at all, and its business, results of operations, financial condition and growth prospects would be adversely affected. Furthermore, AxoGen’s third party clinical trial investigators may be delayed in conducting its clinical trials for reasons outside of their control.
U.S. governmental regulation could restrict the use of AxoGen’s Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane product, restrict AxoGen’s procurement of tissue or increase costs.
In addition to the FDA requirements for biological products, the Avance® Nerve Graft will continue to be subject to, as is the Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, various requirements for human tissue under 21 CFR Part 1271 controls. Human tissues intended for transplantation have been regulated by the FDA since 1993. In May 2005, three new comprehensive regulations went into effect that address manufacturing activities associated with HCT/P. The first regulation requires that companies that produce and distribute HCT/Ps register with the FDA. The second regulation provides criteria that must be met for donors to be eligible to donate tissues and is referred to as the “Donor Eligibility” rule. The third regulation governs the processing and distribution of the tissues and is often referred to as the “Current Good Tissue Practices” rule. The Current Good Tissue Practices rule covers all stages of allograft processing, from procurement of tissue to distribution of final allografts. Together, the three basic requirements of 21 CFR Part 1271 are designed to ensure that sound, high quality practices are followed to reduce the risk of tissue contamination and of communicable disease transmission to recipients. These regulations increased regulatory scrutiny within the industry in which AxoGen operates and have led to increased enforcement actions, which affects the conduct of its business. In addition, new guidance was issued by the FDA in late 2017 on Regulatory Considerations for Human Cells, Tissues, and Cellular and Tissue-Based Products: Minimal Manipulation and Homologous Use. FDA actions interpreting the
guidance will need to be followed closely, and the potential implications on the regulatory status of Avive® and future HCT/P products is being evaluated by the Company.
Additional regulations or guidance documents may be implemented by the FDA in the future. These changes may require new documentation requirements, process changes or testing that could increase costs and regulatory burden. See “Business — Government Regulations.” These regulations can also increase the cost of tissue recovery activities. Finally, Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane are subject to certain state and local regulations, as well as compliance with the standards of the tissue bank industry’s accrediting organization, the AATB.
The procurement and transplantation of allograft nerve tissue is also subject to federal law pursuant to the National Organ Transplant Act (“NOTA”), a criminal statute which prohibits the purchase and sale of human organs used in human transplantation, including nerve and related tissue, for “valuable consideration.” NOTA only permits reasonable payments associated with the removal, transportation, processing, preservation, quality control, implantation and storage of human nerve tissue. AxoGen makes payments to certain of its clients and tissue banks for their services related to recovering allograft nerve and umbilical cord tissue on its behalf. If NOTA is interpreted or enforced in a manner which prevents AxoGen from receiving payment for services it renders, or which prevents it from paying tissue banks or certain of its clients for the services they render for AxoGen, its business could be materially and adversely affected.
AxoGen has engaged, through its marketing employees, independent sales agents and sales representatives in ongoing efforts designed to educate the medical community as to the benefits of AxoGen products, and AxoGen intends to continue its educational activities. Although AxoGen believes that NOTA permits payments in connection with these educational efforts as reasonable payments associated with the processing, transportation and implantation of AxoGen products, payments in connection with such education efforts are not exempt from NOTA’s restrictions and AxoGen’s inability to make such payments in connection with its education efforts may prevent it from paying AxoGen sales representatives for their education efforts and could adversely affect AxoGen’s business and prospects. No federal agency or court has determined whether NOTA is, or will be, applicable to every allograft nerve tissue-based material which AxoGen’s processing technologies may generate. Assuming that NOTA applies to AxoGen’s processing of allograft nerve and umbilical cord tissue, AxoGen believes that it complies with NOTA, but there can be no assurance that more restrictive interpretations of, or amendments to, NOTA will not be adopted in the future, which would call into question one or more aspects of AxoGen’s method of operations.
Other regulatory entities include state agencies with statutes covering tissue banking. Regulations issued by Florida, New York, California and Maryland, among other states, are particularly relevant to AxoGen’s business. Most states do not currently have tissue banking regulations. However, incidents of allograft related issues in the industry may stimulate the development of regulation in other states. It is possible that third parties may make allegations against AxoGen or against donor recovery groups or tissue banks about non-compliance with applicable FDA regulations or other relevant statutes or regulations. Allegations like these could cause regulators or other authorities to take investigative or other action, or could cause negative publicity for AxoGen’s business and the industry in which it operates.
Healthcare policy changes may have a material adverse effect on AxoGen.
In March 2010, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act, which Act substantially changes the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and encourages improvements in the quality of healthcare items and services. This Act significantly impacts the biotechnology and medical device industries and could have a material adverse impact on numerous aspects of AxoGen’s business.
This Act includes, among other things, the following measures:
|
·
| |
a 2.3% excise tax on any entity that manufactures or imports medical devices offered for sale in the U.S., with limited exceptions, beginning in 2013, referred to as the Device Tax, which has been suspended through 2019; |
|
·
| |
a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research; |
|
·
| |
new reporting and disclosure requirements on healthcare manufacturers for any “transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as reporting of certain physician ownership interests (“Sunshine Act”); |
|
·
| |
payment system reforms, including a national pilot program on payment bundling to encourage hospitals, physicians and other providers to improve the coordination, quality and efficiency of certain healthcare services through bundled payment models; |
|
·
| |
an independent payment advisory board that will submit recommendations to reduce Medicare spending if projected Medicare spending exceeds a specified growth rate; and |
|
·
| |
a new abbreviated pathway for the licensure of biologic products that are demonstrated to be biosimilar or biosimilar and interchangeable with a licensed biologic product. |
There are also a number of states (such as Vermont, Massachusetts, Minnesota) with their own Sunshine Acts that implement the reporting and disclosure requirements on healthcare manufacturers for any “transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as reporting of certain physician ownership interests.
In the future, there may continue to be additional proposals relating to the reform of the U.S. healthcare system. Certain of these proposals could limit the prices AxoGen is able to charge for its products or the amounts of reimbursement available for its products and could also limit the acceptance and availability of its products. The adoption of some or all of these proposals could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Additionally, initiatives sponsored by government agencies, legislative bodies and the private sector to limit the growth of healthcare costs, including price regulation and competitive pricing, are ongoing in markets where AxoGen does business. AxoGen could experience an adverse impact on operating results due to increased pricing pressure in the U.S. and in other markets. Governments, hospitals and other third-party payors could reduce the amount of approved reimbursement for AxoGen’s products or deny coverage altogether. Reductions in reimbursement levels or coverage or other cost-containment measures could unfavorably affect AxoGen’s future operating results.
Risks Related to AxoGen’s Intellectual Property
Failure to protect AxoGen’s IP rights could result in costly and time-consuming litigation and its loss of any potential competitive advantage.
AxoGen’s success will depend, to a large extent, on its ability to successfully obtain and maintain patents, prevent misappropriation or infringement of IP, maintain trade secret protection, and conduct operations without violating or infringing on the IP rights of third parties. See “Business — Intellectual Property.” There can be no assurance that AxoGen’s patented and patent pending technologies will provide it with a competitive advantage, that AxoGen will be able to develop or acquire additional technology that is patentable, or that third parties will not develop and offer technologies which are similar to AxoGen’s. Moreover, AxoGen can provide no assurance that confidentiality agreements with its employees, consultants and other parties, trade secrecy agreements or similar agreements intended to protect unpatented technology will provide the intended protection. IP litigation is extremely expensive and time-consuming, and it is often difficult, if not impossible, to predict the outcome of such litigation. A failure by AxoGen to protect its IP could have a materially adverse effect on its business and operating results and its ability to successfully compete in its industry.
Future protection for AxoGen’s proprietary rights is uncertain which may impact its ability to successfully compete in its industry.
The degree of future protection for AxoGen’s proprietary rights is uncertain. AxoGen cannot ensure that:
|
·
| |
it, or its licensors, were the first to make the inventions covered by each of AxoGen’s patents; |
|
·
| |
it, or its licensors, were the first to file patent applications for these inventions; |
|
·
| |
others will not independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of AxoGen’s technologies; |
|
·
| |
any of AxoGen’s pending patent applications will result in issued patents; |
|
·
| |
any of AxoGen’s issued patents or those of its licensors will be valid and enforceable; |
|
·
| |
any patents issued to AxoGen or its collaborators will provide any competitive advantages or will not be challenged by third parties; |
|
·
| |
it will develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; |
|
·
| |
the patents of others will not have a material adverse effect on its business rights; or |
|
·
| |
the measures AxoGen relies on to protect its IP underlying our products may not be adequate to prevent third parties from using its technology, all of which could harm its ability to compete in the market. |
AxoGen’s commercial success depends in part on its ability and the ability of its collaborators and licensors to avoid infringing patents and proprietary rights of third parties which could expose it to litigation or commercially unfavorable licensing arrangements. Third parties may accuse AxoGen or collaborators and licensors of employing their proprietary technology in AxoGen products, or in the materials or processes used to research or develop AxoGen products, without authorization. Any legal action against AxoGen collaborators, licensors or it claiming damages and/or seeking to enjoin AxoGen’s commercial activities relating to the affected products, materials and processes could, in addition to subjecting AxoGen to potential liability for damages, require it or its collaborators and licensors to obtain a license to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes or to manufacture or market the affected products. AxoGen cannot predict whether it or its collaborators and licensors would prevail in any of these actions or whether any license required under any of these patents would be made available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If AxoGen were unable to obtain such a license, it and its collaborators and licensors may be unable to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes, or manufacture or market the affected products, or AxoGen may be obligated by a court to pay substantial royalties and/or other damages to the patent holder. Even if AxoGen were able to obtain such a license, the terms of such a license could substantially reduce the commercial value of the affected product or products and impair AxoGen’s prospects for profitability. Accordingly, AxoGen cannot predict whether, or to what extent, the commercial value of the affected product or products or AxoGen’s prospects for profitability may be harmed as a result of any of the liabilities discussed above. Furthermore, infringement and other IP claims, with or without merit, can be expensive and time-consuming to litigate and can divert management’s attention from its core business. AxoGen and its licensors may be unable to obtain and enforce IP rights to adequately protect its products and related IP.
The patent protection for our products may expire before we are able to maximize their commercial value which may subject us to increased competition and reduce or eliminate our opportunity to generate product revenue.
The patents for our commercialized products and products in development have varying expiration dates and, when these patents expire, we may be subject to increased competition and we may not be able to recover our development costs. For example, the material U.S. patents covering the formulations used in our AxoGuard® product line, which are held by Cook Biotech, have expired. Expiration of these patents could adversely affect our ability to successfully execute our business strategy to maximize the value of AxoGuard® products and could negatively impact our future financial condition and results of operations.
Others may claim an ownership interest in AxoGen IP which could expose it to litigation and have a significant adverse effect on its prospects.
A third party may claim an ownership interest in one or more of AxoGen’s patents or other IP. A third party could bring legal actions against AxoGen claiming it infringes their patents or proprietary rights, and seek monetary damages and/or enjoin clinical testing, manufacturing and marketing of the affected product or products. While AxoGen believes it owns the right, title and interest in the patents for which it or its licensors have applied and AxoGen’s other IP (including that which is licensed from third parties), and is presently unaware of any claims or assertions by third-parties with respect to AxoGen’s patents or IP, it cannot guarantee that a third party will not assert a claim or an interest in any of such patents or IP. If AxoGen becomes involved in any litigation, it could consume a substantial portion of AxoGen’s resources and cause a significant diversion of effort by AxoGen’s technical and management personnel regardless of the outcome of the litigation. If any of these actions were successful, in addition to any potential liability for damages, AxoGen could be required to obtain a license to continue to manufacture or market the affected product, in which case AxoGen may be required to pay substantial royalties or grant cross-licenses to AxoGen’s patents. AxoGen cannot, however, assure you that any such license will be available on acceptable terms, if at all. Ultimately, AxoGen could be
prevented from commercializing a product or be forced to cease some aspect of its business operations as a result of claims of patent infringement or violation of other IP rights, which could have a material and adverse effect on AxoGen’s business, financial condition, and results of operations. Further, the outcome of IP litigation is subject to uncertainties that cannot be adequately quantified in advance, including the demeanor and credibility of witnesses and the identity of the adverse party. This is especially true in IP cases that may turn on the testimony of experts as to technical facts upon which experts may reasonably disagree.
AxoGen depends on maintenance of exclusive licenses.
AxoGen depends fundamentally on keeping and satisfying the terms of exclusive licenses of its nerve repair technologies from UFRF and UTA where the original technologies are purported to have been invented. Though AxoGen makes an effort to follow these agreements strictly, a disagreement between AxoGen and either party could have a negative impact on its ability to operate its business effectively. In addition, AxoGen could learn that the technologies it has licensed from UFRF and UTA do not perform as purported, are not efficacious, or are not the property of UFRF or UTA, or some similar problem with the license, any of which would have an immediate and negative impact on AxoGen’s business.
AxoGen Trademarks are Valuable
In the U.S. and other countries, we currently hold issued trademark registrations and have trademark applications pending, any of which may be the subject of a governmental or third party objection, which could prevent the maintenance or issuance of the same. As our products mature, our reliance on our trademarks to differentiate us from our competitors increases and as a result, if we are unable to prevent third parties from adopting, registering or using trademarks and trade dress that infringe, dilute or otherwise violate our trademark rights, our business could be materially adversely affected.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
An active trading market in our common stock may not be maintained.
The trading market in our common stock has been extremely volatile. The quotation of our common stock on The NASDAQ Capital Market does not assure that a meaningful, consistent and liquid trading market will exist. We cannot predict whether an active market for our common stock will be maintained in the future. An absence of an active trading market could adversely affect our shareholders’ ability to sell our common stock at current market prices in short time periods, or possibly at all. Additionally, market visibility for our common stock may be limited and such lack of visibility may have a depressive effect on the market price for our common stock. As of December 31, 2017, approximately 8.56% of our outstanding shares of common stock was held by our officers, directors, beneficial owners of 5% or more of our securities and their respective affiliates, which adversely affects the liquidity of the trading market for our common stock, in as much as federal securities laws restrict sales of our shares by these shareholders. If our affiliates continue to hold their shares of common stock, there will be limited trading volume in our common stock, which may make it more difficult for investors to sell their shares or increase the volatility of our stock price.
The price of AxoGen’s common stock could be highly volatile due to a number of factors, which could lead to losses by investors and costly securities litigation.
Our common stock is listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “AXGN.” The stock market in general, and the market for medical technology companies in particular, have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The trading price of our common stock has experienced substantial volatility and is likely to continue to be highly volatile in response to a number of factors including, without limitation, the following:
|
·
| |
limited daily trading volume resulting in the lack of a liquid market; |
|
·
| |
fluctuations in price and volume due to investor speculation and other factors that may not be tied to the financial performance of AxoGen; |
|
·
| |
performance by AxoGen in the execution of its business plan; |
|
·
| |
actual or anticipated variations in our operating results; |
|
·
| |
announcements of developments by us or our competitors; |
|
·
| |
market conditions in our industry; |
|
·
| |
announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments; |
|
·
| |
adoption of new accounting standards affecting our industry; |
|
·
| |
additions or departures of key personnel; |
|
·
| |
introduction of new products by us or our competitors; |
|
·
| |
sales of our common stock or other securities in the open market; |
|
·
| |
regulatory developments in both the United States and foreign countries; |
|
·
| |
performance of products sold and advertised by licensees in the marketplace; |
|
·
| |
economic and other external factors; |
|
·
| |
period-to-period fluctuations in financial results; and |
|
·
| |
other events or factors, including the other factors described in this “Risk Factors” section, many of which are beyond our control. |
The stock market is subject to significant price and volume fluctuations. In the past, and several recent situations, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has been initiated against such company. Litigation initiated against us, whether or not successful, could result in substantial costs and diversion of our management’s attention and resources, which could harm our business and financial condition.
We do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
The operation and expansion of our business will continue to require funding. In addition, the MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement prohibit us from paying cash dividends to our shareholders. Accordingly, we do not anticipate that we will pay any cash dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon results of operations, financial condition, contractual restrictions, restrictions imposed by applicable law and other factors our board of directors deems relevant. Accordingly, if any investor purchases shares of common stock, realization of a gain on such investment will depend on the appreciation of the price of our common stock, which may never occur. Investors seeking cash dividends in the foreseeable future should not purchase our common stock.
Anti-takeover provisions in Minnesota law may deter acquisition bids for us that you might consider favorable.
We are governed by the provisions of Sections 302A.671, 302A.673 and 302A.675 of the Minnesota Business Corporation Act (the “MBCA”). These provisions may discourage a negotiated acquisition or unsolicited takeover of us and deprive our shareholders of an opportunity to sell their common stock at a premium over the market price.
In general, Section 302A.671 of the MBCA provides that a corporation’s shares acquired in a control share acquisition have no voting rights unless voting rights are approved in a prescribed manner. A “control share acquisition” is a direct or indirect acquisition of beneficial ownership of shares that would, when added to all other shares beneficially owned by the acquiring person, entitle the acquiring person to have voting power of 20% or more in the election of directors.
In general, Section 302A.673 of the MBCA prohibits a public Minnesota corporation from engaging in a business combination with an interested shareholder for a period of four years after the date of the transaction in which the person became an interested shareholder, unless the business combination is approved in a prescribed manner. The term “business combination” includes mergers, asset sales and other transactions resulting in a financial benefit to the interested shareholder. An “interested shareholder” is a person who is the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 10% or more of a corporation’s voting stock or who is an affiliate or associate of the corporation, and who, at any time within four years before the date in question, was the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 10% or more of the
corporation’s voting stock. Section 302A.673 does not apply if a committee of our Board of Directors consisting of all of its disinterested directors (excluding current and former officers) approves the proposed transaction or the interested shareholder’s acquisition of shares before the interested shareholder becomes an interested shareholder.
If a tender offer is made for our common stock, Section 302A.675 of the MBCA precludes the offeror from acquiring additional shares of stock (including in acquisitions pursuant to mergers, consolidations or statutory share exchanges) within two years following the completion of the tender offer, unless shareholders selling their shares in the later acquisition are given the opportunity to sell their shares on terms that are substantially the same as those contained in the earlier tender offer. Section 302A.675 does not apply if a committee of our Board of Directors consisting of all of its disinterested directors (excluding its current and former officers) approves the proposed acquisition before any shares are acquired pursuant to the earlier tender offer.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
On March 16, 2016, AxoGen Corporation, a Delaware corporation and wholly owned subsidiary of AxoGen, Inc. (“AC”) entered into the Fourth Amendment to Lease (“Fourth Amendment”) with SNH Medical Office Properties Trust, a Maryland real estate investment trust (“SNH”). SNH is the landlord of AC’s currently leased 11,761 square foot corporate headquarters facility at 13631 Progress Boulevard, Suite 400, Alachua, Florida 32615 (the “Current Premises”) pursuant to that certain lease dated as of February 6, 2007, as amended (the “Lease”). The Fourth Amendment expands the Current Premises by 7,050 square feet (the “Expansion Premises”). The Fourth Amendment also provides that the Expiration Date (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) of the Lease will be extended to approximately five years from the Occupancy Date (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) which was June 2016. The original expiration date of the Current Premises remains unchanged; provided, however, that AC shall have the right to extend the Current Premises Term (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) for three additional periods (the “Current Premises Extended Term”), the first such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2018 and end on October 31, 2019, the second such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2019 and end on October 31, 2020, and the third such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2020 and end on the Expiration Date. AC also has the right to extend the term of the then current Leased Premises (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) for an additional period of five years commencing on the day immediately after the Expiration Date.
AC’s annual cost of the Current Premises and Expansion Premises ranges from approximately $248,000 to $324,000 per year over the life of the lease.
On January 23, 2017 AC entered into a lease (the “13709 Lease”) for a five-year term commencing on April 1, 2017 with SNH, for 1,431 square feet at 13709 Progress Boulevard, Alachua, Florida 32615. Pursuant to the 13709 Lease, AC uses the space for general office and biomedical research. The 13709 Lease has a term of approximately five years with rent payments commencing on the earlier of April 1, 2017 or the “Substantial Completion Date” (as defined in the 13709 Lease). AC’s annual cost of the premises will range from approximately $26,000 to $29,000 over the life of the 13709 Lease.
On October 25, 2013, AC entered into a commercial lease with Ja-Cole L.P. (“Ja-Cole”). Under the terms of the commercial lease AC occupied 5,400 square feet of warehouse/office space comprising the Burleson, Texas Distribution Facility until November 30, 2016 at an annual cost of $43,200. On April 21, 2015, AC entered into a new commercial lease, as amended by the addendum on such date (as amended, the “Commercial Lease”), with Ja-Cole. The Commercial Lease superseded and replaced the original lease with Ja-Cole dated October 25, 2013. Under the terms of the new Commercial Lease, AC leased an additional 2,100 square feet of warehouse space at the Distribution Facility. The Commercial Lease is for a three-year term expiring April 21, 2018. On October 25, 2016, AC, entered into Commercial Lease Amendment 2 (the “Ja-Cole Amendment”), to the Commercial Lease. Under the terms of the Ja-Cole Amendment, AC leased an additional 2,500 square feet of warehouse/office space at the Distribution Facility. The
Distribution Facility now comprises a total of 10,000 square feet, all of which, pursuant to the Ja-Cole Amendment, will be leased until March 31, 2019. The annual rental cost of the Distribution Facility is now approximately $88,000.
The Distribution Facility houses raw material storage and product distribution while allowing same day order fulfillment for both the east and west coasts of the United States.
On August 6, 2015, AC entered into a License and Services Agreement (the “CTS Agreement”) with Community Blood Center (d/b/a Community Tissue Services) (“CTS”), Dayton, Ohio, an FDA registered tissue establishment. Processing of the Avance® Nerve Graft pursuant to the CTS Agreement began in February 2016. The CTS Agreement is for a five-year term, subject to earlier termination by either party for cause (subject to the non-terminating party’s right to cure, in certain circumstances), or without cause upon 18 months’ notice. Under the CTS Agreement, AC pays CTS a facility fee for clean room/manufacturing, storage and office space. CTS also provides services in support of AC’s manufacturing such as routine sterilization of daily supplies, providing disposable supplies, microbial services and office support.
In addition, AxoGen leases space and maintains records at certain other facilities, including the Company’s prior corporate headquarters at 1407 South Kings Highway, Texarkana, Texas 75501.
The aggregate cost of all of the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ properties is approximately $494,000 per year. AxoGen believes that its facilities will be sufficient to operate its business for the next 12 months and that current lease obligations will not change materially.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
AxoGen and its subsidiaries do not have any active or pending material legal proceedings.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
None.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED SHAREHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
AxoGen’s common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “AXGN.” On February 26, 2018, the last reported closing sale price of the Company common stock on the NASDAQ Capital Market was $29.50 per share.
The following table sets forth, for each of the calendar periods indicated, the high and low sales price of the Company’s common stock on the NASDAQ Capital Market.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
Year Ended
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2017
|
|
December 31, 2016
|
|
|
|
|
High
|
|
Low
|
|
High
|
|
Low
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter
|
|
$
|
11.25
|
|
$
|
8.75
|
|
$
|
5.60
|
|
$
|
4.52
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Second Quarter
|
|
$
|
16.90
|
|
$
|
10.05
|
|
$
|
6.88
|
|
$
|
4.90
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Third Quarter
|
|
$
|
19.45
|
|
$
|
14.30
|
|
$
|
9.88
|
|
$
|
6.41
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fourth Quarter
|
|
$
|
28.90
|
|
$
|
18.10
|
|
$
|
9.28
|
|
$
|
7.65
|
|
Dividend Policy
AxoGen currently intends to retain earnings, if any, to finance the growth and development of its business, and does not expect to pay any cash dividends to its shareholders in the foreseeable future. In addition, the MC Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement prohibit AxoGen from paying cash dividends to its shareholders. AxoGen did not declare any cash dividends on its common stock in 2016 and 2017.
Shareholders
As of February 26, 2018, the Company had 34,496,854 shares of common stock outstanding, and approximately 272 common shareholders of record, based upon information received from our stock transfer agent. However, this number does not include beneficial owners whose shares were held of record by nominees or broker dealers. The Company estimates that there are more than 8,800 individual owners.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total shareholder return on our common stock for the period from December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2017 with (i) the Nasdaq Stock Market Composite Index; and (ii) the Nasdaq Stock Market Biotechnology Index. The graph assumes an investment of $100 in our common stock and the respective indices for the period of December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2017. The comparisons set forth in the graph are provided pursuant to SEC rules and are not intended to forecast or be indicative of the future performance of our common stock or either of the included indices. The performance graph shall not be deemed incorporated by reference by any general statement incorporating by reference this annual report into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, except to the extent we specifically incorporate this information by reference, and shall not otherwise be deemed filed under such acts.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
We did not repurchase any of our securities in the fourth quarter of 2017.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
We had no sales of unregistered securities in 2017 that have not been previously disclosed in a current report on Form 8-K or quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The selected financial data set forth below has been derived from our audited financial statements. This data should be read in conjunction with the financial statements, the notes thereto and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this report.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31,
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
2014
|
|
2013
|
|
Statement of Operations Data:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
60,426,395
|
|
$
|
41,107,538
|
|
$
|
27,331,092
|
|
$
|
16,817,403
|
|
$
|
10,947,361
|
|
Cost of goods sold
|
|
|
9,311,585
|
|
|
6,467,250
|
|
|
4,848,396
|
|
|
3,442,183
|
|
|
2,439,818
|
|
Gross Profit
|
|
|
51,114,810
|
|
|
34,640,288
|
|
|
22,482,696
|
|
|
13,375,220
|
|
|
8,507,543
|
|
Costs and Expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales and marketing
|
|
|
37,635,871
|
|
|
28,425,503
|
|
|
20,089,369
|
|
|
13,193,795
|
|
|
10,259,153
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
6,699,120
|
|
|
4,212,023
|
|
|
3,237,171
|
|
|
3,033,325
|
|
|
2,125,476
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
14,731,105
|
|
|
10,132,624
|
|
|
8,422,866
|
|
|
6,948,890
|
|
|
5,715,119
|
|
Total costs and expenses
|
|
|
59,066,096
|
|
|
42,770,150
|
|
|
31,749,406
|
|
|
23,176,010
|
|
|
18,099,748
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
(7,951,286)
|
|
|
(8,129,862)
|
|
|
(9,266,710)
|
|
|
(9,800,790)
|
|
|
(9,592,205)
|
|
Other income (expense):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(2,216,845)
|
|
|
(5,386,268)
|
|
|
(3,988,619)
|
|
|
(6,812,315)
|
|
|
(4,819,708)
|
|
Interest expense - deferred financing costs
|
|
|
(246,557)
|
|
|
(875,389)
|
|
|
(127,912)
|
|
|
(1,100,520)
|
|
|
(178,864)
|
|
Other (expense)
|
|
|
(30,774)
|
|
|
(19,625)
|
|
|
26,816
|
|
|
3,149
|
|
|
33,892
|
|
Total other income (expense)
|
|
|
(2,494,176)
|
|
|
(6,281,282)
|
|
|
(4,089,715)
|
|
|
(7,909,686)
|
|
|
(4,964,680)
|
|
Net loss
|
|
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
|
(13,356,425)
|
|
|
(17,710,476)
|
|
|
(14,556,885)
|
|
Loss per common share - basic and diluted
|
|
|
(0.31)
|
|
|
(0.47)
|
|
|
(0.51)
|
|
|
(0.99)
|
|
|
(1.08)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
2014
|
|
2013
|
|
Balance Sheet Data:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
$
|
55,740,667
|
|
$
|
44,037,252
|
|
$
|
35,051,374
|
|
$
|
14,411,088
|
|
$
|
25,658,606
|
|
Total assets
|
|
|
58,874,698
|
|
|
46,360,478
|
|
|
36,700,326
|
|
|
16,400,789
|
|
|
27,684,270
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
13,718,746
|
|
|
11,081,369
|
|
|
3,709,245
|
|
|
2,445,312
|
|
|
2,098,060
|
|
Total long-term obligations, net of current maturities and deferred financing fees
|
|
|
19,973,917
|
|
|
20,357,960
|
|
|
24,795,490
|
|
|
25,201,157
|
|
|
25,449,577
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
33,692,663
|
|
|
31,439,329
|
|
|
28,504,735
|
|
|
27,646,469
|
|
|
27,547,637
|
|
Total shareholders' equity (deficit)
|
|
|
25,182,035
|
|
|
14,921,149
|
|
|
8,195,591
|
|
|
(11,245,680)
|
|
|
136,633
|
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following information should be read in conjunction with “Selected Financial Data” contained in Item 6 of this Form 10-K, our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto contained in Item 8 of this Form 10-K, the “Cautionary Notice Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” contained in Part 1 of this Form 10-K, “Risk Factors” contained in Item 1A of this Form 10-K, and the other information appearing elsewhere in, or incorporated by reference into, in this Form 10-K.
Overview
We are a global leader in innovative surgical solutions for physical damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves. We provide products and education to improve surgical treatment algorithms for peripheral nerve damage or discontinuity. Our portfolio of products includes Avance® Nerve Graft, an off-the-shelf processed human nerve allograft for bridging severed peripheral nerves without the comorbidities associated with a second surgical site, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a porcine submucosa extracellular matrix (“ECM”) coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed peripheral nerves, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect injured peripheral nerves and reinforce the nerve reconstruction while preventing soft tissue attachments and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane a minimally processed human umbilical cord membrane that may be used as a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed. Along with these core surgical products, we also offer the AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System. These evaluation and measurement tools assist healthcare professionals in detecting changes in sensation, assessing return of sensory, grip and pinch function, evaluating effective treatment interventions, and providing feedback to patients on peripheral nerve function. Our portfolio of products is available in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and several European and other international countries.
Revenue from the distribution of AxoGen’s peripheral nerve repair products, the Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, in the United States is the main contributor to AxoGen’s total reported sales and has been the key component of its growth to date. AxoGen revenues increased in 2017 compared to 2016 primarily as a result of revenue growth through product penetration in active accounts, and to a lesser extent, the development and growth of new accounts.
We have experienced that surgeons initially are cautious adopters for peripheral nerve repair products. Surgeons typically start with a few cases and then wait and see the results of these initial cases. Active accounts are usually past this wait period and have developed some level of product reorder. These active accounts have typically gone through the committee approval process, have at least one surgeon who has converted a portion of his or her treatment algorithms of peripheral nerve repair to the AxoGen portfolio and have ordered AxoGen products at least six times in the last 12 months.
As such, revenue growth primarily occurs from increased purchasing from active accounts, followed by revenue growth from new accounts. Each new period of measurement is thus benefited from growth in active accounts which may include those that were new accounts in the prior measurement period. AxoGen has continued to broaden its sales and marketing focus which is expected to have a positive contribution to its revenue growth in the long term. In 2017 revenue growth continued to exceed the growth in expenses, demonstrating improved productivity of our commercial strategy.
Results of Operations
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations is based upon the Company’s consolidated financial statements which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“USGAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure
of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and reported amount of expenses during the period reported. Management bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience, observance of trends in the industry, information provided by outside sources and on various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We have identified the following policies as critical to our business operations and the understanding of our consolidated results of operations:
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed and determinable, delivery has occurred and there is a reasonable assurance of collection of the sales proceeds. Revenues for manufactured products, services and products sold to a customer or under a distribution agreement are recognized when the product is delivered to the customer or distributor, at which time title passes to the customer or distributor, provided, however, that in the case of revenues from consigned sales delivery is determined when the product is utilized in a surgical procedure. Once a product is delivered, the Company has no further performance obligations. Delivery is defined as delivery to a customer location or segregation of product into a contracted distribution location. At such time, this product cannot be sold to any other customer. Fees charged to customers for shipping are recognized as revenues when products are shipped to the customer, distributor or end user. Revenues from research grants are recognized in the period the associated costs are incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Concentration
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are maintained at financial institutions and, at times, balances may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has never experienced any losses related to these balances and does not believe it is exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable and Concentration of Credit Risk — Doubtful Accounts
Trade accounts receivable are recorded at the invoiced amount and do not bear interest. The carrying amount of accounts receivable is reduced by an allowance for doubtful accounts which reflects management’s best estimate of the amounts that are uncollectable. In establishing the required allowance, management considers customers’ financial condition, credit history and current economic conditions. Account balances are charged off after all means of collection have been exhausted and the potential for recovery is considered remote. Our internal financial operations have primary responsibility for billing and collecting our accounts receivable and utilize various processes and procedures in our collection efforts including monthly statements, written collection notices and telephonic follow-ups. In the event the current conditions as to doubtful accounts negatively change, management will consider increasing the reserve for doubtful accounts. Management judgment as to identifying negative trends is important in its assumption of exposure to uncollectable receivables requiring a reserve and if revenues expand as expected accounts receivable will rise, potentially causing management to reevaluate its underlying assumptions. The allowance for doubtful accounts reserve balance was approximately $461,000 and $272,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Inventories
Inventories are comprised of unprocessed tissue, work-in-process, Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System, AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and supplies and are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value.
We regularly review the inventory status to determine the expected reserve level required. The Company policy is to monitor the shelf life of its products and reserve amounts based on the expiration date of the finished goods inventory. We also reserve a portion of raw materials based on our historical experience of tissue that fails during the inspection
and debridement stage due to medical history, serology compliance or poor quality. Our inventory reserve balance was approximately $812,000 and $960,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Income Taxes
The Company has not recorded current income tax expense due to the generation of net operating losses. Deferred income taxes are accounted for using the balance sheet approach which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more-likely-than-not that a deferred tax asset will not be realized. A full valuation allowance has been established on the deferred tax asset as it is more-likely-than-not that a future tax benefit will not be realized. In addition, future utilization of the available net operating loss carryforward may be limited under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 as a result of changes in ownership.
The Company identifies and evaluates uncertain tax positions, if any, and recognizes the impact of uncertain tax positions for which there is a less than more-likely-than-not probability of the position being upheld when reviewed by the relevant taxing authority. Such positions are deemed to be unrecognized tax benefits and a corresponding liability is established on the balance sheet. The Company has not recognized a liability for uncertain tax positions. If there were an unrecognized tax benefit, the Company would recognize interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in interest expense and penalties in operating expenses. The Company’s remaining open tax years subject to examination by the Internal Revenue Service include the years ended December 31, 2014 through 2016; however, there currently are no examinations in process.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The respective carrying value of certain on-balance-sheet financial instruments approximated their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. These financial instruments include cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt approximates its carrying value based upon current rates available to the Company.
Share-Based Compensation
The Company measures all employee stock-based compensation awards using a fair value method and records such expense in its consolidated financial statements. The estimated value of the portion of the award that is ultimately expected to vest, with forfeitures accounted for as they occur, is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. The Company estimates the grant date fair value of stock option awards generally on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
With respect to performance stock units (“PSUs”), the number of shares that vest and are issued to the recipient is based upon the Company’s performance as measured against specified targets over the measurement period. The fair value of the PSUs is based on the Company’s closing stock price on the grant date and its estimate of achieving such performance targets. For further discussion and disclosures, see Note 10: “Stock Incentive Plan.”, in Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included herein.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with USGAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Earnings (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock
There were no dilutive instruments as of December 31, 2017 and 2016. The basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding were 33,322,767 and 30,702,164 for the twelve months ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Basic and diluted net loss per share of common stock for all periods presented is computed by dividing the net loss attributable to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding and common stock equivalents outstanding, when dilutive. Potentially dilutive common stock equivalents include shares of common stock which would potentially be issued pursuant to stock warrants and stock options. Common stock equivalents are not included in determining the fully diluted loss per share if their effect is antidilutive.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
Revenues
Revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 increased 47.0% to $60.4 million as compared to $41.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily a result of continuing growth in active accounts as a result of improved sales efficiency and penetration within these active accounts. In the fourth quarter of 2017 we had 591 active accounts, an increase of 31% from 452 at the end of 2016. In addition, the Company received grant revenue of $56,000 in the year ended December 31, 2017, as compared to grant revenue of $290,000 in the year ended December 31, 2016.
Gross Profit
Gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2017 increased 47.7% to $51.1 million as compared to approximately $34.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily attributable to the increased revenues in 2017, coupled with a product price increase instituted in March 2017. As a result, gross profit margin also improved to 84.6% in 2017 as compared to 84.2% for 2016.
Costs and Expenses
Total cost and expenses increased 38.1% to $59.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to $42.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. These increases were primarily due to variable costs associated with increased sales activity, continuing product development and clinical study activities, expanded surgeon education programs, increases in compensation and general expenses associated with expanded infrastructure to support the Company’s growth. As a percentage of revenues, total cost and expenses decreased to 97.8% in 2017 compared to 104.1% in 2016 as a result of improving leverage of our business model.
Sales and marketing expenses increased 32.4% to $37.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to $28.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily due to: (a) increased compensation expenses related to AxoGen’s direct sales force as a result of increased sales and hiring of additional personnel; (b) increased commissions to independent distributors as a result of increased sales; (c) expansion of the Company’s surgeon education program; and (d) increased marketing activity. As a percentage of revenues, sales and marketing expenses were 62.3% for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to 69.1% for the year ended December 31, 2016. The decrease in sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of revenue was a result of productivity improvements of our commercial team, including the increased penetration in active accounts as revenue growth outpaced the related growth of expenses.
General and administrative expenses increased 45.5% to $14.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to $10.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily the result of increased general expenses related to infrastructure expansion to support the Company’s growth, including professional fees, salaries and $2.5 million of non-cash stock compensation. As a percentage of revenues, general and administrative
expenses decreased slightly to 24.3% for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to 24.6% for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Research and development expenses increased 59.5% to $6.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to approximately $4.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. Research and development costs include AxoGen’s product development and clinical efforts substantially focused on its BLA for the Avance® Nerve Graft and the RECON and RANGER® studies. These activities vary from quarter to quarter due to the timing of certain projects. The increase in expenses for 2017 relate to expenditures for these clinical activities, including the pivotal clinical trial to support the BLA, and hiring additional personal to support both clinical and product development activity. It is expected that costs associated with the BLA will continue to increase as more patients are enrolled in the trial over the next year. Although AxoGen’s products are developed for sale in their current use, it continues to conduct product development efforts focused on new products and new applications for existing products. AxoGen is active in pursuing research grants to support research and early product development. AxoGen’s product pipeline development continued to contribute to a portion of the research and development expenses in 2017, with grant revenue offsetting a portion of this activity. As a result, research and development expenses increased to 11.1% in 2017 from 10.2% in 2016, as a percentage of revenues.
Other Income and Expenses
Interest expense decreased 59.3% to $2.2 million in 2017 as compared to $5.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This decrease was primarily due to the lower interest rate as a result of the refinancing of our debt facility in October 2016, as well as the charges associated with the refinancing. As part of that refinancing, we incurred costs for prepayment fees and the write-off of previously recorded deferred interest charges associated with the extinguishment of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement. Under the terms of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement, the Company paid Three Peaks a final payment of $2.4 million inclusive of prepayment fees and accrued interest through October 25, 2016. As a result of the accounting treatment for the Three Peaks transaction, the Company had recorded a total of $750,000 of deferred interest charges which were offset against those prepayment fees. The net impact of those transactions resulted in a net interest charge of $1.7 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016.
Interest expense — deferred financing costs decreased to $247,000 for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to $875,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016. This decrease is primarily due to the write off of the remaining Three Peaks financing costs of approximately $750,000 in 2016 as the result of the extinguishment of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement; however, the decrease was partially offset by the deferred financing costs associated with the new credit facility amortizing over a shorter time period.
Income Taxes
AxoGen had no income tax expenses or income tax benefit for 2017 or 2016 due to incurrence of net operating loss for the year, the benefits of which have been fully reserved. AxoGen does not believe there are any additional tax expenses or benefits currently available.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
Revenues
Revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 increased 50.5% to $41.1 million as compared to $27.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily a result of growth in active accounts and to a lesser extent the establishment and growth of new accounts. In addition, the Company received grant revenue of $290,000 in the year ended December 31, 2016, as compared to grant revenue of $433,000 in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Gross Profit
Gross profit for the year ended December 31, 2016 increased 53.8% to $34.6 million as compared to $22.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily attributable to the increased revenues in 2016, manufacturing efficiencies, a favorable change in product mix and a product price increase instituted in March 2016. As a result, gross profit margin also improved to 84.2% in 2016 as compared to 82.4% for 2015.
Costs and Expenses
Total cost and expenses increased 35.0% to $42.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $31.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increases were primarily due to increasing sales activity, expanded surgeon education programs, increases in compensation and increased general expenses associated with increased revenues and greater corporate size. As a percentage of revenue, total cost and expenses decreased to 104.1% in 2016 compared to 116.1% in 2015 demonstrating the improved productivity of our business model.
Sales and marketing expenses increased 41.3% to $28.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $20.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily due to: (a) increased compensation expenses related to AxoGen’s direct sales force as a result of increased sales and hiring of additional personnel; (b) increased commissions to independent distributors as a result of increased sales; (c) expansion of our surgeon education program; and (d) increased marketing activity. As a percentage of revenues, sales and marketing expenses were 69.1% for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to 73.6% for the year ended December 31, 2015. The decrease in sales and marketing expenses as a percentage of revenue was a result of improved productivity of our commercial team, including the improved penetration of active accounts as revenue growth outpaced the related growth of expenses.
General and administrative expenses increased 20.2% to $10.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to approximately $8.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily the result of increased professional fees, increased general expenses related to a larger organization and increases in salaries and bonus compensation. As a percentage of revenues, general and administrative expenses were 24.6% for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to 30.8% for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Research and development expenses increased 31.3% to $4.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $3.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. Research and development costs included AxoGen’s product development and clinical efforts substantially focused on its BLA for the Avance® Nerve Graft. This activity varies from quarter to quarter due to the timing of certain projects. The increase in expenses for 2016 related to expenditures for such clinical activity, including preparation for, and the start of, the pivotal clinical trial to support the BLA, and hiring additional personal to support both clinical and product development activity, offset by certain projects that have been completed or were near completion. It was expected that costs associated with the BLA would continue to increase as more patients were enrolled in the trial through approximately 2018. AxoGen’s product pipeline development contributed to a portion of the research and development expenses in 2016, with grant revenue offsetting a portion of that activity. As a percentage of revenues, research and development expenses declined to 10.2% in 2016 from 11.7% in 2015.
Other Income and Expenses
Interest expense increased 35.0% to $5.4 million in 2016 as compared to $4.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily due to the net impact of prepayment fees and the write-off of previously recorded deferred interest charges associated with the extinguishment of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement on October 25, 2016. Under the terms of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement the Company paid Three Peaks a final payment of $2.4 million inclusive of prepayment fees and accrued interest through October 25, 2016. As a result of the accounting treatment for the Three Peaks transaction, the Company had previously recorded a total of $750,000 of deferred interest charges which were offset against those prepayment fees. The net impact of those transactions resulted in a net interest charge of $1.7 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016.
Additionally, interest expense included non-cash, deferred interest charges of approximately $0 and $462,000 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, that was expected to be paid in the future based upon the terms of the Three Peaks transaction and increases in AxoGen’s revenues.
Interest expense — deferred financing costs increased to $875,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to $128,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily due to the write off of the Three Peaks financing costs of $750,000 in 2016 as the result of the extinguishment of the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement.
Income Taxes
AxoGen had no income tax expenses or income tax benefit for 2016 or 2015 due to incurrence of net operating loss for the year, the benefits of which had been fully reserved. AxoGen did not believe there were any additional tax expenses or benefits available.
Effect of Inflation
Inflation did not have a significant impact on AxoGen’s net sales, revenues or income from continuing operations in 2015, 2016 or 2017.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Term and Revolving Loan Agreements
On November 12, 2014, AxoGen, as borrower, and AxoGen Corporation (“AC”), as guarantor, entered into that certain Term Loan Agreement (the “Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement”), dated November 12, 2014, by and among AxoGen, as borrower, AC, as guarantor, the lenders party thereto and Three Peaks Capital S.a.r.l. (“Three Peaks”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Oberland Capital Healthcare Master Fund LP, as administrative and collateral agent for the lenders. Under the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement, Three Peaks provided AxoGen a term loan of $25 million which had a six-year term and required interest only payments and a final principal payment due at the end of the term. Interest was payable quarterly at 9.0% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 1.0% which as of November 13, 2014 resulted in a 10% rate.
In addition, on November 12, 2014, AxoGen entered into that certain Revenue Interest Agreement (the “Revenue Interest Agreement”) with Three Peaks. Royalty payments were based on a royalty rate of 3.75% of AxoGen’s revenues up to a maximum of $30 million in revenues in any 12-month period.
On October 26, 2016, the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement were paid in full and the Company had no further obligations pursuant to such agreements.
On October 25, 2016 (the “Closing Date”), AxoGen and AC, each as borrowers, entered into a Credit and Security Agreement (Term Loan) (the “MC Term Loan Agreement”) with the lenders party thereto and MidCap Financial Trust (“MidCap”), as administrative agent and a lender. Under the MC Term Loan Agreement, MidCap provided the Company a term loan in the aggregate principal amount of $21 million (the "Term Loan") which has a maturity date of May 1, 2021 and requires interest only payments through December 1, 2018, and thereafter, 30 monthly payments of principal and interest resulting in the Term Loan being fully paid by the maturity date. Interest is payable monthly at 8.00% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5%, which, as of December 31, 2017, resulted in an 9.36% rate. In addition to the interest charged on the Term Loan, the Company is also obligated to pay certain fees, including an annual agency fee of 0.25% of the aggregate principal amount of the Term Loan.
Under the MC Term Loan Agreement, the Company has the option at any time to prepay the Term Loan in whole or in part, provided that prepayments shall be: (i) in an amount equal to $2,500,000 or a higher integral multiple of $1,000,000; and (ii) accompanied by certain prepayment and exit fees. There can be no more than three partial
voluntary prepayments allowed during the term of the MC Term Loan Agreement. MidCap and certain of the lenders have the right to demand prepayment, along with prepayment and exit fees upon an event of default which includes, but is not limited to: (i) default of the Revolving Loan (as defined below); (ii) a change of control of the Company; (iii) sale of the majority of the Company's assets; or (iv) a material adverse change to the Company. The prepayment fee is determined by multiplying the amount being prepaid by the following applicable percentage amount: (a) 3.0% during the first year following the Closing Date; (b) 2.0% during the second year following the Closing Date, and (c) 1.0% thereafter. No prepayment fee is due in the event the prepayment is a result of refinancing the Term Loan and Revolving Loan with MidCap or an affiliate of MidCap. Upon any repayment of any portion of the Term Loan (whether voluntary, involuntary or mandatory), other than scheduled amortization payments, and on the final payment of principal of the Term Loan, an exit fee of 5.0% of the principal amount of the Term Loan is also owed based on the portion of any prepayment made and at maturity upon the original principal amount less any prepayments of the Term Loan.
In addition, on October 25, 2016, AxoGen and AC, each as borrowers, also entered into a Credit and Security Agreement (Revolving Loan) ( the “Revolving Loan Agreement”) with the lenders party thereto and MidCap, as administrative agent and a lender. Under the Revolving Loan Agreement, MidCap agreed to lend to the Company up to $10 million under a revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Loan") which amount may be drawn down by the Company based upon an available borrowing base which includes certain accounts receivable and inventory. The Revolving Loan may be increased to up to $15 million at the Company’s request and with the approval of MidCap. As of December 31, 2017, the Company’s borrowing base under the Revolving Loan provided availability of approximately $7.7 million. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had borrowed $4.0 million of the Revolving Loan. The maturity date of the Revolving Loan is May 1, 2021. Interest is payable monthly at 4.5% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5% on outstanding advances, which, as of December 31, 2017, resulted in an 5.86% rate. In addition to the interest charged on the Revolving Loan, the Company is also obligated to pay certain fees, including a collateral management fee of 0.5% per annum of the principal amount outstanding on the Revolving Loan from time to time and an unused line fee of 0.5% per annum on the difference between the average amount outstanding on the Revolving Loan minus the total amount of the Revolving Loan commitment. The Revolving Loan is subject to a minimum balance, such that the Company pays the greater of: (i) interest accrued on the actual amount drawn under the Revolving Loan Facility; and (ii) interest accrued on 30% of the average borrowing base. If the Revolving Loan is terminated or permanently reduced prior to the maturity date, MidCap is owed a deferred revolving loan origination fee determined by multiplying the agreed total lending amount by the following applicable percentage amount: (a) 3.0% during the first year following the Closing Date; (b) 2.0% during the second year following the Closing Date, and (c) 1.0% thereafter. No deferred revolving loan origination fee is due in the event the Revolving Loan is paid in full or the termination of the revolving credit facility is a result of refinancing the Term Loan and Revolving Loan with MidCap or an affiliate of MidCap. Termination of the Revolving Loan may occur, at the option of MidCap and certain of the lenders, upon an event of default which includes, but is not limited to: (i) default in payment of the Term Loan; (ii) a change of control of the Company; (iii) sale of the majority of the Company's assets; or (iv) a material adverse change to the Company.
Under the MidCap agreements, the Company must maintain certain covenants including, but not limited to, limiting new indebtedness, restrictions on the payment of dividends and maintaining certain levels of revenue. As of December 31, 2017, the Company was in compliance with the agreements’ covenants. MidCap, on behalf of the lenders under the Revolving Loan Agreement, has a first perfected security interest in the assets of the Company to guarantee the payment in full of the MC Term Loan and Revolving Loan. Upon the payment in full to MidCap and the lenders of the MC Term Loan and Revolving Loan, the Company would have no further obligations to MidCap or the lenders under the MC Term Loan or the Revolving Loan or the Revolving Loan Agreement.
AxoGen used the aggregate proceeds of $25 million from the MidCap Term Loan and the Revolving Loan to pay the outstanding indebtedness owed to Three Peaks and the other lenders to terminate the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and the Revenue Interest Agreement. Expenses and fees of $800,000 to complete the negotiation and documentation of the Term Loan and the Revolving Loan and prepayment fees of approximately $2.3 million owed to Three Peaks were paid from AxoGen’s own funds.
Commitments for Capital Expenditures
The Company had no material commitments for capital expenditures at December 31, 2017 or 2016.
Public Offering of Common Stock
On February 5, 2015, AxoGen entered into an underwriting agreement with Wedbush Securities Inc., as underwriter (the “Wedbush”), in connection with the offering, issuance and sale of 4,728,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.01 per share, at a price to the public of $2.75 per share (the “February 2015 Offering”). The Company also granted to Wedbush a 30-day option to purchase up to an aggregate of 709,200 additional shares of common stock to cover over-allotments, if any.
On February 13, 2015, the February 2015 Offering was completed with the sale of 5,437,200 shares of common stock, which included the full exercise of the over-allotment option, at $2.75 per share, resulting in gross proceeds to AxoGen from the February 2015 Offering of approximately $15.0 million, before deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other estimated offering expenses payable by AxoGen estimated at approximately $1.4 million. The shares of common stock were listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. The February 2015 Offering was made pursuant to the Company’s effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-195588) previously filed with the SEC on April 30, 2014, and pursuant to the prospectus supplement and the accompanying prospectus describing the terms of the February 2015 Offering, dated February 5, 2015.
On August 26, 2015, the Company entered into the Purchase Agreement with EW Healthcare Partners L.P. (formerly Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P.)(“Essex”) for the purchase of 4,861,111 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $3.60 per share, raising approximately $17.5 million in gross proceeds (the “August 2015 Offering”). The expenses directly related to the August 2015 Offering were approximately $300,000 and were paid as of December 31, 2015. Those expenses include the Company’s legal and accounting fees, printing expenses, transfer agent fees and miscellaneous fees and costs related to the August 2015 Offering. The Company provided certain demand and “piggy-back” registration rights in connection with that sale of common stock. The August 2015 Offering was made pursuant to the Company’s effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-195588) previously filed with the SEC on April 30, 2014 and pursuant to the prospectus supplement and the accompanying prospectus describing the terms of the August 2015 Offering, dated August 26, 2015.
On October 7, 2016, AxoGen entered into an underwriting agreement with JMP Securities LLC, as representative of the several underwriters (collectively, the “2016 Offering Underwriters”), to issue and sell 2,333,334 shares of the Company’s common stock in an underwritten registered public offering (the “2016 Offering”) at an offering price of $7.50 per share. Pursuant to the underwriting agreement, the Company also granted the 2016 Offering Underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to an additional 350,000 shares of common stock, which the 2016 Offering Underwriters exercised in full on October 7, 2016. Five of the Company’s directors and officers purchased an aggregate of approximately 32,666 Shares in the 2016 Offering and such purchases were made on the same terms and conditions as purchases by the public in the 2016 Offering. The 2016 Offering closed on October 13, 2016, and the Company received net proceeds of approximately $18.67 million from the sale of 2,683,334 shares of common stock, which included the additional 350,000 shares of common stock, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses. The 2016 Offering was pursuant to a prospectus supplement dated October 7, 2016, which was filed with the SEC in connection with the Company’s shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-207829) that was filed with the SEC on November 5, 2015 and declared effective on December 11, 2015 and the related prospectus dated December 11, 2015.
On November 16, 2017, AxoGen entered into a certain underwriting agreement (the “Leerink Underwriting Agreement”) with Leerink Partners LLC, as representative of the several underwriters named therein (collectively, the “2017 Offering Underwriters”) and Essex, pursuant to which (i) the Company agreed to issue and sell 700,000 shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-207829), filed with the SEC on November 5, 2015, and declared effective by the SEC on December 11, 2015, and the prospectus contained therein, as supplemented by the prospectus supplement dated November 16, 2017, and (ii) Essex agreed to sell 1,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-220770), filed with the SEC on October 2, 2017, and declared effective by the SEC on October 11, 2017, and the prospectus contained therein, as supplemented by the Prospectus Supplement, in an underwritten registered public offering at an offering price of $21.00 per share. The Company and Essex granted the 2017 Offering Underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to
an aggregate of 255,000 additional shares of common stock, at the public offering price, less the underwriting discounts and commissions, which was exercised in full on November 16, 2017. The Company received net proceeds of approximately $15.65 million after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses. The Company intends to use the net proceeds of this offering for general working capital purposes; however, the Company’s management will retain broad discretion over the allocation of the net proceeds.
Cash Flow Information
AxoGen had working capital of approximately $42.02 million and a current ratio of 4.06 at December 31, 2017, compared to working capital of $32.96 million and a current ratio of 3.97 at December 31, 2016. The increase in working capital at December 31, 2017 as compared to December 31, 2016 was primarily due the increase in cash from the net proceeds of the November 2017 stock offering, along with increases in accounts receivable as a result the Company’s revenue growth. The small increase in the current ratio was primarily attributable to the net proceeds from the November 2017 stock offering, which was partially offset by the increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses and a portion of the Company’s long-term debt being classified as current as of December 31, 2017 in accordance with the terms of the MC Term Loan. The Company believes it has sufficient cash resources to meet its liquidity requirements for at least the next 12 months.
AxoGen’s future capital requirements depend on a number of factors including, without limitation, revenue increases consistent with its business plan, cost of products and acquisition and/or development of new products. AxoGen could face increasing capital needs. Such capital needs could be substantial depending on the extent to which AxoGen is unable to increase revenue.
If AxoGen needs additional capital in the future, it may raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, debt financings or from other sources. The sale of additional equity would result in dilution to AxoGen’s shareholders. There is no assurance that AxoGen will be able to secure funding on terms acceptable to it, or at all. The increasing need for capital could also make it more difficult to obtain funding through either equity or debt. Should additional capital not become available to AxoGen as needed, AxoGen may be required to take certain action, such as slowing sales and marketing expansion, delaying regulatory approvals or reducing headcount.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company had a net increase in cash and cash equivalents of $6.5 million as compared to a net increase of cash and cash equivalents of approximately $4.1 million in the year ended December 31, 2016. The Company’s principal sources and uses of funds are explained below.
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
AxoGen used $9.2 million of cash for operating activities in 2017, as compared to using $11.2 million of cash for operating activities in 2016. This decrease in cash used in operating activities was primarily attributed to a decrease in the net loss for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 2016, partially offset by the decrease in accounts payable and accrued expenses during 2017.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
Investing activities for 2017 used $1.3 million of cash as compared to 2016 which used $1.2 million. This increase in use was principally attributable to the growth in certain fixed assets in 2017 related to our continuing expansion of infrastructure to support our growth.
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
Financing activities in 2017 provided $17.0 million of cash as compared to providing $16.5 million of cash in 2016. The increase was primarily due to an increase in proceeds for the exercise of stock options during 2017 as compared to 2016.
Cash paid for interest was $2.2 million in 2017 compared to $5.8 million in 2016. The decrease was primarily due to the lower interest rate on the MidCap Term and Revolving loan agreements when compared to the costs in 2016 to repay the Three Peaks Term Loan and Revenue Interest Agreements.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
AxoGen does not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our obligations with regard to our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017, and the expected timing of maturities of these contractual obligations. This table should be read in conjunction with the notes to consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report on Form 10-K.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Contractual Obligations
|
|
Total
|
|
Less than 1 year
|
|
1-3 years
|
|
3-5 years
|
|
More than 5 years
|
|
Long-term debt
|
|
$
|
21,000,000
|
|
$
|
700,000
|
|
$
|
16,800,000
|
|
$
|
3,500,000
|
|
$
|
-
|
|
Operating leases
|
|
|
871,905
|
|
|
437,900
|
|
|
347,366
|
|
|
86,639
|
|
|
-
|
|
Capital lease minimum lease payments
|
|
|
98,889
|
|
|
35,017
|
|
|
41,733
|
|
|
22,139
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
|
$
|
21,970,794
|
|
$
|
1,172,917
|
|
$
|
17,189,099
|
|
$
|
3,608,778
|
|
$
|
-
|
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, issued a new standard on revenue recognition which outlines a single comprehensive model to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. The core principle of the revenue model is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The standard is designed to create greater comparability for financial statement users across industries and jurisdictions and also requires enhanced disclosures. The guidance is effective for the Company beginning on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. The standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the adoption date. During the quarter ended December 31, 2017, we completed our evaluation of the new standard, including an assessment of existing revenue contracts with our customers on our most significant revenue streams, business practices and processes, and our controls over financial reporting, and we do not believe there will be a material change to the timing and amounts of our revenue, processes or internal controls. During 2018, we will be required to provided additional disclosures in the notes to the consolidated financial statements. We will utilize the modified retrospective method upon adoption.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases (Topic 842)”. This update will increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. This update is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact this standard will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments (Topic 230). The ASU was issued intending to reduce diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows by providing guidance on eight specific cash flow issues. The guidance is effective for the Company on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. We do not believe the adoption of this standard will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), guidance that a statement of cash flows explains the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. The guidance is effective for the Company on
January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2108. We do not believe the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on our Statement of Cash Flows.
In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-09, “Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Scope of Modification Accounting.” ASU 2017-09 provides clarity on which changes to the terms or conditions of share-based payment awards require entities to apply the modification accounting provisions required in Topic 718. ASU 2017-09 is effective for the Company on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. We do not believe the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
The Company’s management has reviewed and considered all other recent accounting pronouncements and believe there are none that could potentially have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial condition, results of operations, or disclosures.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
The Company is exposed to market risk from interest rates. For our cash and cash equivalents, a change in interest rates affects the amount of interest income that can be earned. For our debt instruments, changes in interest rates affect the amount of interest expense incurred. If the variable rate of interest on our credit facility experiences an upward increase of 1%, our annual interest expense would increase by approximately $250,000.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
CONTENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and
Board of Directors of
AxoGen, Inc.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of AxoGen, Inc. and Subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes and financial statement schedules listed in the index appearing under item 15(a)(2) (collectively referred to as the "consolidated financial statements"). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9a. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company's consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of the financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of the financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting
principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
|
|
|
|
/s/ Lurie, LLP
|
|
|
|
|
Minneapolis, Minnesota
|
|
|
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2004.
|
|
AXOGEN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2017 and 2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
Assets
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents
|
|
$
|
36,506,624
|
|
$
|
30,014,405
|
|
|
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of approximately $461,000 and $272,000, respectively
|
|
|
11,064,720
|
|
|
8,052,203
|
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
7,315,942
|
|
|
5,458,840
|
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other
|
|
|
853,381
|
|
|
511,804
|
|
|
Total current assets
|
|
|
55,740,667
|
|
|
44,037,252
|
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
|
2,197,039
|
|
|
1,494,247
|
|
|
Intangible assets
|
|
|
936,992
|
|
|
828,979
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
58,874,698
|
|
$
|
46,360,478
|
|
|
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Borrowings under revolving loan agreement
|
|
$
|
4,000,000
|
|
$
|
4,025,023
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
8,952,061
|
|
|
7,002,165
|
|
|
Current maturities of long term obligations
|
|
|
735,017
|
|
|
20,899
|
|
|
Deferred revenue, current
|
|
|
31,668
|
|
|
33,282
|
|
|
Total current liabilities
|
|
|
13,718,746
|
|
|
11,081,369
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long Term Obligations, net of current maturities and deferred financing fees
|
|
|
19,905,286
|
|
|
20,265,745
|
|
|
Deferred revenue
|
|
|
68,631
|
|
|
92,215
|
|
|
Total liabilities
|
|
|
33,692,663
|
|
|
31,439,329
|
|
|
Shareholders’ equity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $0.01 par value per share; 50,000,000 shares authorized; 34,350,329 and 33,008,865 shares issued and outstanding
|
|
|
343,503
|
|
|
330,088
|
|
|
Additional paid-in capital
|
|
|
153,167,817
|
|
|
132,474,884
|
|
|
Accumulated deficit
|
|
|
(128,329,285)
|
|
|
(117,883,823)
|
|
|
Total shareholders’ equity
|
|
|
25,182,035
|
|
|
14,921,149
|
|
|
|
|
$
|
58,874,698
|
|
$
|
46,360,478
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
AXOGEN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
|
$
|
60,426,395
|
|
$
|
41,107,538
|
|
$
|
27,331,092
|
|
|
Cost of goods sold
|
|
|
9,311,585
|
|
|
6,467,250
|
|
|
4,848,396
|
|
|
Gross profit
|
|
|
51,114,810
|
|
|
34,640,288
|
|
|
22,482,696
|
|
|
Costs and expenses:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales and marketing
|
|
|
37,635,871
|
|
|
28,425,503
|
|
|
20,089,369
|
|
|
Research and development
|
|
|
6,699,120
|
|
|
4,212,023
|
|
|
3,237,171
|
|
|
General and administrative
|
|
|
14,731,105
|
|
|
10,132,624
|
|
|
8,422,866
|
|
|
Total costs and expenses
|
|
|
59,066,096
|
|
|
42,770,150
|
|
|
31,749,406
|
|
|
Loss from operations
|
|
|
(7,951,286)
|
|
|
(8,129,862)
|
|
|
(9,266,710)
|
|
|
Other income (expense):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest expense
|
|
|
(2,216,845)
|
|
|
(5,386,268)
|
|
|
(3,988,619)
|
|
|
Interest expense — deferred financing costs
|
|
|
(246,557)
|
|
|
(875,389)
|
|
|
(127,912)
|
|
|
Other (expense)
|
|
|
(30,774)
|
|
|
(19,625)
|
|
|
26,816
|
|
|
Total other income (expense)
|
|
|
(2,494,176)
|
|
|
(6,281,282)
|
|
|
(4,089,715)
|
|
|
Net Loss
|
|
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
|
(13,356,425)
|
|
|
Weighted Average Common Shares outstanding — basic and diluted
|
|
|
33,322,767
|
|
|
30,702,164
|
|
|
26,075,670
|
|
|
Loss Per Common share — basic and diluted
|
|
$
|
(0.31)
|
|
$
|
(0.47)
|
|
$
|
(0.51)
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
AXOGEN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
|
|
Common Stock
|
|
Paid-in
|
|
Accumulated
|
|
Shareholders’
|
|
|
|
|
Shares
|
|
Amount
|
|
Capital
|
|
Deficit
|
|
Equity/(Deficit)
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2014
|
|
19,488,814
|
|
$
|
194,888
|
|
$
|
78,675,686
|
|
$
|
(90,116,254)
|
|
$
|
(11,245,680)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,316,509
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,316,509
|
|
|
Exercise of stock options
|
|
197,466
|
|
|
1,975
|
|
|
510,826
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
512,801
|
|
|
Issuance of common shares
|
|
10,298,311
|
|
|
102,983
|
|
|
30,865,403
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
30,968,386
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
(13,356,425)
|
|
|
(13,356,425)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2015
|
|
29,984,591
|
|
$
|
299,846
|
|
$
|
111,368,424
|
|
$
|
(103,472,679)
|
|
$
|
8,195,591
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,390,277
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,390,277
|
|
|
Exercise of stock options
|
|
340,940
|
|
|
3,409
|
|
|
1,074,924
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,078,333
|
|
|
Issuance of common shares
|
|
2,683,334
|
|
|
26,833
|
|
|
18,641,259
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
18,668,092
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2016
|
|
33,008,865
|
|
$
|
330,088
|
|
$
|
132,474,884
|
|
$
|
(117,883,823)
|
|
$
|
14,921,149
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
3,608,918
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
3,608,918
|
|
|
Exercise of stock options
|
|
536,464
|
|
|
5,365
|
|
|
1,429,160
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,434,525
|
|
|
Issuance of common shares
|
|
805,000
|
|
|
8,050
|
|
|
15,654,855
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
15,662,905
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2017
|
|
34,350,329
|
|
$
|
343,503
|
|
$
|
153,167,817
|
|
$
|
(128,329,285)
|
|
$
|
25,182,035
|
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
AXOGEN, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
Cash flows from operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss
|
|
$
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
$
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
$
|
(13,356,425)
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used for operating activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
487,611
|
|
|
361,617
|
|
|
203,140
|
|
Amortization of intangible assets
|
|
|
78,993
|
|
|
74,871
|
|
|
45,828
|
|
Amortization of deferred financing costs
|
|
|
246,557
|
|
|
124,915
|
|
|
127,913
|
|
Write off of deferred financing costs
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
750,474
|
|
|
—
|
|
Provision for bad debt
|
|
|
223,323
|
|
|
79,593
|
|
|
125,371
|
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
|
3,608,918
|
|
|
1,390,277
|
|
|
1,316,509
|
|
Interest added to note payable
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
1,924,279
|
|
|
461,643
|
|
Change in assets and liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable
|
|
|
(3,235,840)
|
|
|
(3,348,807)
|
|
|
(2,036,052)
|
|
Inventory
|
|
|
(1,857,102)
|
|
|
(1,524,880)
|
|
|
(720,340)
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other
|
|
|
(341,577)
|
|
|
(86,879)
|
|
|
(315,556)
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses
|
|
|
1,926,664
|
|
|
3,411,507
|
|
|
1,117,733
|
|
Deferred liabilities
|
|
|
70,316
|
|
|
17,582
|
|
|
(21,583)
|
|
Net cash used for operating activities
|
|
|
(9,237,599)
|
|
|
(11,236,595)
|
|
|
(13,051,819)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from investing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of property and equipment
|
|
|
(1,105,212)
|
|
|
(931,634)
|
|
|
(408,782)
|
|
Acquisition of intangible assets
|
|
|
(187,006)
|
|
|
(225,768)
|
|
|
(146,736)
|
|
Net cash used for investing activities
|
|
|
(1,292,218)
|
|
|
(1,157,402)
|
|
|
(555,518)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock
|
|
|
15,662,905
|
|
|
18,668,092
|
|
|
30,968,386
|
|
Borrowing on revolving loan
|
|
|
57,599,165
|
|
|
6,684,894
|
|
|
—
|
|
Payments on revolving loan
|
|
|
(57,624,188)
|
|
|
(6,684,894)
|
|
|
—
|
|
Repayments of long-term debt
|
|
|
(20,899)
|
|
|
(2,446,676)
|
|
|
—
|
|
Debt issuance costs
|
|
|
(29,472)
|
|
|
(800,847)
|
|
|
(180,139)
|
|
Proceeds from exercise of stock options
|
|
|
1,434,525
|
|
|
1,078,333
|
|
|
512,799
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities
|
|
|
17,022,036
|
|
|
16,498,902
|
|
|
31,301,046
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents
|
|
|
6,492,219
|
|
|
4,104,905
|
|
|
17,693,709
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year
|
|
|
30,014,405
|
|
|
25,909,500
|
|
|
8,215,791
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period
|
|
$
|
36,506,624
|
|
$
|
30,014,405
|
|
$
|
25,909,500
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow activity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid for interest
|
|
$
|
2,198,286
|
|
$
|
5,769,372
|
|
$
|
3,525,978
|
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments of fixed assets in accounts payable
|
|
$
|
55,385
|
|
$
|
32,153
|
|
$
|
168,775
|
|
Payments of long term debt with proceeds from term loan of $21,000,000 and revolver loan of $4,000,000
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
$
|
25,000,000
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
Capital lease additions
|
|
$
|
61,959
|
|
$
|
—
|
|
$
|
—
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
AXOGEN, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
1.Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of AxoGen, Inc. (the “Company” or “AxoGen”) and its wholly owned subsidiaries, AxoGen Corporation (“AC”) and AxoGen Europe GmbH, established in the fourth quarter of 2016, as of December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016 and for the three years ended December 31, 2017. The Company’s consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
2.Organization and Business
We are a global leader in innovative surgical solutions for physical damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves. AxoGen is the leading company focused specifically on the science, development and commercialization of technologies for peripheral nerve regeneration and repair. We are passionate about restoring nerve function and quality of life to patients with physical damage or discontinuity to peripheral nerves by providing innovative, clinically proven and economically effective repair solutions for surgeons and health care providers. Peripheral nerves provide the pathways for both motor and sensory signals throughout the body. Every day, people suffer traumatic injuries or undergo surgical procedures that impact the function of their peripheral nerves. Physical damage to a peripheral nerve or the inabiltiy to properly reconnect peripheral nerves can result in the loss of muscle or organ function, the loss of sensory feeling, or the initiation of pain.
Our portfolio of products includes Avance® Nerve Graft, an off-the-shelf processed human nerve allograft for bridging severed peripheral nerves without the comorbidities associated with a second surgical site, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, a porcine submucosa extracellular matrix (“ECM”) coaptation aid for tensionless repair of severed peripheral nerves, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, a porcine submucosa ECM product used to wrap and protect injured peripheral nerves and reinforce the nerve reconstruction while preventing soft tissue attachments and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, a minimally processed human umbilical cord membrane that may be used as a resorbable soft tissue covering to separate tissues and modulate inflammation in the surgical bed. Along with these core surgical products, we also offer the AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System. These evaluation and measurement tools assist healthcare professionals in detecting changes in sensation, assessing return of sensory, grip and pinch function, evaluating effective treatment interventions, and providing feedback to patients on peripheral nerve function. Our portfolio of products is available in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom and several European and other international countries.
Avance® Nerve Graft and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane are processed in the United States by AxoGen at its processing facility in Dayton, Ohio. AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and AxoGuard® Nerve Protector are manufactured in the United States by Cook Biotech Incorporated and are distributed worldwide exclusively by AxoGen. The AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System and AxoTouch® Two Point Discriminator are contract manufactured by Viron Technologies, LLC. (formerly Cybernetics Research Laboratories) (“Viron”) Tucson, Arizona. Viron supplies the AcroVal® and AxoTouch® unpackaged and they are packaged at AxoGen’s distribution facility in Burleson, Texas. AxoGen maintains its corporate offices in Alachua, Florida and is the parent company of its wholly owned operating subsidiary, AC.
3.Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed and determinable, delivery has occurred and there is a reasonable assurance of collection of the sales proceeds. Revenues for manufactured
products, services and products sold to a customer or under a distribution agreement are recognized when the product is delivered to the customer or distributor, at which time title passes to the customer or distributor, provided, however, that in the case of revenues from consigned sales delivery is determined when the product is utilized in a surgical procedure. Once a product is delivered, the Company has no further performance obligations. Delivery is defined as delivery to a customer location or segregation of product into a contracted distribution location. At such time, this product cannot be sold to any other customer. Fees charged to customers for shipping are recognized as revenues when products are shipped to the customer, distributor or end user. Revenues from research grants are recognized in the period the associated costs are incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Concentration
For purposes of the statement of cash flows, the Company considers any highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents are maintained at financial institutions and, at times, balances may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has never experienced any losses related to these balances and does not believe it is exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable and Concentration of Credit Risk
Accounts receivable are carried at the original invoice amount less an estimate made for doubtful accounts based on a review of all outstanding amounts on a monthly basis. Management determines the allowance for doubtful accounts by regularly evaluating individual customer receivables and considering a customer’s financial condition, credit history and current economic conditions. Accounts receivable are written off when deemed uncollectible. Recoveries of accounts receivable previously written off are recorded when received.
We regularly review all accounts that exceed 60 days from the invoice date and based on an assessment of current credit worthiness, estimate the portion, if any, of the balance that will not be collected. The analysis excludes certain receivables due to our past successful experience in collectability. Specific accounts that are deemed uncollectible are reserved at 100% of their outstanding balance. In the event that we exhaust all collection efforts and deem an account uncollectible, we would subsequently write off the account. The allowance for doubtful accounts reserve balance was approximately $461,000 and $272,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to accounts receivable are limited because a large number of geographically diverse customers make up the Company’s customer base, thus spreading the trade credit risk. The Company also controls credit risk through credit approvals and monitoring procedures.
Inventories
Inventories are comprised of unprocessed tissue, work-in-process, Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing System, AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and supplies and are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value.
We regularly review the inventory status to determine the expected reserve level required. The Company policy is to monitor the shelf life of its products and reserve amounts based on the expiration date of the finished goods inventory. We also reserve a portion of raw materials based on our historical experience of tissue that fails during the inspection and debridement stage due to medical history, serology compliance or poor quality. Our inventory reserve balance was approximately $812,000 and $960,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Property and Equipment
Depreciation and amortization is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture and equipment
|
|
2
|
-
|
5
|
years
|
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
|
5
|
|
|
years (or lease term if less)
|
|
|
Processing equipment
|
|
5
|
-
|
7
|
years
|
|
Major additions and improvements are capitalized, while replacements, maintenance and repairs, which do not improve or extend the life of the respective assets, are expensed as incurred. When assets are retired or otherwise disposed of, related costs and accumulated depreciation and amortization are removed and any gain or loss is reported as other income or expense.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets consist primarily of license agreements for exclusive rights to use various patented and patent-pending technologies described in Note 6 and other costs related to the license agreements, including patent prosecution and protection costs. Such costs are capitalized and amortized on a straight-line basis over the underlying terms of the license agreements or estimated useful life of patents, ranging from 5 to 20 years.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets, Including License Agreements
The Company reviews its long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company did not record any impairment loss.
Deferred Financing Costs
The Company records as a discount to debt all third-party costs incurred, including equity-based payments, associated with the issuance of long-term debt. The costs are amortized to interest expense over the term of the debt using the effective interest method.
Advertising
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising costs were $204,000, $40,000 and $31,000 for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are included in sales and marketing expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
Research and Development Costs
Research and Development costs are expensed as incurred and were approximately $6.7 million, $4.2 million and $3.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Income Taxes
The Company has not recorded current income tax expense due to the generation of net operating losses. Deferred income taxes are accounted for using the balance sheet approach which requires recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more-likely-than-not that a deferred tax asset will not be realized. A full valuation allowance has been established on the deferred tax asset as it is more-likely-
than-not that the future tax benefit will not be realized. In addition, future utilization of the available net operating loss carryforward may be limited under Internal Revenue Code Section 382 as a result of changes in ownership.
The Company identifies and evaluates uncertain tax positions, if any, and recognizes the impact of uncertain tax positions for which there is a less than more-likely-than-not probability of the position being upheld when reviewed by the relevant taxing authority. Such positions are deemed to be unrecognized tax benefits and a corresponding liability is established on the balance sheet. The Company has not recognized a liability for uncertain tax positions. If there were an unrecognized tax benefit, the Company would recognize interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in interest expense and penalties in operating expenses. The Company’s remaining open tax years subject to examination by the Internal Revenue Service include the years ended December 31, 2014 through 2016; however, there currently are no examinations in process.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The respective carrying value of certain on-balance-sheet financial instruments approximated their fair values due to the short-term nature of these instruments. These financial instruments include cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt approximates its carrying value based upon current rates available to the Company.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company measures all employee stock-based compensation awards using a fair value method and records such expense in its consolidated financial statements. The estimated value of the portion of the award that is ultimately expected to vest, with forfeitures accounted for as they occur, is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. The Company estimates the grant date fair value of stock option awards generally on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing models.
With respect to performance stock units (“PSUs”), the number of shares that vest and are issued to the recipient is based upon the Company’s performance as measured against specified targets over the measurement period. The fair value of the PSUs is based on the Company’s closing stock price on the grant date and its estimate of achieving such performance targets. For further discussion and disclosures, see Note 10, “Stock Incentive Plan.”
Earnings (Loss) Per Share of Common Stock
Earnings (loss) per share of common stock (EPS) is calculated for basic EPS by dividing net income (loss) available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period.
There were no dilutive instruments as of December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. The basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding were 33,322,767 and 30,702,164 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Basic and diluted net loss per commons share for all periods presented is computed by dividing the net loss attributable to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding and common share equivalents outstanding, when dilutive. Potentially dilutive common share equivalents include common shares which would potentially be issued pursuant to stock warrants and stock options. Common share equivalents are not included in determining the fully diluted loss per share if their effect is antidilutive.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, issued a new standard on revenue recognition which outlines a single comprehensive model to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. The core principle of the revenue model is that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The standard is designed to create greater comparability for financial statement users across industries and jurisdictions and also requires enhanced disclosures. The guidance is effective for the Company beginning on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. The standard may be applied retrospectively to each prior period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect recognized as of the adoption date. During the quarter ended December 31, 2017, we completed our evaluation of the new standard, including an assessment of existing revenue contracts with our customers on our most significant revenue streams, business practices and processes, and our controls over financial reporting, and we do not believe there will be a material change to the timing and amounts of our revenue, processes or internal controls. During 2018, we will be required to provided additional disclosures in the notes to the consolidated financial statements. We will utilize the modified retrospective method upon adoption.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases (Topic 842)”. This update will increase transparency and comparability among organizations by recognizing lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. This update is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact this standard will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments (Topic 230). The ASU was issued intending to reduce diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows by providing guidance on eight specific cash flow issues. The guidance is effective for the Company on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. We do not believe the adoption of this standard will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230), guidance that a statement of cash flows explains the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. The guidance is effective for the Company on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. We do not believe the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on our Statement of Cash Flows.
In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-09, “Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Scope of Modification Accounting.” ASU 2017-09 provides clarity on which changes to the terms or conditions of share-based payment awards require entities to apply the modification accounting provisions required in Topic 718. ASU 2017-09 is effective for the Company on January 1, 2018, including interim reporting periods during the year ending December 31, 2018. We do not believe the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
The Company’s management has reviewed and considered all other recent accounting pronouncements and believe there are none that could potentially have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial condition, results of operations, or disclosures.
4. Inventories
Inventories are comprised of unprocessed tissue, work-in-process, Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane, AcroVal® Neurosensory and Motor Testing
System, AxoTouch® Two-Point Discriminator and supplies and are valued at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value and consist of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finished goods
|
|
$
|
5,489,360
|
|
$
|
4,132,036
|
|
|
Work in process
|
|
|
470,187
|
|
|
205,116
|
|
|
Raw materials
|
|
|
1,356,395
|
|
|
1,121,688
|
|
|
Inventories
|
|
$
|
7,315,942
|
|
$
|
5,458,840
|
|
Inventories are net of reserve of approximately $812,000 and $960,000 at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
5.Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consist of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furniture and equipment
|
|
$
|
1,934,669
|
|
$
|
1,270,173
|
|
|
Leasehold improvements
|
|
|
711,319
|
|
|
447,650
|
|
|
Processing equipment
|
|
|
1,839,800
|
|
|
1,577,561
|
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization
|
|
|
(2,288,749)
|
|
|
(1,801,137)
|
|
|
Property and equipment, net
|
|
$
|
2,197,039
|
|
$
|
1,494,247
|
|
6.Intangible Assets
The Company’s intangible assets consist of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
License agreements
|
|
$
|
1,007,566
|
|
$
|
984,342
|
|
|
Patents
|
|
|
459,903
|
|
|
308,212
|
|
|
Less: accumulated amortization
|
|
|
(530,477)
|
|
|
(463,575)
|
|
|
Intangible assets, net
|
|
$
|
936,992
|
|
$
|
828,979
|
|
License agreements are being amortized over periods ranging from 17-20 years. Certain patent costs of $22,000 were being amortized over three years. As of December 31, 2017, these patents were fully amortized, and the remaining patents of $460,000 are a combination of pending and issued patent costs, $102,000 of which is being amortized over periods up to 20 years. Amortization expense for 2017, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $79,000, $75,000 and $46,000, respectively. As of December 31, 2017, future amortization of license agreements is expected to be $74,000 for 2018 through 2023 and $134,000, thereafter .
License Agreements
The Company has entered into multiple license agreements (together, the “License Agreements”) with the University of Florida Research Foundation (“UFRF”) and University of Texas at Austin (“UTA”). Under the terms of the License Agreements, the Company acquired exclusive worldwide licenses for underlying technology used in repairing and regenerating nerves. The licensed technologies include the rights to issued patents and patents pending in the United States and international markets. The effective term of the License Agreements extends through the term of the related patents and the agreements may be terminated by the Company with 60 days prior written notice. Additionally, in the
event of default, licensors may terminate an agreement if the Company fails to cure a breach after written notice. The License Agreements contain the key terms listed below:
|
·
| |
AxoGen pays royalty fees ranging from 1% to 3% under the License Agreements based on net sales of licensed products. One of the agreements also contains a minimum royalty of $12,500 per quarter, which may include a credit in future quarters in the same calendar year for the amount the minimum royalty exceeds the royalty fees. Also, when AxoGen pays royalties to more than one licensor for sales of the same product, a royalty stack cap applies, capping total royalties at 3.75%; |
|
·
| |
If AxoGen sublicenses technologies covered by the License Agreements to third parties, AxoGen would pay a percentage of sublicense fees received from the third party to the licensor. Currently, AxoGen does not sublicense any technologies covered by License Agreements. The Company is not considered a sub-licensee under the License Agreements and does not owe any sub-licensee fees for its own use of the technologies; |
|
·
| |
AxoGen reimburses the licensors for certain legal expenses incurred for patent prosecution and defense of the technologies covered by the License Agreements; and |
|
·
| |
Currently, under the UTA agreement, AxoGen would owe a $15,000 milestone fee upon receiving a Phase II Small Business Innovation Research or Phase II Small Business Technology Transfer grant involving the licensed technology. The Company has not received either grant and does not owe such a milestone fee. A milestone fee to the UFRF of $2,000 is due if AxoGen receives FDA approval of its Avance® Nerve Graft, a milestone fee of $25,000 is due upon the first commercial use of certain licensed technology to provide services to manufacture products for third parties and a milestone fee of $10,000 is due upon the first use to manufacture products that utilize certain technology that is not currently incorporated into AxoGen products. |
Royalty fees were approximately $1.2 million, $812,000 and $526,000 during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and are included in sales and marketing expense on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations.
7.Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses
Accounts payable and accrued expenses consists of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable
|
|
$
|
3,237,962
|
|
$
|
3,614,015
|
|
|
Accrued expenses
|
|
|
1,770,956
|
|
|
804,691
|
|
|
Accrued compensation
|
|
|
3,943,143
|
|
|
2,583,459
|
|
|
Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses
|
|
$
|
8,952,061
|
|
$
|
7,002,165
|
|
8.Term Loan Agreements and Long-Term Debt
Term Loan Agreements and Long Term Debt consist of the following:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31,
|
|
December 31,
|
|
|
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Term Loan Agreement with MidCap Financial Trust (“MidCap”) for a total of $21,000,000, net of $554,100 of unamortized deferred financing fees at December 31, 2017, and $771,185 at December 31, 2016. Interest is payable monthly at 8.0% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5% which as of December 31, 2017 resulted in a 9.36% rate.
|
|
$
|
20,445,900
|
|
$
|
20,228,815
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revolving Loan Agreement with MidCap for up to $10,000,000 with borrowings based upon eligible accounts receivable and inventory. Interest is payable monthly at 4.5% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5% which as of December 31, 2017 resulted in a 5.86% rate.
|
|
|
4,000,000
|
|
|
4,025,023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment Lease Agreement with Cisco Capital for a total lease amount of $58,875 which has a 36 month term and requires no lease payments for the first three months of the lease and 33 equal payments of principal and interest until the end of the term. Interest on the lease is payable monthly at 3.5% per annum.
|
|
|
36,930
|
|
|
57,829
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment Lease Agreement with Raymond Leasing Corporation for a total lease amount of $29,998 which has a 48 month term with equal payments for principal and interest until the end of the term. Interest on the lease is payable monthly at 6.7% per annum.
|
|
|
29,998
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equipment Lease Agreement with B&B Office Systems for a total lease amount of $31,961 which has a 60 month term with equal payments for principal and interest until the end of the term. Interest on the lease is payable monthly at 8.5% per annum.
|
|
|
31,961
|
|
|
—
|
|
|
Total
|
|
|
24,544,789
|
|
|
24,311,667
|
|
|
Less current revolving loan
|
|
|
(4,000,000)
|
|
|
(4,025,023)
|
|
|
Less current maturities of long term debt
|
|
|
(735,017)
|
|
|
(20,899)
|
|
|
Long-term portion
|
|
$
|
19,809,772
|
|
$
|
20,265,745
|
|
Term and Revolving Loans
Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement
On November 12, 2014, AxoGen, as borrower, and AC, as guarantor, entered into that certain Term Loan Agreement, (the “Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement”), dated November 12, 2014, by and among AxoGen, as borrower, AC, as guarantor, the lenders party thereto and Three Peaks Capital S.a.r.l. (“Three Peaks”), an indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Oberland Capital Healthcare Master Fund LP, as administrative and collateral agent for the lenders. Under the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement, Three Peaks provided AxoGen a term loan of $25 million which had a six-year term and required interest only payments and a final principal payment due at the end of the term. Interest was payable quarterly at 9.00% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 1.0% which as of November 13, 2014 resulted in a 10% rate.
In addition, on November 12, 2014, AxoGen entered into the Revenue Interest Agreement (the “Revenue Interest Agreement”) with Three Peaks. Royalty payments were based on a royalty rate of 3.75% of AxoGen’s revenues up to a maximum of $30 million in revenues in any 12 month period.
On October 26, 2016, the Three Peaks Term Loan Agreement and Revenue Interest Agreement were paid in full and the Company had no further obligations pursuant to such agreements.
MidCap Term Loan Agreement
On October 25, 2016 (the “Closing Date”), AxoGen and AC, each as borrowers, entered into a Credit and Security Agreement (Term Loan) (the ''MC Term Loan Agreement") with the lenders party thereto and MidCap Financial Trust (“MidCap”), as administrative agent and a lender. Under the MC Term Loan Agreement, MidCap provided the Company a term loan in the aggregate principal amount of $21 million (the "Term Loan") which has a maturity date of May 1, 2021 and requires interest only payments through December 1, 2018, and thereafter, 30 monthly payments of principal and interest resulting in the Term Loan being fully paid by the maturity date. Interest is payable monthly at 8.00% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5%, which, as of December 31, 2017, resulted in an 9.36% rate. In addition to the interest charged on the Term Loan, the Company is also obligated to pay certain fees, including an annual agency fee of 0.25% of the aggregate principal amount of the Term Loan.
Under the MC Term Loan Agreement, the Company has the option at any time to prepay the Term Loan in whole or in part, provided that prepayments shall be: (i) in an amount equal to $2,500,000 or a higher integral multiple of $1,000,000; and (ii) accompanied by certain prepayment and exit fees. There can be no more than three partial voluntary prepayments allowed during the term of the MC Term Loan Agreement. MidCap and certain of the lenders have the right to demand prepayment, along with prepayment and exit fees upon an event of default which includes, but is not limited to: (i) default of the Revolving Loan (as defined below); (ii) a change of control of the Company; (iii) sale of the majority of the Company's assets; or (iv) a material adverse change to the Company. The prepayment fee is determined by multiplying the amount being prepaid by the following applicable percentage amount: (a) 3.0% during the first year following the Closing Date; (b) 2.0% during the second year following the Closing Date, and (c) 1.0% thereafter. No prepayment fee is due in the event the prepayment is a result of refinancing the Term Loan and Revolving Loan with MidCap or an affiliate of MidCap. Upon any repayment of any portion of the Term Loan (whether voluntary, involuntary or mandatory), other than scheduled amortization payments, and on the final payment of principal of the Term Loan, an exit fee of 5.0% of the principal amount of the Term Loan is also owed based on the portion of any prepayment made and at maturity upon the original principal amount less any prepayments of the Term Loan. The Company used the aggregate proceeds of $25 million from the MidCap Term Loan and the Revolving Loan to pay the outstanding indebtedness owed to Three Peaks and the other lenders to terminate the Term Loan Agreement and the Revenue Interest Agreement. Expenses and fees of approximately $800,000 to complete the negotiation and documentation of the MidCap Term Loan and the Revolving Loan and prepayment fees of approximately $2.3 million owed to Three Peaks were paid from the Company’s own funds.
MidCap Revolving Loan Agreement
On October 25, 2016, AxoGen and AC, each as borrowers, also entered into a Credit and Security Agreement (Revolving Loan) (the ''Revolving Loan Agreement") with the lenders party thereto and MidCap, as administrative agent and a lender. Under the Revolving Loan Agreement, MidCap agreed to lend to the Company up to $10 million under a revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Loan") which amount may be drawn down by the Company based upon an available borrowing base which includes certain accounts receivable and inventory. The Revolving Loan may be increased to up to $15 million at the Company’s request and with the approval of MidCap. As of December 31, 2017, the Company’s borrowing base under the Revolving Loan provided availability of approximately $7.7 million. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had borrowed $4.0 million of the Revolving Loan. The maturity date of the Revolving Loan is May 1, 2021. Interest is payable monthly at 4.5% per annum plus the greater of LIBOR or 0.5% on outstanding advances, which, as of December 31, 2017, resulted in an 5.86% rate. In addition to the interest charged on the Revolving Loan, the Company is also obligated to pay certain fees, including a collateral management fee of 0.5% per annum of the principal amount outstanding on the Revolving Loan from time to time and an unused line fee of 0.5% per annum on the difference between the average amount outstanding on the Revolving Loan minus the total amount of the Revolving Loan commitment. The Revolving Loan is subject to a minimum balance, such that the Company pays the greater of: (i) interest accrued on the actual amount drawn under the Revolving Loan Facility; and (ii) interest accrued on 30% of the average borrowing base. If the Revolving Loan is terminated or permanently reduced prior to the maturity
date, MidCap is owed a deferred revolving loan origination fee determined by multiplying the agreed total lending amount by the following applicable percentage amount: (a) 3.0% during the first year following the Closing Date; (b) 2.0% during the second year following the Closing Date, and (c) 1.0% thereafter. No deferred revolving loan origination fee is due in the event the Revolving Loan is paid in full or the termination of the revolving credit facility is a result of refinancing the Term Loan and Revolving Loan with MidCap or an affiliate of MidCap. Termination of the Revolving Loan may occur, at the option of MidCap and certain of the lenders, upon an event of default which includes, but is not limited to: (i) default in payment of the Term Loan; (ii) a change of control of the Company; (iii) sale of the majority of the Company's assets; or (iv) a material adverse change to the Company.
The MC Term Loan Agreement and the Revolving Loan Agreement each contain covenants that place restrictions on AxoGen’s operations, including, without limitation, covenants related to debt restrictions, investment restrictions, dividend restrictions, restrictions on transactions with affiliates and certain revenue covenants. As of December 31, 2017, the Company was in compliance with the agreements’ covenants. MidCap, on behalf of the lenders under the agreements, has a first perfected security interest in the assets of the Company to guarantee the payment in full of the agreements. Upon the payment in full to MidCap and the lenders of the Term Loan Agreement and Revolving Loan Agreement, the Company would have no further obligations to MidCap or the lenders under the Term Loan Agreement or the Revolving Loan Agreement.
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $2.2 million compared to $5.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The 2016 amount included a final payment to Three Peaks of approximately $2.4 million inclusive of prepayment fees and accrued interest through October 25, 2016. In addition, as a result of the accounting treatment for the Three Peaks transaction, the Company had previously recorded a total of $750,000 of deferred interest charges which were offset against those prepayment fees. The net impact of those transactions resulted in a net interest charge of approximately $1.7 million in 2016, which is included in interest expense. Additionally, as the result of the extinguishment of the debt facility with Three Peaks, the Company wrote off approximately $750,000 of prepaid financing fees to interest expense – deferred financing costs in 2016.
Annual maturities of the Company’s long-term obligations are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ending December 31
|
|
Amount
|
|
2018
|
|
$
|
735,017
|
|
2019
|
|
|
8,427,916
|
|
2020
|
|
|
8,413,817
|
|
2021
|
|
|
3,514,892
|
|
2022
|
|
|
7,247
|
|
|
|
|
21,098,889
|
|
Less unamortized debt issuance costs
|
|
|
(554,100)
|
|
TOTAL
|
|
$
|
20,544,789
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.Shareholders’ Equity (Deficit)
AxoGen, Inc. Classes of Stock
AxoGen, Inc.’s authorized capital stock consists of 50,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share. The authorized capital stock is divisible into the classes and series, has the designation, voting rights, and other rights and preferences and is subject to the restrictions that the AxoGen Board of Directors may establish from time to time. Unless otherwise designated by the AxoGen Board of Directors, all shares are common stock. AxoGen has not designated any shares other than common stock.
Public Offering
On February 5, 2015, AxoGen entered into an underwriting agreement with Wedbush Securities Inc., as underwriter (the “Wedbush”), in connection with the offering, issuance and sale of 4,728,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.01 per share, at a price to the public of $2.75 per share (the “February 2015 Offering”). The Company also granted to Wedbush a 30-day option to purchase up to an aggregate of 709,200 additional shares of common stock to cover over-allotments, if any.
On February 13, 2015, the February 2015 Offering was completed with the sale of 5,437,200 shares of common stock, which included the full exercise of the over-allotment option, at $2.75 per share, resulting in gross proceeds to AxoGen from the February 2015 Offering of approximately $15.0 million, before deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other estimated offering expenses payable by AxoGen estimated at approximately $1.4 million. The shares of common stock were listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market. The February 2015 Offering was made pursuant to the Company’s effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-195588) previously filed with the SEC on April 30, 2014, and pursuant to the prospectus supplement and the accompanying prospectus describing the terms of the February 2015 Offering, dated February 5, 2015.
On August 26, 2015, the Company entered into the Purchase Agreement with EW Healthcare Partners L.P. (formerly Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P.)(“Essex”) for the purchase of 4,861,111 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $3.60 per share, raising approximately $17.5 million in gross proceeds (the “August 2015 Offering”). The expenses directly related to the August 2015 Offering were approximately $300,000 and were paid as of December 31, 2015. Those expenses include the Company’s legal and accounting fees, printing expenses, transfer agent fees and miscellaneous fees and costs related to the August 2015 Offering. The Company provided certain demand and “piggy-back” registration rights in connection with that sale of common stock. The August 2015 Offering was made pursuant to the Company’s effective shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-195588) previously filed with the SEC on April 30, 2014 and pursuant to the prospectus supplement and the accompanying prospectus describing the terms of the August 2015 Offering, dated August 26, 2015.
On October 7, 2016, AxoGen entered into an underwriting agreement with JMP Securities LLC, as representative of the several underwriters (collectively, the “2016 Offering Underwriters”), to issue and sell 2,333,334 shares of the Company’s common stock in an underwritten registered public offering (the “2016 Offering”) at an offering price of $7.50 per share. Pursuant to the underwriting agreement, the Company also granted the 2016 Offering Underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to an additional 350,000 shares of common stock, which the underwriters exercised in full on October 7, 2016. Five of the Company’s directors and officers purchased an aggregate of approximately 32,666 Shares in the 2016 Offering and such purchases were made on the same terms and conditions as purchases by the public in the 2016 Offering. The 2016 Offering closed on October 13, 2016, and the Company received net proceeds of approximately $18.67 million from the sale of 2,683,334 shares of common stock, which included the additional 350,000 shares of common stock, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses. The 2016 Offering was pursuant to a prospectus supplement dated October 7, 2016, which was filed with the SEC in connection with the Company’s shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-207829) that was filed with the SEC on November 5, 2015 and declared effective on December 11, 2015 and the related prospectus dated December 11, 2015.
On November 16, 2017, AxoGen entered into a certain underwriting agreement (the “Leerink Underwriting Agreement”) with Leerink Partners LLC, as representative of the several underwriters named therein (collectively, the “2017 Offering Underwriters”) and Essex, pursuant to which (i) the Company agreed to issue and sell 700,000 shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-207829), filed with the SEC on November 5, 2015, and declared effective by the SEC on December 11, 2015, and the prospectus contained therein, as supplemented by the prospectus supplement dated November 16, 2017, and (ii) Essex agreed to sell 1,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock pursuant to a registration statement on Form S-3 (File No. 333-220770), filed with the SEC on October 2, 2017, and declared effective by the SEC on October 11, 2017, and the prospectus contained therein, as supplemented by the Prospectus Supplement, in an underwritten registered public offering at an offering price of $21.00 per share. The Company and Essex granted the 2017 Offering Underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to
an aggregate of 255,000 additional shares of common stock, at the public offering price, less the underwriting discounts and commissions, which was exercised in full on November 16, 2017. The Company received net proceeds of approximately $15.65 million after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses. The Company intends to use the net proceeds of this offering for general working capital purposes; however, the Company’s management will retain broad discretion over the allocation of the net proceeds.
10.Stock Incentive Plan
The Company maintains the AxoGen 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended (the “AxoGen Plan”), which allows for issuance of incentive stock options, non-qualified stock options, performance stock units (PSU) and restricted stock awards (RSU) to employees, directors and consultants at exercise prices not less than the fair market value at the date of grant. At the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders the AxoGen Plan was amended to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the AxoGen Plan to 5,500,000 shares, and at the 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, the AxoGen Plan was amended to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the AxoGen Plan to 7,700,000 shares. At the 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, the shareholders approved the adoption of the AxoGen 2017 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2017 ESPP”), which allows for eligible employees to acquire shares of our common stock through payroll deductions at a discount from market value. The 2017 ESPP authorized a total of 600,000 shares of our common stock with the first offering period beginning January 1, 2018.
The options to employees typically vest 25% one year after the grant date and 12.5% every six months thereafter for the remaining three-year period until fully vested after four years and those to directors and certain executive officers have vested 25% per quarter over one year or had no vesting period. Beginning in June 2017, options to employees typically vest 50% two years after the grant and 12.5% every six months thereafter for the remaining four-year period until fully vested after five years. Options issued to consultants have vesting provisions based on the engagement ranging from no vesting to vesting over the service period ranging from three to ten years. Options have terms ranging from seven to ten years.
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense of $3.6 million, $1.4 million and $1.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, which consisted of compensation expense related to employee stock options, PSUs and RSUs based on the value of share-based payment awards that are ultimately expected to vest during the period.
The Company estimates the fair value of each option award issued under such plans on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing models that use the assumptions noted in the table below. The Company estimates the volatility of its common stock at the date of grant based on the volatility of comparable peer companies which are publicly traded, for the periods prior to the Company’s merger with LecTec Corporation in 2011 (the “Merger”), and based on the Company’s common stock for periods subsequent to the Merger. However for options granted on and after December 29, 2016, the Company began using a Multiple Point Black-Scholes option-pricing model which uses a weighted average of historical volatility and peer company volatility. The Company determines the expected life giving consideration to the contractual terms, vesting schedules and post-vesting forfeitures. The Company uses the risk-free interest rate on the implied yield currently available on U.S. Treasury issues with an equivalent remaining term approximately equal to the expected life of the award.
The Company used the following weighted-average assumptions for stock awards granted during the year ended December 31:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year ended December 31,
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Expected term (in years)
|
|
6.16
|
|
4.60
|
|
4.00
|
|
|
Expected volatility
|
|
50.43
|
%
|
59.58
|
%
|
69.08
|
%
|
|
Risk free rate
|
|
2.12
|
%
|
1.72
|
%
|
1.40
|
%
|
|
Expected dividends
|
|
—
|
%
|
—
|
%
|
—
|
%
|
The weighted average fair value of options granted at market during 2017 and 2016 was $8.40 and $3.84 per option, respectively.
The following is a summary of stock award activity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted
|
|
Remaining
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average
|
|
Contractual
|
|
|
|
|
Stock Awards
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
Term(Years)
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2014:
|
|
2,743,818
|
|
3.03
|
|
5.94
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
946,250
|
|
4.31
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(290,478)
|
|
(3.12)
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
(171,563)
|
|
(2.99)
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015:
|
|
3,228,027
|
|
3.40
|
|
5.43
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
1,529,850
|
|
7.67
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(75,938)
|
|
(3.74)
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
(340,942)
|
|
(3.16)
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2016:
|
|
4,340,997
|
|
4.92
|
|
5.93
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
1,298,355
|
|
19.99
|
|
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(94,777)
|
|
(6.29)
|
|
|
|
|
Exercised
|
|
(568,135)
|
|
(3.43)
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2017
|
|
4,976,440
|
|
8.99
|
|
6.39
|
|
|
Exercisable at December 31, 2017
|
|
2,343,796
|
|
4.12
|
|
4.26
|
|
The intrinsic value of equity awards exercised during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $7.8 million and $1.5 million, respectively. The intrinsic value of equity awards outstanding at December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $96.1 million and $17.7 million, respectively. The intrinsic value of equity awards exercisable at December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $56.7 million and $12.9 million, respectively. The increase in the intrinsic values of the equity awards was primarily the result of the increase in the Company’s stock price to $28.30 per share as of the last trading day for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to $9.00 per share for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Total future compensation expense related to nonvested awards is expected to be approximately $16.8 million at December 31, 2017 which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 4.00 years. The following table represents non-vested share-based payment activity:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average
|
|
|
|
|
Number of Awards
|
|
Exercise Price
|
|
|
Nonvested options - December 31, 2014:
|
|
1,159,486
|
|
3.37
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
946,250
|
|
4.31
|
|
|
Vested
|
|
(635,289)
|
|
(3.32)
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(290,478)
|
|
(3.12)
|
|
|
Nonvested options - December 31, 2015:
|
|
1,179,969
|
|
4.21
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
1,529,850
|
|
7.67
|
|
|
Vested
|
|
(512,562)
|
|
(4.21)
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(75,938)
|
|
(3.74)
|
|
|
Nonvested options - December 31, 2016:
|
|
2,121,319
|
|
6.72
|
|
|
Granted
|
|
1,298,355
|
|
19.99
|
|
|
Vested
|
|
(692,253)
|
|
(6.49)
|
|
|
Forfeited
|
|
(94,777)
|
|
(6.29)
|
|
|
Nonvested options - December 31, 2017:
|
|
2,632,644
|
|
13.33
|
|
On December 18, 2017, the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors approved a PSU to certain Company’s officers. The performance measure is based on achieving 2019 specified revenues and the PSUs vest one-
third each February 15, 2020, 2021 and 2022. The PSUs have payout opportunities of between 0% and 150%. The performance measure is a target revenue amount for the year ended December 31, 2019.
The Company estimated the fair value of the PSUs based on its closing stock price at the time of grant and its estimate of achieving such performance target and records compensation expense on a graded vesting attribution method, which recognizes compensation cost on a straight-line basis over each separately vesting portion of the award. Over the performance period, the number of shares of common stock that will ultimately vest and be issued and the related compensation expense is adjusted based upon the Company’s estimate of achieving such performance target. The number of shares delivered to recipients and the related compensation cost recognized as an expense will be based on the actual performance metrics as set forth in the applicable PSU award agreement.
The December 18, 2017 PSU awards consisted of a total target award of 114,700 shares. The amount actually awarded will be based upon achievement of the performance measure and can range from 0 to 172,050, or up to 150% of the target award. The grant date fair value of the common stock on December 18, 2017 was $27.00. The total unrecognized future compensation expense related to this PSU assuming achievement of 100% of the target award is $3.1 million. Assuming the minimum of 0% and the maximum of 150% payout opportunity for the PSU, the range of total future compensation expense related to this PSU award is between $0 and $4.6 million as of December 31, 2017.
On December 18, 2017 the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors also approved PSU awards to certain executives related to their work on the Company’s BLA. The PSU awards consist of a targeted total award of 200,000 shares. The number of shares are allocated to certain milestones related to the BLA submission to and approval by the FDA. The performance measure is based upon achieving each of the specific milestones and will vest 100% upon achieving each of the milestones.
The Company estimated the fair value of the PSUs based on its closing stock price at the time of grant and its estimate of achieving such performance target and will record compensation expense as the milestones are achieved. Over the performance period, the number of shares of common stock that will ultimately vest and be issued and the related compensation expense will be adjusted based upon the Company’s estimate of achieving such performance target. The number of shares delivered to recipients and the related compensation cost recognized as an expense will be based on the actual performance metrics as set forth in the applicable PSU award agreement.
The amount actually awarded will be based upon achievement of the performance measures and can range from 0 to 200,000 shares. The grant date fair value of the common stock on December 18, 2017 was $27.00. The total unrecognized future compensation expense related to this PSU, assuming achievement of 100% of the target award is $5.4 million. Assuming the minimum of 0% and the maximum of 100% payout opportunity for the PSU, the range of total future compensation expense related to this PSU award is between $0 and $5.4 million as of December 31, 2017.
On December 29, 2017, the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors approved a separate PSU award to the Company’s Vice President of Sales. This award amounted to a target payout of 2,500 shares. The grant date fair value of the common stock on December 29, 2017 was $28.30. The amount actually awarded will be based upon achievement of certain quarterly revenue targets in 2018. Assuming a minimum of 0% and a maximum of 150% payout opportunity for the PSU, the range of future compensation expense related to this PSU award is between $0 and $106,000.
11. Income Taxes
The Tax Reform, which was signed into law on December 22, 2017, has resulted in significant changes in the U.S. corporate income tax system. The Tax Reform reduces the corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21%. The effects of changes in tax rates and laws are recognized in the period in which the new legislation is enacted. As a result, we have remeasured our deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 based on the new Federal income tax rate of
21%. The Company has temporary differences between the carrying amount of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and their respective income tax basis, as measured by enacted state and federal rates as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31
|
|
2017
|
|
2016
|
|
2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax assets:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net operating loss carryforwards
|
|
$
|
27,578,200
|
|
$
|
38,299,400
|
|
$
|
33,424,100
|
|
|
Charitable contributions
|
|
|
300
|
|
|
500
|
|
|
500
|
|
|
Inventory reserves
|
|
|
205,800
|
|
|
361,300
|
|
|
267,700
|
|
|
Amortization
|
|
|
22,800
|
|
|
89,500
|
|
|
51,400
|
|
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts
|
|
|
116,900
|
|
|
102,300
|
|
|
72,300
|
|
|
Stock-based compensation
|
|
|
519,900
|
|
|
341,400
|
|
|
260,600
|
|
|
Total deferred tax assets
|
|
|
28,443,900
|
|
|
39,194,400
|
|
|
34,076,600
|
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation
|
|
|
(80,500)
|
|
|
(83,300)
|
|
|
(62,400)
|
|
|
Deferred revenue
|
|
|
(6,400)
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
Net deferred tax assets
|
|
|
28,357,000
|
|
|
39,111,100
|
|
|
34,014,200
|
|
|
Valuation allowance
|
|
$
|
(28,357,000)
|
|
$
|
(39,111,100)
|
|
$
|
(34,014,200)
|
|
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had net operating loss carry forwards of approximately $108.8 million to offset future taxable income which expire in various years through 2037. A valuation allowance is recorded to reduce the deferred tax assets reported if, based on the weight of the evidence, it is more-likely-than-not that a portion or none of the deferred tax assets will be realized. After consideration of all the evidence, including reversal of deferred tax liabilities, future taxable income and other factors, management has determined that a full valuation allowance is necessary as of December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. The valuation allowance decreased by $10.8 million during 2017, primarily due to the remeasurement of our deferred tax assets and liabilities as a result of the Tax Reform, which amounted to $14.5 million, offset by the current year’s net operating loss of $3.7 million. During 2016 and 2015, the valuation allowance increased $5.1 million and $4.5 million, respectively, to offset the deferred tax benefit in the respective years. The difference between the financial statement income tax and the income tax benefit using statutory rates is primarily due to the decrease in the valuation allowance.
The Company had no income tax expense or income tax benefit for 2015, 2016 and 2017 due to incurrence of net operating losses. The Company does not believe there are any additional tax refund opportunities currently available.
12. Employee Benefit Plan
The Company adopted the AxoGen 401(k) plan (the “401(k) Plan”) in December 2015 with contributions starting in January 2016. All full-time employees who have attained the age of 18 are eligible to participate in the 401(k) Plan. Eligibility is immediate upon employment and enrollment is available any time during employment. Participating employees may make annual pretax contributions to their accounts up to a maximum amount as limited by law. The 401(k) Plan requires the Company to make matching contributions of 3% on the first 3% of the employee’s annual salary and 1% of the next 2% of the employee’s annual salary as long as the employee participates in the 401(k) Plan. Both employee contributions and Company contributions vest immediately. The Company contributed $439,000 and $334,000 in matching funds during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company contributed matching funds of $172,000 to the AxoGen Simple IRA plan which was replaced by The 401(k) Plan in December 2015.
13. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases
On March 16, 2016 AC entered into the Fourth Amendment to Lease (“Fourth Amendment”) with SNH Medical Office Properties Trust, a Maryland real estate investment trust (“SNH”). SNH is the landlord of AC’s currently leased 11,761 square foot corporate headquarters facility at 13631 Progress Boulevard, Suite 400, Alachua, Florida 32615 (the “Current Premises”) pursuant to that certain lease dated as of February 6, 2007, as amended (the “Lease”). The Fourth Amendment expands the Current Premises by 7,050 square feet (the “Expansion Premises”). The Fourth Amendment also provides that the Expiration Date (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) of the Lease will be extended to approximately five years from the Occupancy Date (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) which was June 2016. The original expiration date of the Current Premises remains unchanged; provided, however, that AC shall have the right to extend the Current Premises Term (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) for three additional periods (the “Current Premises Extended Term”), the first such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2018 and end on October 31, 2019, the second such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2019 and end on October 31, 2020, and the third such Current Premises Extended Term to commence on November 1, 2020 and end on the Expiration Date. AC also has the right to extend the term of the then current Leased Premises (as defined in the Fourth Amendment) for an additional period of five years commencing on the day immediately after the Expiration Date. AxoGen’s annual cost of such property ranges from approximately $248,000 to $324,000 per year.
On January 23, 2017 AC entered into a lease (the “New SHN Lease”) for a five-year term commencing on April 1, 2017 with SNH, for 1,431 square feet at 13709 Progress Boulevard, Alachua, Florida 32615. Pursuant to the New SHN Lease, AC is to use the space for general office and biomedical research uses. SNH is the landlord of AC’s currently leased corporate headquarters facility at 13631 Progress Boulevard, Alachua, Florida 32615. AC’s additional annual cost of the Premises will range from approximately $26,000 to $29,000 over the life of the lease.
On October 25, 2013, AC entered into a commercial lease with Ja-Cole L.P. (“Ja-Cole”). Under the terms of the commercial lease, AC occupied 5,400 square feet of warehouse/office space comprising the Burleson, Texas Distribution Facility until November 30, 2016 at an annual cost of $43,200. On April 21, 2015, AC entered into a new commercial lease, as amended by the addendum on such date (as amended, the “Commercial Lease”), with Ja-Cole. The Commercial Lease superseded and replaced the original lease with Ja-Cole dated October 25, 2013. Under the terms of the Commercial Lease, AC leased an additional 2,100 square feet of warehouse space at the Distribution Facility. The Commercial Lease is for a three-year term expiring April 21, 2018. On October 25, 2016, AC entered into Commercial Lease Amendment 2 (the “Ja-Cole Amendment”) to the Commercial Lease. Under the terms of the Ja-Cole Amendment, AC leased an additional 2,500 square feet of warehouse/office space at the Distribution Facility. The Distribution Facility now comprises a total of 10,000 square feet, all of which, pursuant to the Ja-Cole Amendment, will be leased until March 31, 2019. The annual rental cost of the Distribution Facility is now approximately $88,000.
The Distribution Facility houses raw material storage and product distribution while allowing same day order fulfillment for both the east and west coasts of the United States.
In addition, AxoGen leases space and maintains records at certain other facilities, including the Company’s prior corporate headquarters at 1407 South Kings Highway, Texarkana, Texas 75501.
The Company leases its lab space on a month-to-month basis.
Estimated future minimum rental payments on the leases are as follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ending December 31
|
|
Amount
|
|
|
2018
|
|
|
437,900
|
|
|
2019
|
|
|
182,251
|
|
|
2020
|
|
|
165,116
|
|
|
2021
|
|
|
86,638
|
|
|
2022
|
|
|
-
|
|
|
TOTAL
|
|
$
|
871,905
|
|
Total rent expense for the Company’s leased office and lab space for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $494,000, $433,000 and $351,000, respectively.
Service Agreements
On August 6, 2015, AxoGen entered into a License and Services Agreement with Community Blood Center (d/b/a Community Tissue Services) (“CTS”), Dayton, Ohio, an FDA registered tissue establishment. Processing of the Avance® Nerve Graft pursuant to the CTS agreement began in February 2016. The CTS agreement is for a five-year term, subject to earlier termination by either party at any time for cause (subject to the non-terminating party’s right to cure, in certain circumstances), or without cause upon 18 months’ prior notice. Under the CTS agreement AxoGen pays CTS a facility fee for clean room/manufacturing, storage and office space. CTS also provides services in support of AxoGen’s manufacturing such as routine sterilization of daily supplies, providing disposable supplies, microbial services and office support. Pursuant to the CTS Agreement, AxoGen pays license fees on a monthly basis to CTS which total an annual amount of approximately $1.4 million.
In August 2008, the Company entered into an agreement to distribute the AxoGuard® product worldwide in the field of peripheral nerve repair, and the parties subsequently amended the agreement on February 26, 2018. Pursuant to the February 2018 amendment, the agreement expires on June 30, 2027. The Cook Biotech agreement also requires certain minimum purchases, although through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforced such provision, and establishes a formula for the transfer cost of the AxoGuard® products. Under the agreement, AxoGen provides purchase orders to Cook Biotech, and Cook Biotech fulfills the purchase orders.
In December 2011, the Company also entered into a Master Services Agreement for Clinical Research and Related Services. The Company was required to pay $151,318 upon execution of this agreement and the remainder monthly based on activities associated with the execution of AxoGen’s phase 3 pivotal clinical trial to support a BLA for Avance® Nerve Graft.
Certain executive officers of the Company are parties to employment contracts. Such contracts have severance payments for certain conditions including change of control.
Concentrations
Vendor
Substantially all of AxoGen’s revenue is currently derived from four products, Avance® Nerve Graft, AxoGuard® Nerve Protector, AxoGuard® Nerve Connector and Avive® Soft Tissue Membrane. AxoGen has an exclusive distribution agreement with Cook Biotech for the purchase of AxoGuard® which expires June 30, 2027. The Cook Biotech agreement also requires certain minimum purchases, although through mutual agreement the parties have not established such minimums and to date have not enforced such provision, and establishes a formula for the transfer cost of the AxoGuard® products.
The agreement allows for termination provisions for both parties. Although there are products that AxoGen believes it could develop or obtain that would replace the AxoGuard® products, the loss of the ability to sell the AxoGuard®
products could have a material adverse effect on AxoGen’s business until other replacement products would be available.
Processor
AxoGen is highly dependent on the continued availability of its processing facilities at CTS and could be harmed if the physical infrastructure of this facility is unavailable for any prolonged period of time. In addition, disruptions could lead to significant costs and reductions in revenues, as well as a potential harm to the AxoGen’s business reputation and financial results. The CTS agreement is for a five-year term, subject to earlier termination by either party at any time for cause (subject to the non-terminating party’s right to cure, in certain circumstances), or without cause, upon 18 months’ prior notice. Although AxoGen believes it can find and make operational a new facility in less than six months, the regulatory process for approval of facilities is time-consuming and unpredictable. AxoGen’s ability to rebuild or find acceptable lease facilities would take a considerable amount of time and expense and could cause a significant disruption in service to its customers. Although AxoGen has business interruption insurance which would, in instances other than lease termination, cover certain costs, it may not cover all costs nor help to regain AxoGen’s standing in the market.
14. Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited)
The following is a summary of the quarterly results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quarter
|
|
|
|
|
|
First
|
|
Second
|
|
Third
|
|
Fourth
|
|
Total
|
|
2017
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
$
|
12,241,073
|
$
|
15,168,064
|
$
|
16,046,253
|
$
|
16,971,005
|
$
|
60,426,395
|
|
Gross profit
|
|
10,325,425
|
|
12,890,863
|
|
13,541,975
|
|
14,356,547
|
|
51,114,810
|
|
Net loss
|
|
(3,762,025)
|
|
(2,060,179)
|
|
(2,124,079)
|
|
(2,499,179)
|
|
(10,445,462)
|
|
Loss per common share - basic and diluted
|
|
(0.11)
|
|
(0.06)
|
|
(0.06)
|
|
(0.07)
|
|
(0.31)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2016
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues
|
$
|
8,111,759
|
$
|
10,381,883
|
$
|
11,205,224
|
$
|
11,408,672
|
$
|
41,107,538
|
|
Gross profit
|
|
6,706,168
|
|
8,847,471
|
|
9,507,781
|
|
9,578,868
|
|
34,640,288
|
|
Net loss
|
|
(3,676,091)
|
|
(2,802,696)
|
|
(2,305,373)
|
|
(5,626,984)
|
|
(14,411,144)
|
|
Loss per common share - basic and diluted
|
|
(0.12)
|
|
(0.09)
|
|
(0.08)
|
|
(0.17)
|
|
(0.47)
|
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
|
1.
| |
EVALUATION OF DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
The Company maintains “disclosure controls and procedures” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, and Board of Directors, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired objectives, and we necessarily are required to apply our judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible disclosure controls and procedures.
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017. Based on their evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective, and that the material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting included in Management’s Annual Report for the year ended December 31, 2016 had been remediated, as described below.
|
2.
| |
MANAGEMENT’S ANNUAL REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING |
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control system is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and includes those policies and procedures that:
|
·
| |
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
|
·
| |
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and |
|
·
| |
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. |
Because of inherent limitations, a system of internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate due to change in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting using the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013).
As a result of this evaluation, management determined the Company had effectively remediated the material weaknesses in its internal controls that existed as of December 31, 2016 relating to the design and operation of key controls around the use of judgment and calculations of significant estimates, as well as quarterly cycle count procedures related to consigned inventories, and that as of December 31, 2017, our internal control over financial reporting was effective. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim consolidated financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
During 2017, we reviewed the design of internal controls over the judgments, calculations and assumptions of significant estimates, as well as our processes and procedures related to our quarterly cycle counts. As a result, we modified our procedures and controls to address the material weaknesses that existed as of December 31, 2016, and have determined that these modifications have resulted in the effective remediation of those material weaknesses.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, Lurie, LLP, who audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of managements internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. This report states that the internal control over financial reporting was effective and appears on page 75 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
CHANGES IN INTERNAL CONTROLS OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
During the year ended December 31, 2017, management modified key control procedures in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d—15(f) under the Exchange Act) related to significant accounting estimates and quarterly inventory cycle counting to address the material weaknesses in those controls reported as of December 31, 2016.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
Information required by this item concerning our directors will be set forth under the caption “Election of Directors” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information required by this item concerning compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, as amended, will be set forth under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information required by this item concerning the audit committee of the Company, the audit committee financial expert of the Company and any material changes to the way in which security holders may recommend nominees to the Company’s Board of Directors will be set forth under the caption “Corporate Governance” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
The Board of Directors adopted a Code of Ethics, which is posted on our website http://ir.axogeninc.com/governance.cfm that is applicable to all employees and directors. We will provide copies of our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics without charge upon request. To obtain a copy, please visit our website or send your written request to Investors Relations, 13631 Progress Blvd., Suite 400, Alachua, FL 32615. With respect to any amendments or waivers of this Code of Business Conduct and Ethics (to the extent applicable to the Company’s chief executive officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions) the Company intends to either post such amendments or waivers on its website or disclose such amendments or waivers pursuant to a Current Report on Form 8-K.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
Information required by this item will be set forth under the caption “Executive Compensation” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED SHAREHOLDER MATTERS
Information required by this item concerning ownership will be set forth under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners”, “Security Ownership of Directors and Executive Officers” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Information required by this item concerning ownership will be set forth under the caption “Corporate Governance — Director Independence” and “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Information required by this item concerning ownership will be set forth under the caption “Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in our definitive proxy statement for our 2018 annual meeting, and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) Documents filed as part of this Report
|
(1)
| |
The following financial statements are filed herewith in Item 8 of Part II of this annual report on Form 10-K: |
|
|
|
|
|
(i)
|
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
|
(ii)
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
|
(iii)
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
|
|
(iv)
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
|
(v)
|
|
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
(2) Exhibits
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.2
|
|
AxoGen, Inc. Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 26, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 4.1
|
|
Warrants to purchase Common Stock of Company attached as exhibits to Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2011, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation, as borrower, Midcap Financial SBIC, LP, as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+4.2
|
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2015, between AxoGen, Inc. and Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P.
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.1
|
|
Patent License Agreement, dated as of August 3, 2005, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Texas System (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.2.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement with Sublicensing Terms, dated as of February 21, 2006, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2.2
|
|
Second Amendment to the Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement No. A5140, effective as of July 5, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 11, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.3
|
|
Sid Martin Biotechnology Development Institute Incubator License Agreement, dated as of September 26, 2006, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of February 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
*10.4.2
|
|
Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of August 9, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.3
|
|
Third Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of March 12, 2012, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.3 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.4
|
|
Fourth Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of September 8, 2014, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014, filed on November 13, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.5.1
|
|
Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.5.2
|
|
Amendment No. 1 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of February 24, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5.2 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+10.5.3
|
|
Amendment No. 2 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2018, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated.
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.6
|
|
AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Company’s Proxy Statement filed on April 8, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.7.1
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 15, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.7.2
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement dated as of July 17, 2017, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Jon S. Gingrich (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A, filed on July 20, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.8.1
|
|
Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Inducement Award Agreement to be granted by AxoGen, Inc. to Jon S. Gingrich on July 17, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A, filed on July 20, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.8.2
|
|
Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.1
|
|
Lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011, filed on November 14, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.2
|
|
Second Amendment to Lease, dated as of February 27, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, filed on March 12, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
10.9.3
|
|
Third Amendment to Lease, dated November 12, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SHN Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10.3 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013, filed on March 6, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.4
|
|
Fourth Amendment to Lease, dated as of March 16, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10.4 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 18, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.10.1
|
|
Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2007).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+**10.10.2
|
|
Amended Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.1
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 1, 2011, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Gregory Freitag (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.2
|
|
Amendment No. 1 to Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of May 11, 2014, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Greg Freitag (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2016, filed on August 4, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.3
|
|
Amendment No. 2 to Employment Agreement, dated as of August 6, 2015, by and between Gregory G. Freitag and AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.4
|
|
Amendment No. 3 to Employment Agreement, dated as of June 1, 2016, by and between Greg Freitag and AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 31, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.1
|
|
Commercial Lease, dated April 21, 2015, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.2
|
|
Addendum to Commercial Lease, dated April 21, 2015 by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.3
|
|
Commercial Lease Amendment 2, dated as of October 25, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 31, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.13
|
|
License and Services Agreement, dated as of August 6, 2015, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Community Blood Center (d/b/a Community Tissue Services) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.14
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of February 25, 2013, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Shawn McCarrey (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2013, filed on April 30, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
| 10.15
|
|
Securities Purchase Agreement dated as of November 12, 2014, between AxoGen, Inc., and PDL BioPharma, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Amendment No. 1 on Form 8-K/A to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 13, 2014, filed on February 4, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.16
|
|
Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2015, between AxoGen, Inc and Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.17
|
|
Development, License & Option Agreement, dated as of November 3, 2014, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Sensory Management Services LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.18
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Peter Mariani (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2016, filed on May 4, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.19
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Kevin Leach (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 14, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 10.20
|
|
Credit and Security Agreement (Term Loan), dated as of October 25, 2016, by and among AxoGen, Inc., AxoGen Corporation, MidCap Financial Trust, MidCap Funding XIII Trust and MidCap Funding V Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 10.21
|
|
Credit and Security Agreement (Revolving Loan), dated as of October 25, 2016, by and among AxoGen, Inc., AxoGen Corporation and MidCap Financial Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.22
|
|
Form of Non-Incentive Stock Option Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.23
|
|
Form of Performance Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of May 26, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.24
|
|
Retention Stock Unit Award Agreement, dated December 29, 2016, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Karen Zaderej, pursuant to AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.25
|
|
Lease, dated as of January 23, 2017, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 26, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**+***10.26
|
|
Form of 2018 Performance Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
| 10.27
|
|
Underwriting Agreement by and between the Company, EW Healthcare Partners L.P. and Leerink Partners LLC, as representative of the underwriters named therein, dated November 16, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 1.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 16, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**+**10.28
|
|
Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+21.1
|
|
Subsidiaries of the Registrant.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+23.1
|
|
Consent of Lurie, LLP.
|
|
|
|
|
|
++24.1
|
|
Power of Attorney.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+31.1
|
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+31.2
|
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+++32.1
|
|
Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer Certifications pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350, as adopted pursuant to section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.INS
|
|
XBRL Instance Document.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.SCH
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.CAL
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.DEF
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.LAB
|
|
XBRL Extension Labels Linkbase.
|
|
|
|
|
|
+101.PRE
|
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document.
|
|
|
|
|
*
|
Confidential treatment has been granted for portions of this Exhibit pursuant to Rule 24b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended. The confidential portions have been deleted and filed separately with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission.
|
|
|
|
|
**
|
Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
|
|
|
|
|
***
|
Confidential treatment has been requested as to certain portions, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
Filed herewith.
|
|
|
|
|
++
|
Included on signature page.
|
|
|
|
|
+++
|
Furnished herewith.
|
ITEM 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
(e) Financial Statement Schedules:
Schedule II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
AXOGEN, INC.
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
THREE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017, 2016 AND 2015
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at Beginning of Year
|
|
Charged to Costs and Expenses
|
|
Deductions (Chargeoffs)
|
|
Balance at End of Year
|
|
Allowance for doubtful accounts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2015
|
|
94,095
|
|
125,371
|
|
(27,204)
|
|
192,262
|
|
2016
|
|
192,262
|
|
103,355
|
|
(23,762)
|
|
271,855
|
|
2017
|
|
271,855
|
|
223,323
|
|
(33,839)
|
|
461,339
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Allowance for expiring inventory
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2015
|
|
404,211
|
|
1,002,919
|
|
(695,765)
|
|
711,365
|
|
2016
|
|
711,365
|
|
1,036,969
|
|
(788,269)
|
|
960,065
|
|
2017
|
|
960,065
|
|
1,290,076
|
|
(1,438,000)
|
|
812,141
|
Schedules not included have been omitted because they are not applicable or because the required information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto.
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Proxy Statement/Prospectus included as part of LecTec Corporation’s Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on August 29, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.2
|
|
AxoGen, Inc. Amended and Restated Bylaws (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 26, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 4.1
|
|
Warrants to purchase Common Stock of Company attached as exhibits to Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2011, by and among AxoGen, Inc. and AxoGen Corporation, as borrower, Midcap Financial SBIC, LP, as administrative agent, and the Lenders listed on Schedule 1 thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+4.2
|
|
Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2015, between AxoGen, Inc. and Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P.
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.1
|
|
Patent License Agreement, dated as of August 3, 2005, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Texas System (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.2.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement with Sublicensing Terms, dated as of February 21, 2006, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2.2
|
|
Second Amendment to the Amended and Restated Standard Exclusive License Agreement No. A5140, effective as of July 5, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 11, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.3
|
|
Sid Martin Biotechnology Development Institute Incubator License Agreement, dated as of September 26, 2006, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.1
|
|
Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of February 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.2
|
|
Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of August 9, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.4.3
|
|
Third Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of March 12, 2012, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.3 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
*10.4.4
|
|
Fourth Amendment to Amended and Restated Nerve Tissue Processing Agreement, dated as of September 8, 2014, by and between AxoGen Corporation and LifeNet Health (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2014, filed on November 13, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
*10.5.1
|
|
Distribution Agreement, dated as of August 27, 2008, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.5.2
|
|
Amendment No. 1 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of February 24, 2012, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5.2 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+10.5.3
|
|
Amendment No. 2 to Distribution Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2018, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Cook Biotech Incorporated.
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.6
|
|
AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Company’s Proxy Statement filed on April 8, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.7.1
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 15, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Karen Zaderej (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.7.2
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement dated as of July 17, 2017, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Jon S. Gingrich (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A, filed on July 20, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.8.1
|
|
Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Inducement Award Agreement to be granted by AxoGen, Inc. to Jon S. Gingrich on July 17, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A, filed on July 20, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.8.2
|
|
Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of September 29, 2011, by and between AxoGen Corporation and John P. Engels (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.1
|
|
Lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and WIGSHAW, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2011, filed on November 14, 2011).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.2
|
|
Second Amendment to Lease, dated as of February 27, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, filed on March 12, 2013).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.3
|
|
Third Amendment to Lease, dated November 12, 2013 to lease dated as of February 6, 2007, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SHN Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10.3 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013, filed on March 6, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.9.4
|
|
Fourth Amendment to Lease, dated as of March 16, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10.4 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 18, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
|
**10.10.1
|
|
Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 26, 2007).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+**10.10.2
|
|
Amended Form of Employee Incentive Stock Option Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.1
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of October 1, 2011, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Gregory Freitag (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011, filed on March 15, 2012).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.2
|
|
Amendment No. 1 to Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of May 11, 2014, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Greg Freitag (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2016, filed on August 4, 2014).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.3
|
|
Amendment No. 2 to Employment Agreement, dated as of August 6, 2015, by and between Gregory G. Freitag and AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.11.4
|
|
Amendment No. 3 to Employment Agreement, dated as of June 1, 2016, by and between Greg Freitag and AxoGen, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 31, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.1
|
|
Commercial Lease, dated April 21, 2015, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.2
|
|
Addendum to Commercial Lease, dated April 21, 2015 by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.12.3
|
|
Commercial Lease Amendment 2, dated as of October 25, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Ja-Cole L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 31, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.13
|
|
License and Services Agreement, dated as of August 6, 2015, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Community Blood Center (d/b/a Community Tissue Services) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.14
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, effective as of February 25, 2013, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Shawn McCarrey (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2013, filed on April 30, 2013).
|
| 10.15
|
|
Securities Purchase Agreement dated as of November 12, 2014, between AxoGen, Inc., and PDL BioPharma, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Amendment No. 1 on Form 8-K/A to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 13, 2014, filed on February 4, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.16
|
|
Securities Purchase Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2015, between AxoGen, Inc and Essex Woodlands Fund IX, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhibit
Number
|
|
Description
|
| 10.17
|
|
Development, License & Option Agreement, dated as of November 3, 2014, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Sensory Management Services LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.18
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of February 25, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Peter Mariani (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2016, filed on May 4, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**10.19
|
|
Executive Employment Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2016, by and between AxoGen Corporation and Kevin Leach (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 14, 2016).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ * 10.20
|
|
Credit and Security Agreement (Term Loan), dated as of October 25, 2016, by and among AxoGen, Inc., AxoGen Corporation, MidCap Financial Trust, MidCap Funding XIII Trust and MidCap Funding V Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+ * 10.21
|
|
Credit and Security Agreement (Revolving Loan), dated as of October 25, 2016, by and among AxoGen, Inc., AxoGen Corporation and MidCap Financial Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, filed on November 5, 2015).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+10.22
|
|
Form of Non-Incentive Stock Option Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+*10.23
|
|
Form of Performance Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of May 26, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
+**10.24
|
|
Retention Stock Unit Award Agreement, dated December 29, 2016, by and between AxoGen, Inc. and Karen Zaderej, pursuant to AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed on March 1, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.25
|
|
Lease, dated as of January 23, 2017, by and between AxoGen Corporation and SNH Medical Office Properties Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 26, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**+***10.26
|
|
Form of 2018 Performance Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
| 10.27
|
|
Underwriting Agreement by and between the Company, EW Healthcare Partners L.P. and Leerink Partners LLC, as representative of the underwriters named therein, dated November 16, 2017 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 1.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 16, 2017).
|
|
|
|
|
|
**+**10.28
|
|
Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement pursuant to the AxoGen, Inc. 2010 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated as of March 23, 2016.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*
|
Confidential treatment has been granted for portions of this Exhibit pursuant to Rule 24b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended. The confidential portions have been deleted and filed separately with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission.
|
|
|
|
|
**
|
Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
|
|
|
|
|
***
|
Confidential treatment has been requested as to certain portions, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
|
|
|
|
|
+
|
Filed herewith.
|
|
|
|
|
++
|
Included on signature page.
|
|
|
|
|
+++
|
Furnished herewith.
|
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
|
|
AXOGEN, INC
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Karen Zaderej
|
|
|
Karen Zaderej
|
|
|
Chief Executive Officer
February 28, 2018
|
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Karen Zaderej (with full power to act alone), as his or her true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent, with full powers of substitution and re-substitution, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of AxoGen, Inc., and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite or necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorney-in-fact and agent, or their substitute or substitutes, lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
In accordance with the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Karen Zaderej
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Karen Zaderej Chief Executive Officer and Director
|
|
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Peter Mariani
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Peter Mariani, CFO
|
|
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer)
|
|
|
|
(Principal Accounting Officer)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Gregory G. Freitag
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Gregory G. Freitag, General Counsel, SVP Business Development and Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Jon Ginrich
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Jon Ginrich
|
|
|
|
Chief Commercial Officer
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Jamie M. Grooms
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Jamie M. Grooms
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Robert J. Rudelius
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Robert J. Rudelius
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dr. Mark Gold
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Mark Gold, M.D.
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Guido J. Neels
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Guido J. Neels
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Amy Wendell
|
|
February 28, 2018
|
|
Amy Wendell
|
|
|
|
Director
|
|
|

